Mathematics
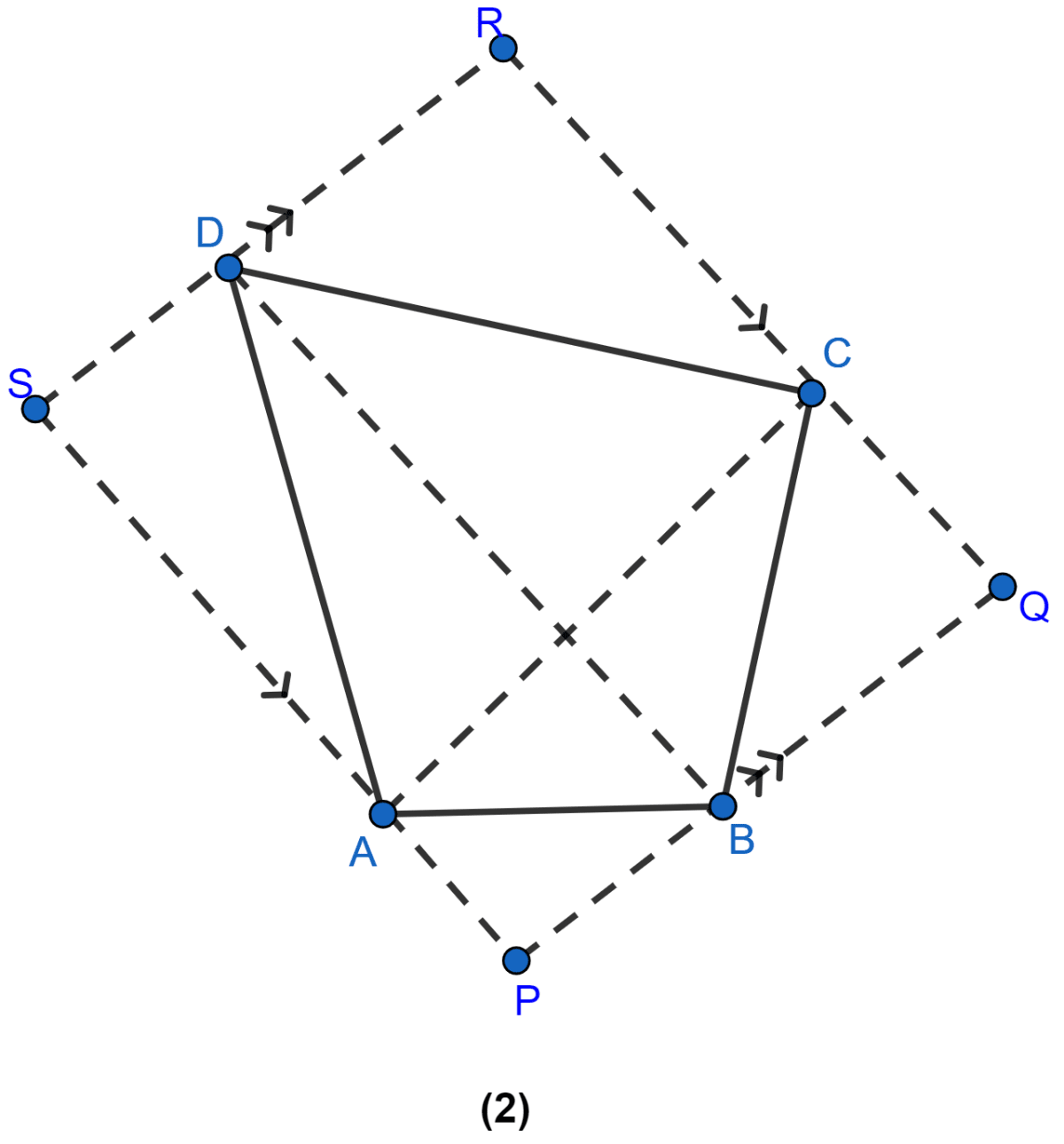
In the figure (2) given below, PQRS is a parallelogram formed by drawing lines parallel to the diagonals of a quadrilateral ABCD through its corners. Prove that area of || gm PQRS = 2 × area of quad. ABCD.
Theorems on Area
10 Likes
Answer
From figure,
Area of ∆ACD = Area of || gm ACRS [As both are on same base AC and between the same parallel lines AC and SR]
⇒ Area of || gm ACRS = 2 Area of ∆ACD …….(i)
Similarly,
Area of ∆ABC = Area of || gm ∆APQC [As both are on same base AC and between the same parallel lines AC and PQ]
⇒ Area of || gm APQC = 2 Area of ∆ABC …….(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii),
⇒ Area of || gm ACRS + Area of || gm APQC = 2 Area of ∆ACD + 2 Area of ∆ABC
⇒ Area of || gm PQRS = 2[Area of ∆ACD + Area of ∆ ABC]
⇒ Area of || gm PQRS = 2(Area of quad. ABCD)
Hence, proved that area of || gm PQRS = 2 x area of quad. ABCD.
Answered By
6 Likes
Related Questions
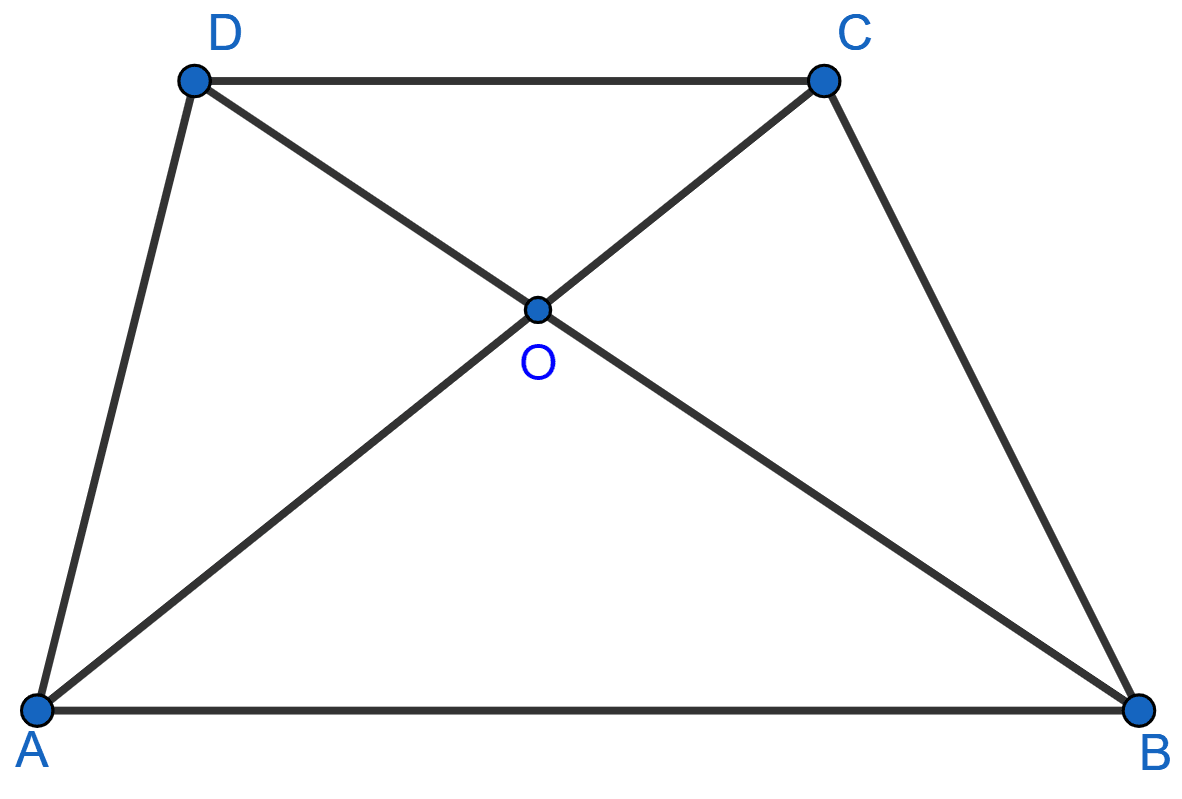
In the adjoining figure, AB || DC and AB ≠ DC. If the diagonals AC and BD of the trapezium ABCD intersect at O, then which of the following statements is not true ?
area of △ABC = area of △ABD
area of △ACD = area of △BCD
area of △OAB = area of △OCD
area of △OAD = area of △OBC
In the figure (1) given below, ABCD is a rectangle (not drawn to scale) with side AB = 4 cm and AD = 6 cm. Find
(i) the area of parallelogram DEFC
(ii) area of △EFG.

In the parallelogram ABCD, P is a point on the side AB and Q is a point on the side BC. Prove that
(i) area of ∆CPD = area of ∆AQD
(ii) area of ∆ADQ = area of ∆APD + area of ∆CPB.
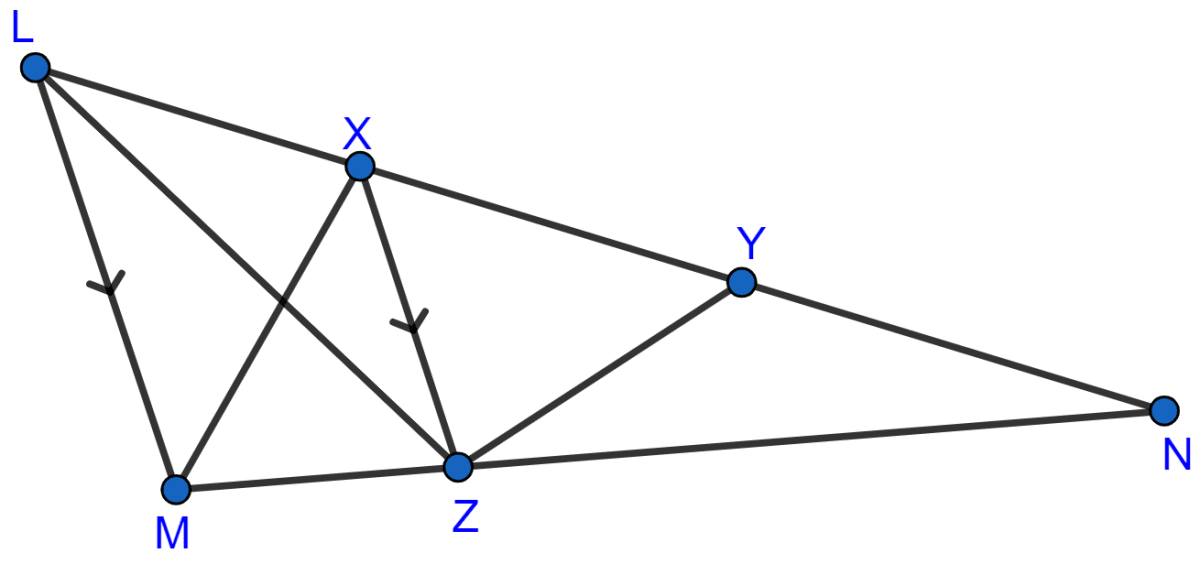
In the adjoining figure, X and Y are points on the side LN of triangle LMN. Through X, a line is drawn parallel to LM to meet MN at Z. Prove that area of ∆LZY = area of quad. MZYX.