Mathematics
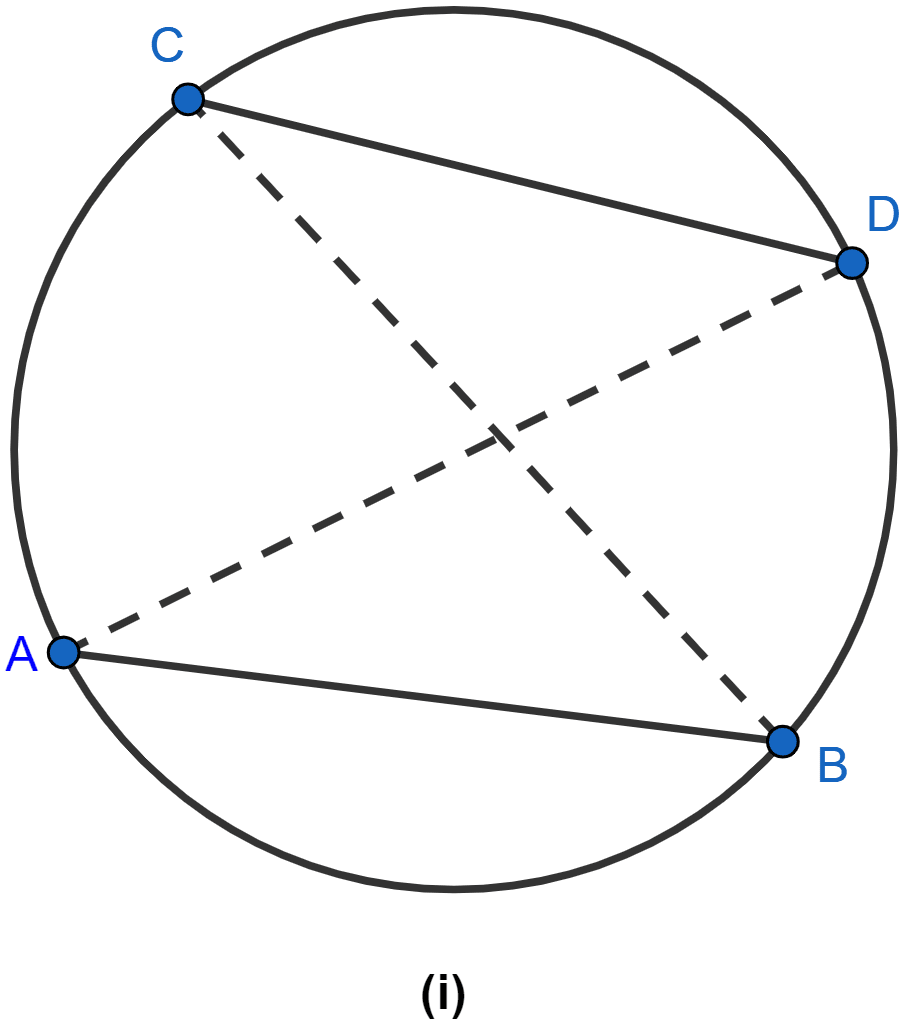
In the figure (i) given below, ABDC is a cyclic quadrilateral. If AB = CD, prove that AD = BC.
Circles
8 Likes
Answer
Join AC and BD.
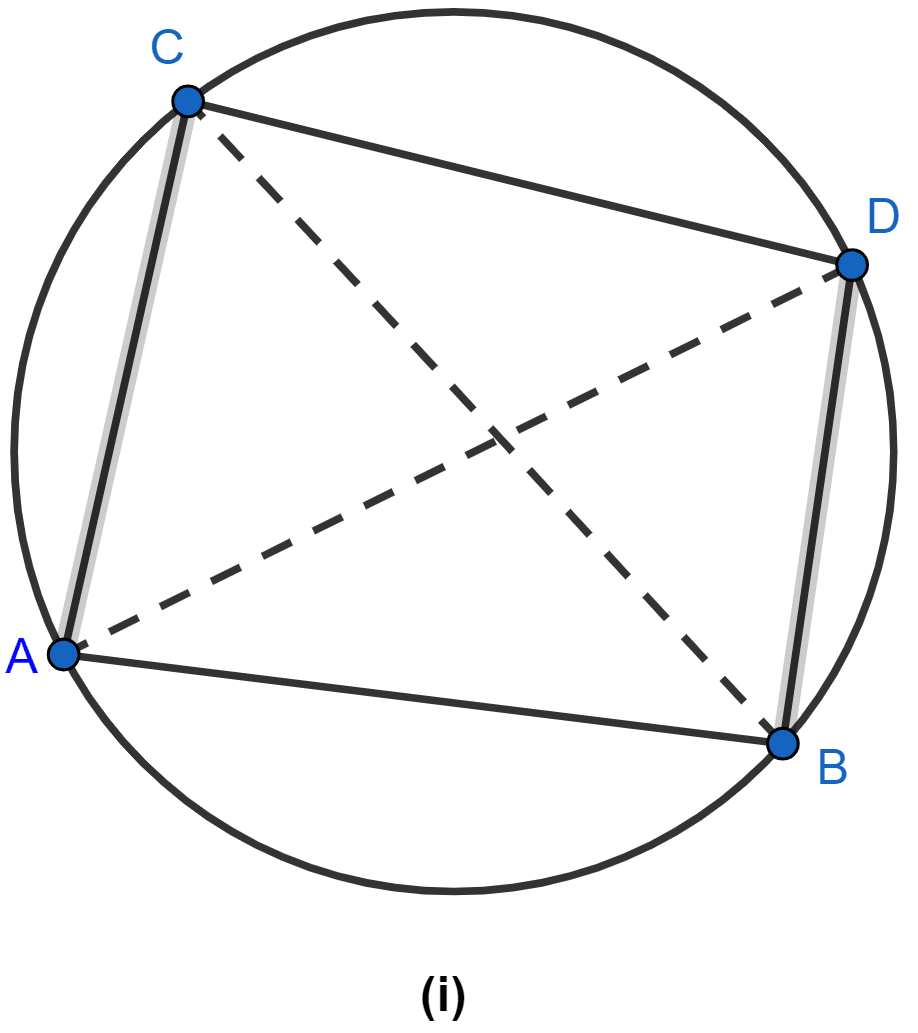
In △ABD and △CBD,
AB = CD (Given)
BD = BD (Common side)
∠BAD = ∠BCD (∵ angles in same segment are equal.)
∴ △ABD ≅ △CBD. (By SSA axiom of congruency.)
∴ BC = AD (As corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent.)
Hence, proved that BC = AD.
Answered By
6 Likes
Related Questions
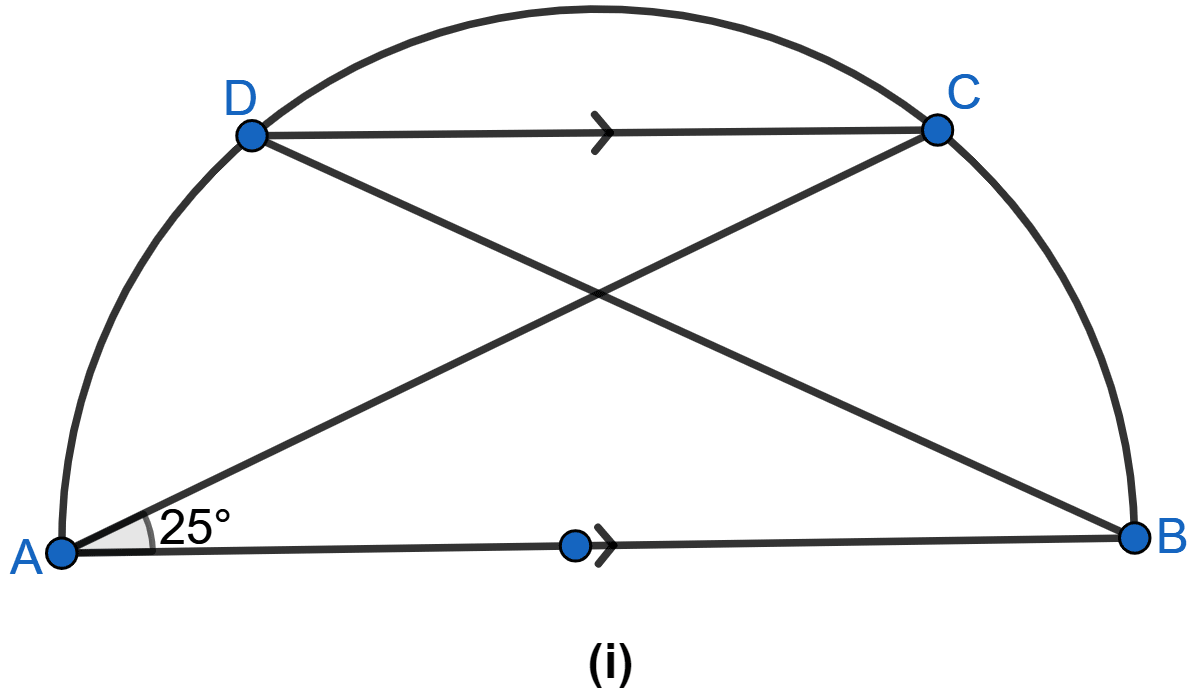
In the figure (i) given below, AB is diameter of a circle. If DC is parallel to AB and ∠CAB = 25°, find (i) ∠ADC (ii) ∠DAC.
In the figure (ii) given below, ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC. If ∠ABC = 50°, find ∠BDC and ∠BEC.

A point P is 13 cm from the centre of a circle. The length of the tangent drawn from P to the circle is 12 cm. Find the distance of P from the nearest point of the circle.
In the figure (ii) given below, sides AB and DC of a cyclic quadrilateral are produced to meet at a point P and the sides AD and BC produced to meet at a point Q. If ∠ADC = 75° and ∠BPC = 50°, find ∠BAD and ∠CQD.
