Mathematics
In figure given below, ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = 13 cm, DC = 12 cm, BC = 3 cm, ∠ABD = ∠BCD = 90°. Calculate the length of AB.

Pythagoras Theorem
47 Likes
Answer
In right angle △DBC,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ DB2 = DC2 + BC2
⇒ DB2 = 122 + 32
⇒ DB2 = 144 + 9
⇒ DB2 = 153.
⇒ DB = .
In right angle △ABD,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ AD2 = AB2 + DB2
⇒ 132 = AB2 + 153
⇒ 169 - 153 = AB2
⇒ AB2 = 16
⇒ AB = = 4 cm.
Hence, AB = 4 cm.
Answered By
38 Likes
Related Questions
ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC = 12 cm and BC = 8 cm. Find the altitude on BC and hence calculate its area.
Find the area and the perimeter of a square whose diagonal is 10 cm long.
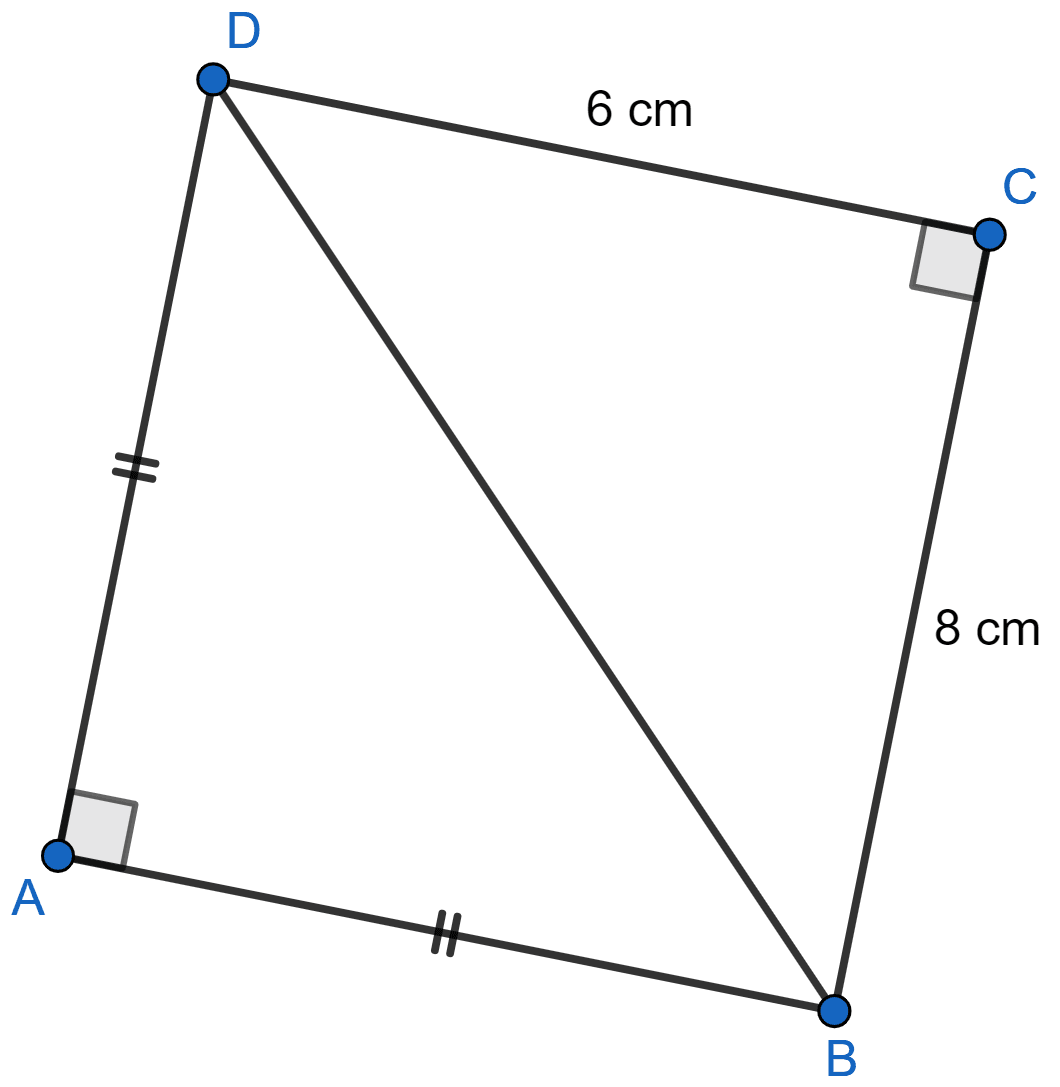
In figure given below, ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB = AD, ∠A = 90° = ∠C, BC = 8 cm and CD = 6 cm. Find AB and calculate the area of △ABD.
In figure given below, AB = 12 cm, AC = 13 cm, CE = 10 cm and DE = 6 cm. Calculate the length of BD.
