Physics
The figure alongside shows a simple pendulum of mass 200 g. It is displaced from the mean position A to the extreme position B. The potential energy at the position A is zero. At the position B the pendulum bob is raised by 5 m.
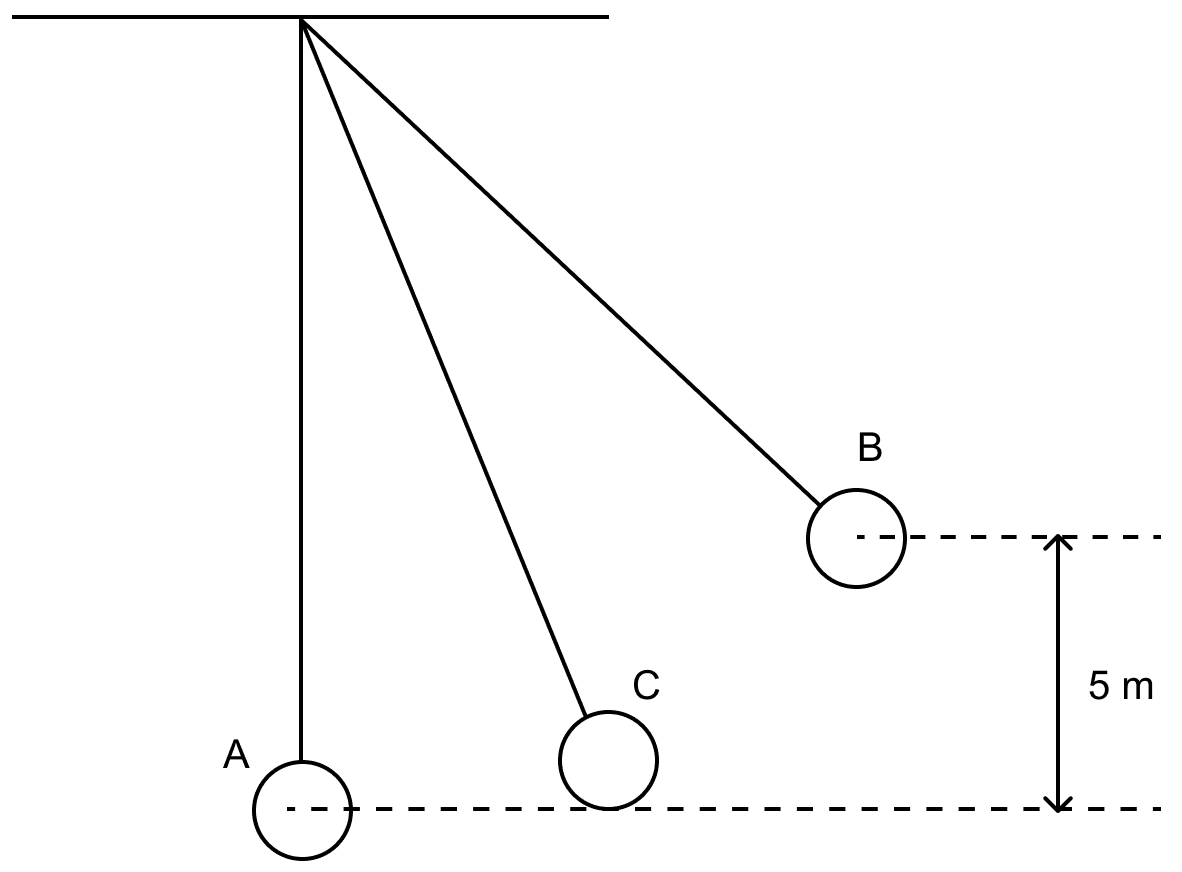
(i) What is the potential energy of the pendulum at the position B?
(ii) What is the total mechanical energy at point C?
(iii) What is the speed of the bob at the position A when released from B?
(Take g = 10 ms-2 and there is no loss of energy.)
Work, Energy & Power
ICSE 2020
ICSE Sp 2024
405 Likes
Answer
Given,
h = 5 m, m = 200 g = 0.2 kg, g = 10 ms-2
(i) Potential energy UB at B is given by
UB = m x g x h
Substituting the values we get,
B = 0.2 \times 10 \times 5 \\[0.5em] \Rightarrow UB = 10 J
Hence, the potential energy of the pendulum at the position B = 10 J
(ii) Total mechanical energy at point C = 10 J
The total mechanical energy is same at all points of the path due to conservation of mechanical energy.
(iii) At A, bob has only kinetic energy which is equal to potential energy at B,
Therefore,
A)^{2} = UB \\[0.5em] 0.5 \times 0.2 \times (vA)^{2} = 10 \\[0.5em] (vA)^{2} = \dfrac{10}{0.1} \\[0.5em] \Rightarrow vA = \sqrt{100} \\[0.5em] \Rightarrow vA = 10 \text{ m s}^{-1}
Answered By
310 Likes
Related Questions
A nucleus 84X202 of an element emits an alpha particle followed by a beta particle. The final nucleus is aYb. Find a and b.
The diagram alongside shows a loop of wire carrying current I:

(i) What is the magnetic polarity of the loop that faces us?
(ii) With respect to the diagram how can we increase the strength of the magnetic field produced by this loop?
(i) With reference to the direction of action, how does a centripetal force differ from a centrifugal force during uniform circular motion?
(ii) Is centrifugal force the force of reaction of centripetal force?
(iii) Compare the magnitudes of centripetal and centrifugal force.
A block and tackle system of pulleys has velocity ratio 4.
(i) Draw a neat, labelled diagram of the system indicating clearly the points of application and direction of load and effort.
(ii) What will be it's V.R. if the weight of the movable block is doubled?