Mathematics
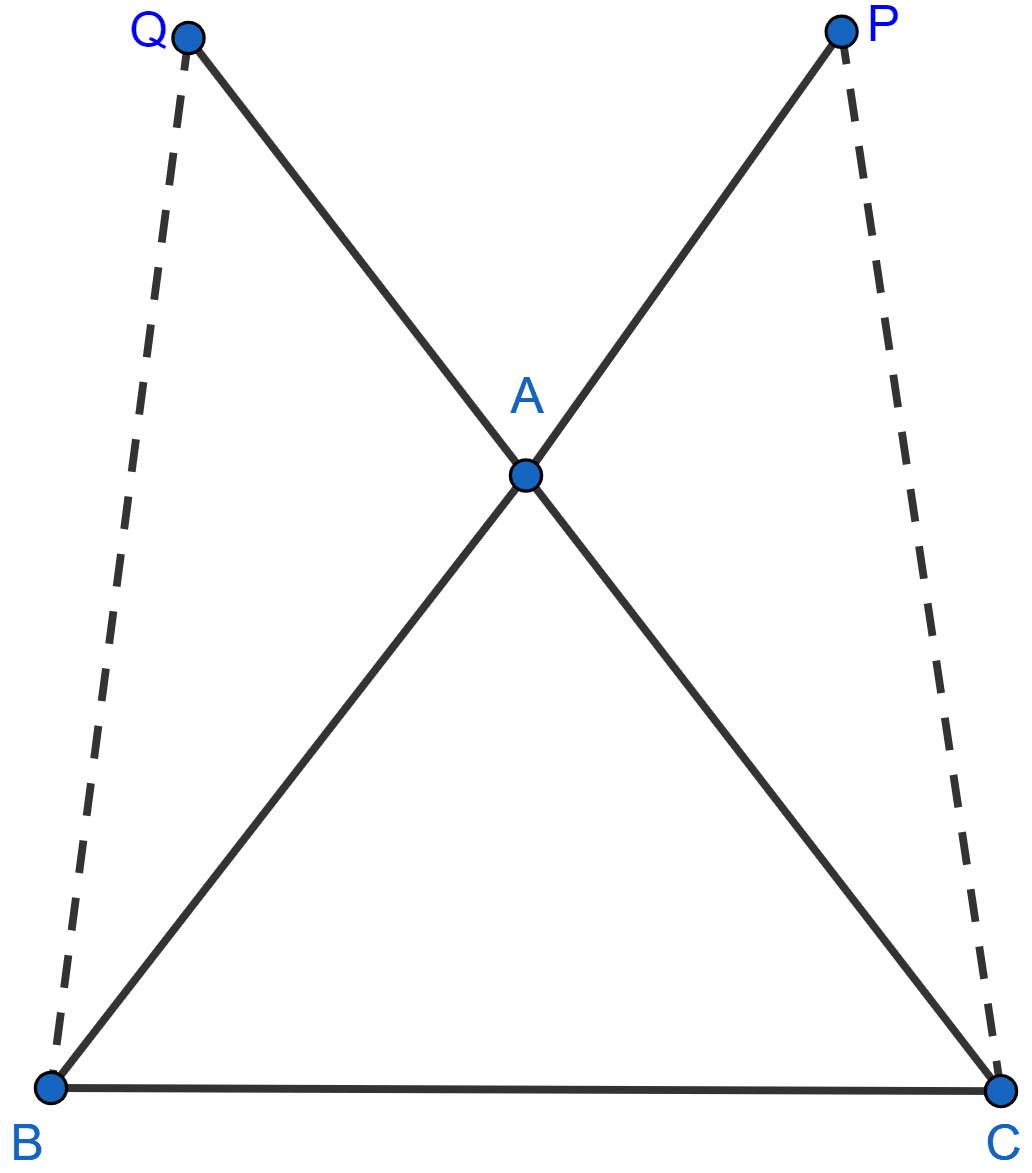
In the adjoining figure, AB = AC and AP = AQ. Prove that
(i) △APC ≅ △AQB
(ii) CP = BQ
(iii) ∠APC = ∠AQB.

Triangles
126 Likes
Answer
(i) In △APC and △AQB we have,
AB = AC (Given)
AP = AQ (Given)
∠PAC = ∠QAB (Common angles)
Hence, by SAS axiom △APC ≅ △AQB.
(ii) As, △APC ≅ △AQB.
We know that corresponding sides of congruent triangles are equal.
∴ CP = BQ.
Hence, proved that CP = BQ.
(iii) As, △APC ≅ △AQB.
We know that corresponding angles of congruent triangles are equal.
∴ ∠APC = ∠AQB.
Hence, proved that ∠APC = ∠AQB.
Answered By
77 Likes
Related Questions
It is given that △ABC ≅ △RPQ. Is it true to say that BC = QR? Why?
"If two sides and an angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and an angle of another triangle, then the two triangles must be congruent." Is the statement true? Why?
In the adjoining figure, AB = AC, P and Q are points on BA and CA respectively such that AP = AQ. Prove that
(i) △APC ≅ △AQB
(ii) CP = BQ
(iii) ∠ACP = ∠ABQ.
In the adjoining figure, AD = BC and BD = AC. Prove that:
∠ADB = ∠BCA and ∠DAB = ∠CBA.
