Mathematics
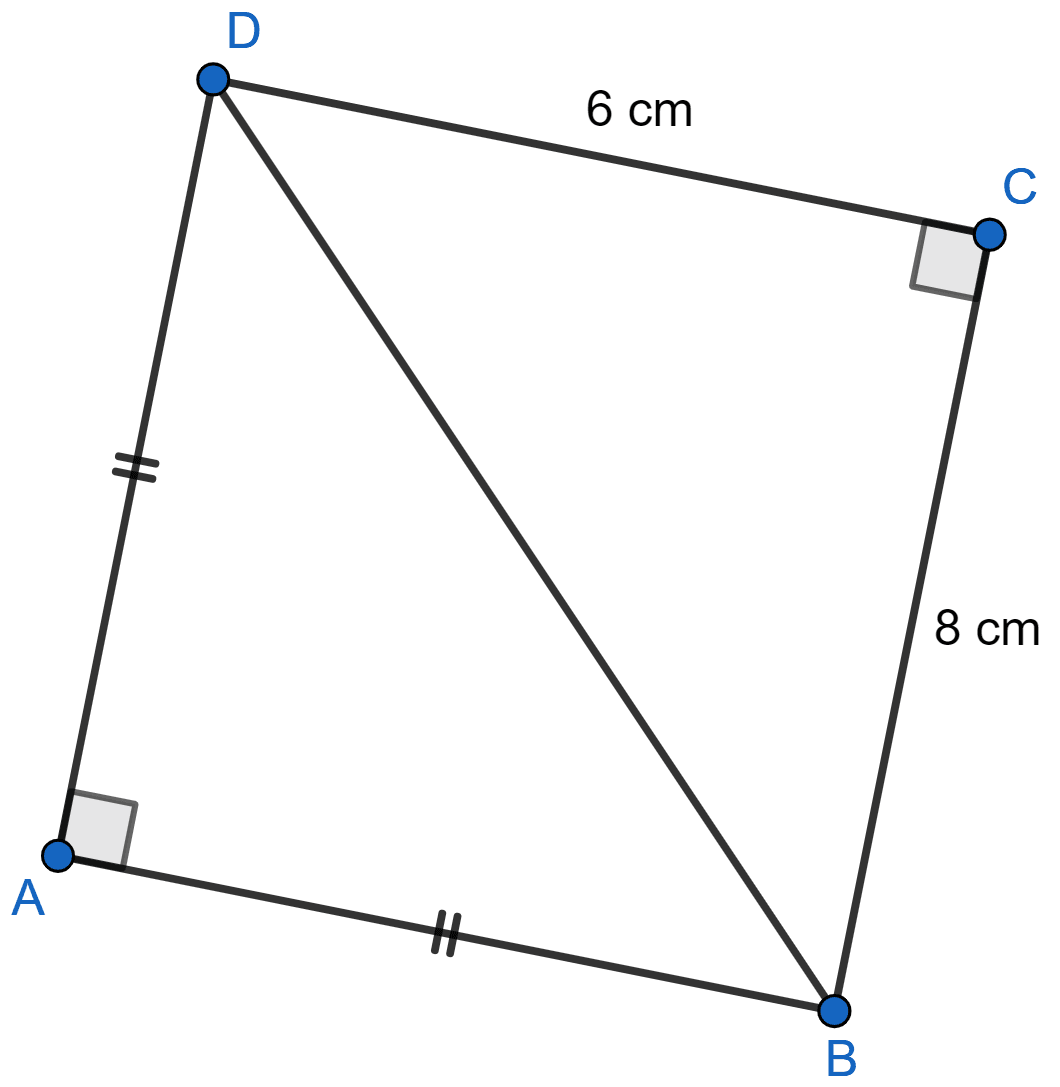
In figure given below, ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB = AD, ∠A = 90° = ∠C, BC = 8 cm and CD = 6 cm. Find AB and calculate the area of △ABD.
Pythagoras Theorem
36 Likes
Answer
Let AB = AD = x cm.
In right angle △BCD,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ BD2 = BC2 + CD2
⇒ BD2 = 82 + 62
⇒ BD2 = 64 + 36
⇒ BD2 = 100
⇒ BD = = 10 cm.
In right angle △ABD,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ BD2 = AB2 + AD2
⇒ 102 = x2 + x2
⇒ 100 = 2x2
⇒ x2 = 50
⇒ x = cm.
Area of right angle △ABD
Hence, AB = cm and area of right angle △ABD = 25 cm2.
Answered By
26 Likes
Related Questions
Find the area and the perimeter of a square whose diagonal is 10 cm long.
In figure given below, ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = 13 cm, DC = 12 cm, BC = 3 cm, ∠ABD = ∠BCD = 90°. Calculate the length of AB.

In figure given below, AB = 12 cm, AC = 13 cm, CE = 10 cm and DE = 6 cm. Calculate the length of BD.

In figure given below, ∠PSR = 90°, PQ = 10 cm, QS = 6 cm and RQ = 9 cm. Calculate the length of PR.
