Physics
The bob of a simple pendulum is imparted a velocity of 5 m s-1 when it is at its mean position. To what maximum vertical height will it rise on reaching at its extreme position if 60% of its energy is lost in overcoming the friction of air?
(Take g = 10 m s-2).
Work, Energy & Power
90 Likes
Answer
Given,
Energy lost = 0.6 x KE
KE = x mass x velocity2
Substituting the values we get,
Amount of energy lost,
Amount of energy available,
Applying the rule for the conservation of energy we get,
Kinetic energy available = potential energy
∴ Maximum vertical height reached = 0.5m
Answered By
60 Likes
Related Questions
A metal ball of mass 2kg is allowed to fall freely from rest from a height of 5m above the ground.
- Taking g = 10ms-1, calculate:
- the potential energy possessed by the ball when it is initially at rest.
- the kinetic energy of the ball just before it hits the ground?
- What happens to the mechanical energy after the ball hits the ground and comes to rest?
- Taking g = 10ms-1, calculate:
The diagram given below shows a ski jump. A skier weighing 60kgf stands at A at the top of ski jump. He moves from A and takes off for his jump at B.
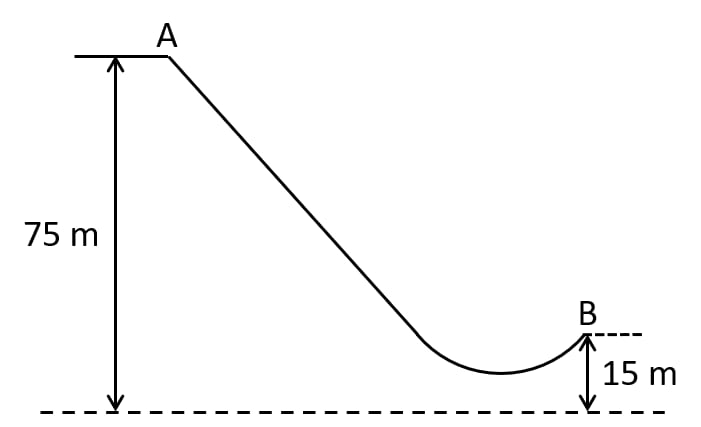
(a) Calculate the change in the gravitational potential energy of the skier between A and B.
(b) If 75% of the energy in part (a) becomes the kinetic energy at B, calculate the speed at which the skier arrives at B.
(Take g = 10 ms-2).
A hydroelectric power station takes its water from a lake whose water level is 50m above the turbine. Assuming an overall efficiency of 40%, calculate the mass of water which must flow through the turbine each second to produce power output of 1MW. (Take g = 10 m s-2).
The figure alongside shows a simple pendulum of mass 200 g. It is displaced from the mean position A to the extreme position B. The potential energy at the position A is zero. At the position B the pendulum bob is raised by 5 m.
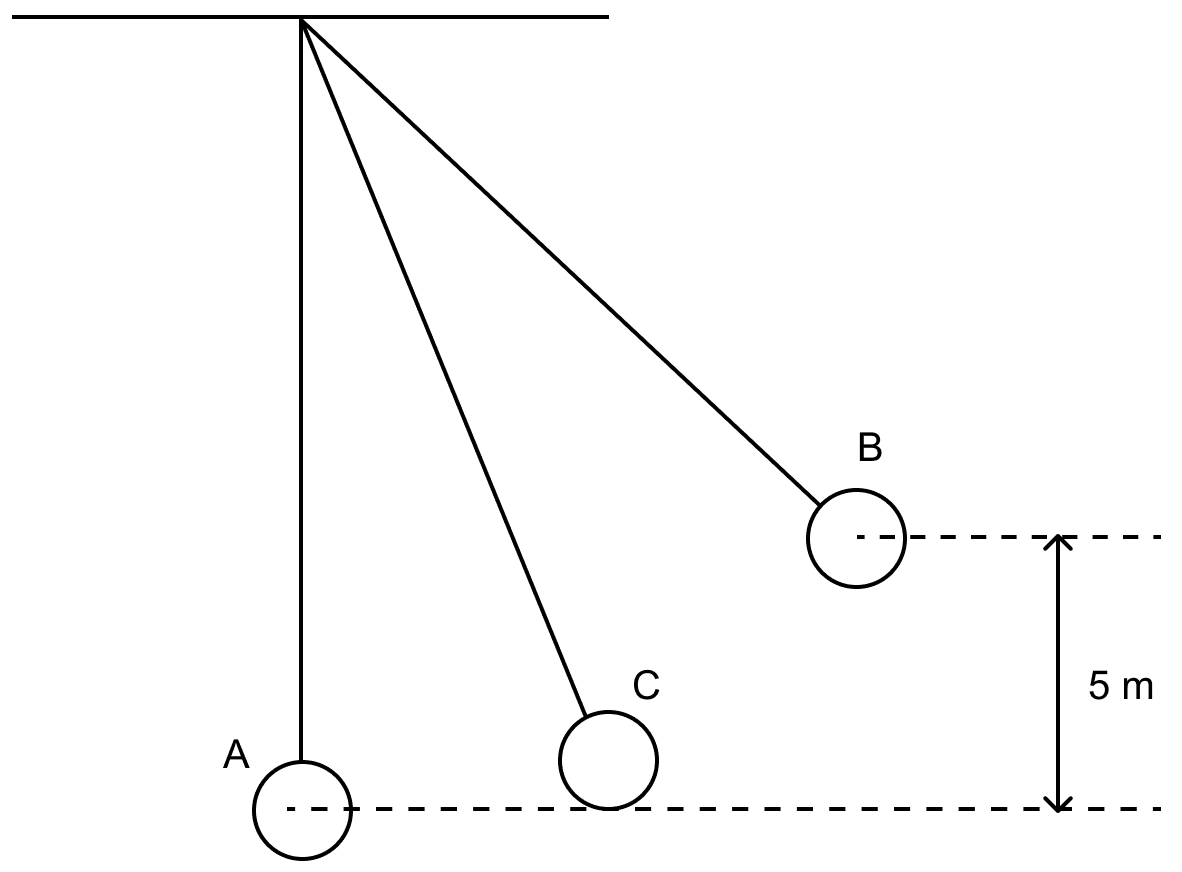
(i) What is the potential energy of the pendulum at the position B?
(ii) What is the total mechanical energy at point C?
(iii) What is the speed of the bob at the position A when released from B?
(Take g = 10 ms-2 and there is no loss of energy.)