Mathematics
The sides of a right-angled triangle, containing the right angle, are 3(x + 1) cm and (2x - 1) cm. If the area of the triangle is 30 cm2, find the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
Quadratic Equations
1 Like
Answer
Let ABC be the right angle triangle with base = (2x - 1) cm and height = 3(x + 1) cm.
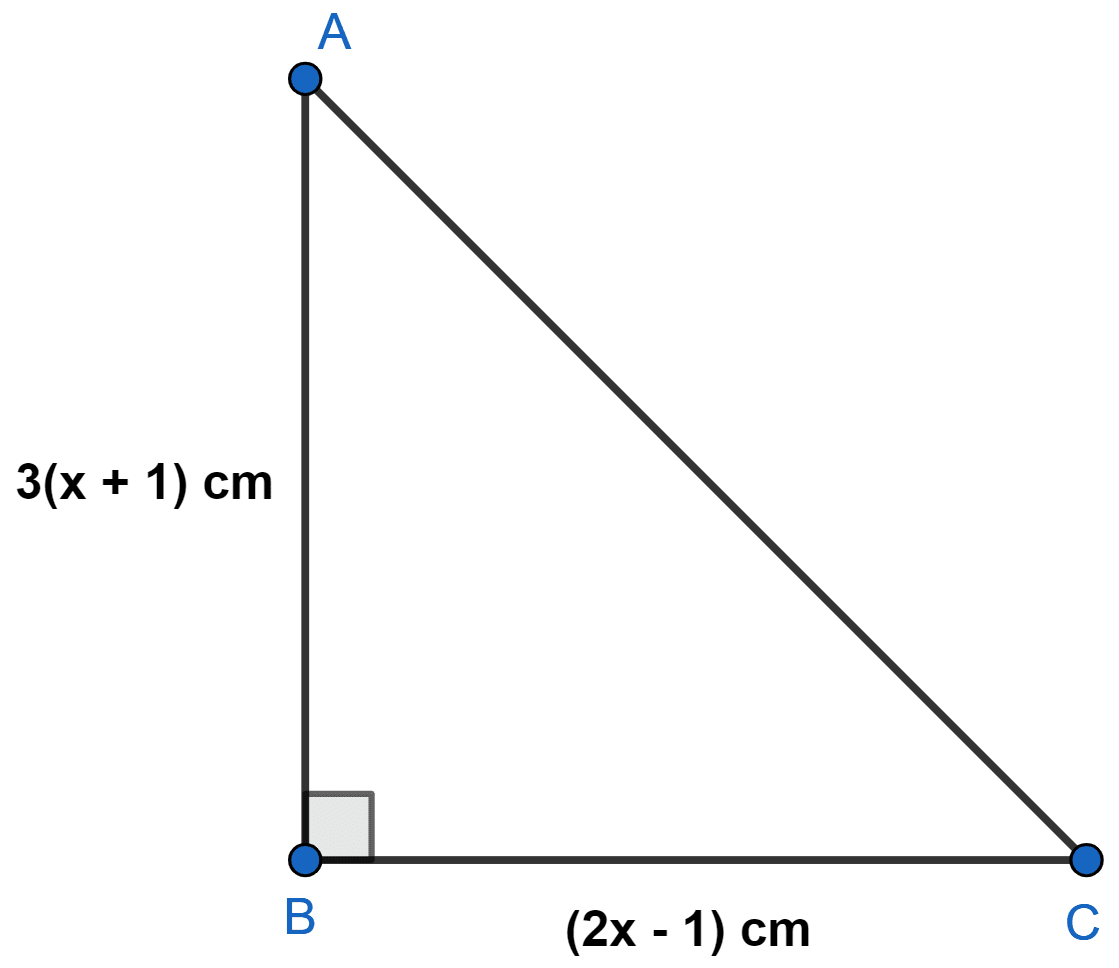
Area of right angle triangle = base × height
Substituting values we get :
Since, side cannot be negative.
∴ x = 3 cm.
AB = 3(x + 1) = 3(3 + 1) = 3 × 4 = 12 cm,
BC = (2x - 1) = (2 × 3 - 1) = 6 - 1 = 5 cm.
In right angle triangle ABC,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ AC2 = 122 + 52
⇒ AC2 = 144 + 25
⇒ AC2 = 169
⇒ AC = = 13 cm.
Hence, length of sides of triangle are 5, 12 and 13 cm.
Answered By
1 Like
Related Questions
Solve the inequation 3 ≥ , x ∈ I (integers). Graph the solution on a real number line.
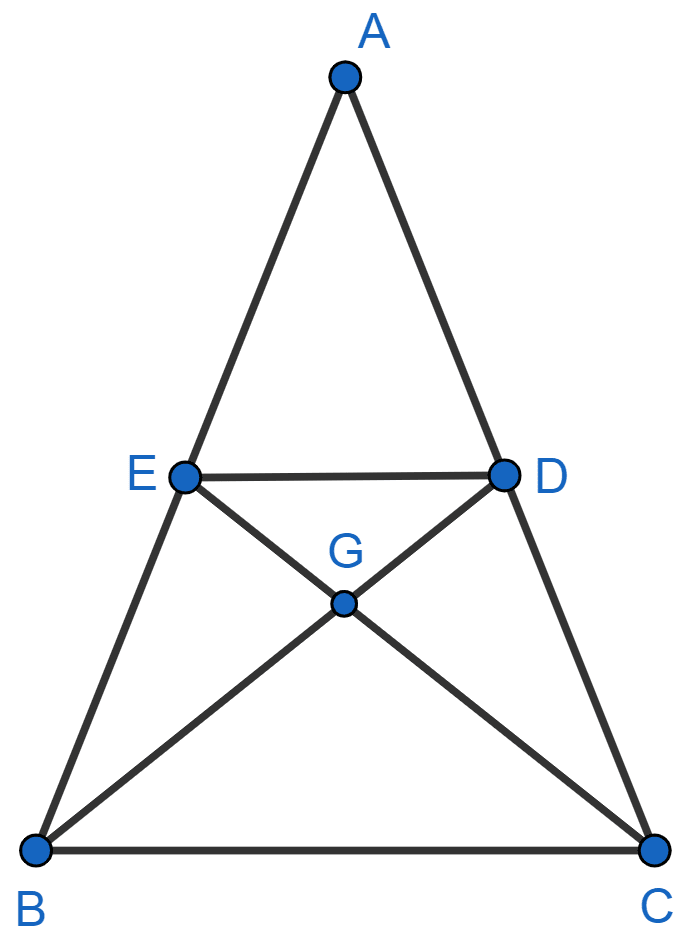
In the given figure, the median BD and CE of triangle ABC meet at point G. Show that BG = 2GD.
The daily wages of 160 workers in a factory are given below :
Wages (in ₹) No. of workers 50-60 12 60-70 20 70-80 30 80-90 38 90-100 24 100-110 16 110-120 12 120-130 8 Draw a cumulative frequency curve and estimate :
(i) median wage
(ii) inter-quartile range
(iii) percentage of workers who earn more than ₹ 95 per day.
Solve for x : .