Mathematics
Answer
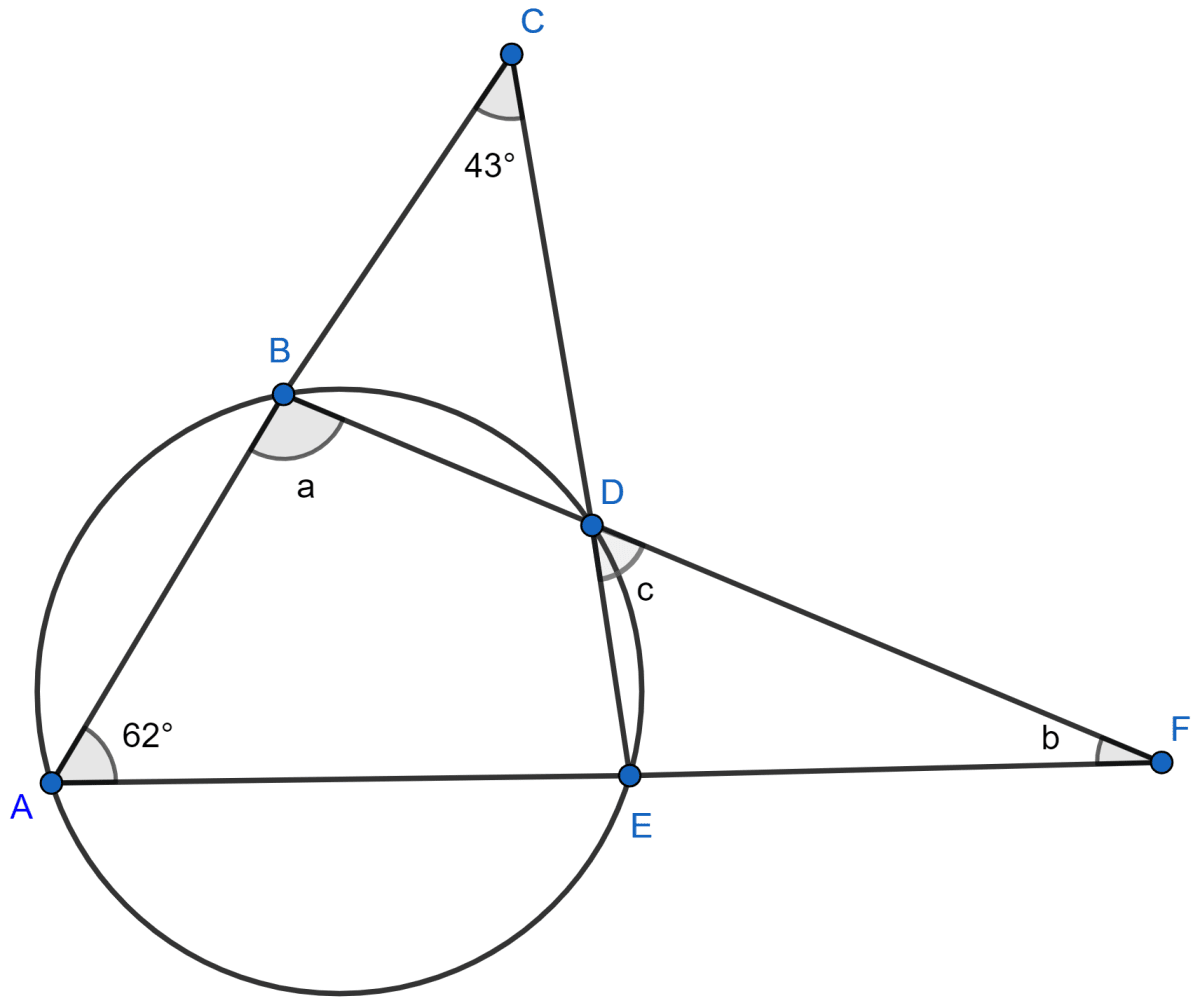
In △AEC,
⇒ ∠ACE + ∠CAE + ∠AEC = 180°
⇒ 43° + 62° + ∠AEC = 180°
⇒ ∠AEC = 180° - 105° = 75°.
From figure,
⇒ ∠ABD + ∠AED = 180° [As sum of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral = 180°]
⇒ a + ∠AEC = 180° [From figure, ∠AED = ∠AEC]
⇒ a + 75° = 180°
⇒ a = 180° - 75° = 105°.
∠BDC = c [Vertically opposite angles are equal]
∠DBC = 180° - a [Linear pairs]
= 180° - 105°
= 75°.
In △DBC,
⇒ ∠DBC + ∠BCD + ∠BDC = 180° [Angle sum property of triangle]
⇒ 75° + 43° + c = 180°
⇒ 118° + c = 180°
⇒ c = 180° - 118° = 62°.
In △BAF,
⇒ ∠ABF + ∠BAF + ∠AFB = 180° [Angle sum property of triangle]
⇒ a + 62° + b = 180°
⇒ 105° + 62° + b = 180°
⇒ b + 167° = 180°
⇒ b = 180° - 167° = 13°.
Hence, a = 105°, b = 13° and c = 62°.
Related Questions
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of a circle with center O. If chord AC = chord AD, prove that :
(i) arc BC = arc DB
(ii) AB is the bisector of ∠CAD.
Further, if the length of arc AC is twice the length of arc BC, find :
(a) ∠BAC
(b) ∠ABC

In the given figure, AB is parallel to DC, ∠BCE = 80° and ∠BAC = 25°.
Find :
(i) ∠CAD
(ii) ∠CBD
(iii) ∠ADC

In cyclic quadrilateral ABCD; AD = BC, ∠BAC = 30° and ∠CBD = 70°; find :
(i) ∠BCD
(ii) ∠BCA
(iii) ∠ABC
(iv) ∠ADC
In the figure, given below, CP bisects angle ACB. Show that DP bisects angle ADB.