Mathematics
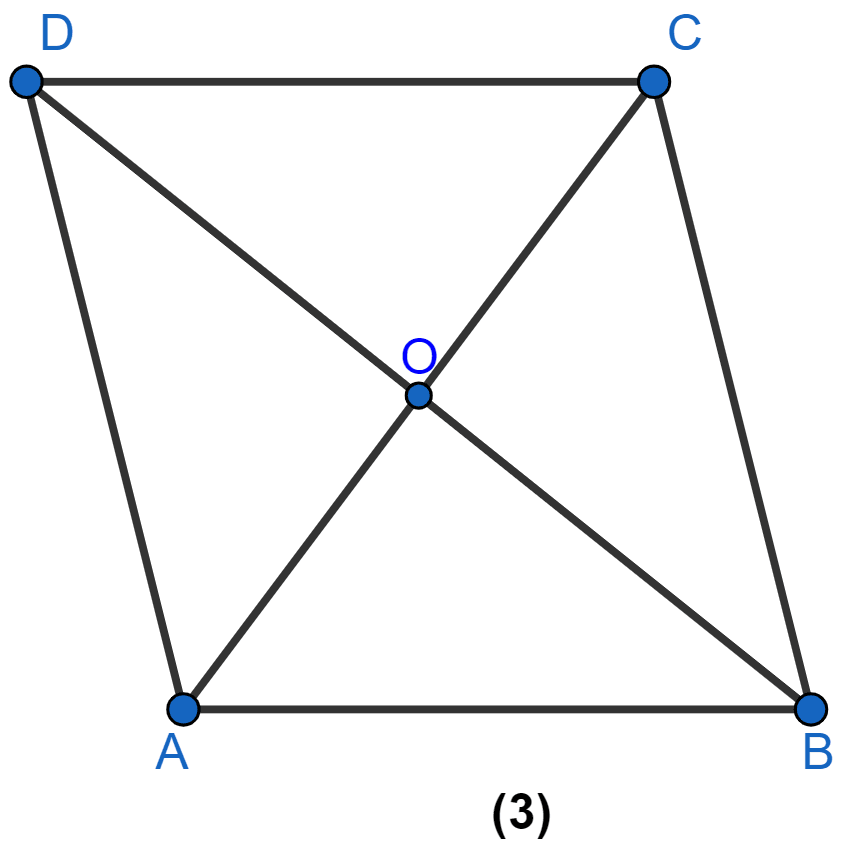
In figure (3) given below, ABCD is a rhombus and diagonals intersect at O. If ∠OAB : ∠OBA = 3 : 2, find the angles of the △AOD.
Rectilinear Figures
74 Likes
Answer
Let ∠OAB = 3x and ∠OBA = 2x.
The diagonals of rhombus are perpendicular to each other.
∴ ∠AOB = 90°
In △AOB,
⇒ ∠AOB + ∠OAB + ∠OBA = 180°
⇒ 90° + 3x + 2x = 180°
⇒ 5x = 90°
⇒ x =
⇒ x = 18°.
∠OAB = 3x = 3(18°) = 54°.
∠OBA = 2x = 2(18°) = 36°.
Since, diagonals of rhombus bisect vertex angles.
∴ ∠OAD = ∠OAB = 54°,
∠AOD = 90° (The diagonals of rhombus are perpendicular to each other.)
In △AOD,
⇒ ∠AOD + ∠OAD + ∠ODA = 180°
⇒ 90° + 54° + ∠ODA = 180°
⇒ ∠ODA + 144° = 180°
⇒ ∠ODA = 180° - 144°
⇒ ∠ODA = 36°.
Hence, ∠ODA = 36°, ∠OAD = 54°, ∠AOD = 90°.
Answered By
46 Likes
Related Questions
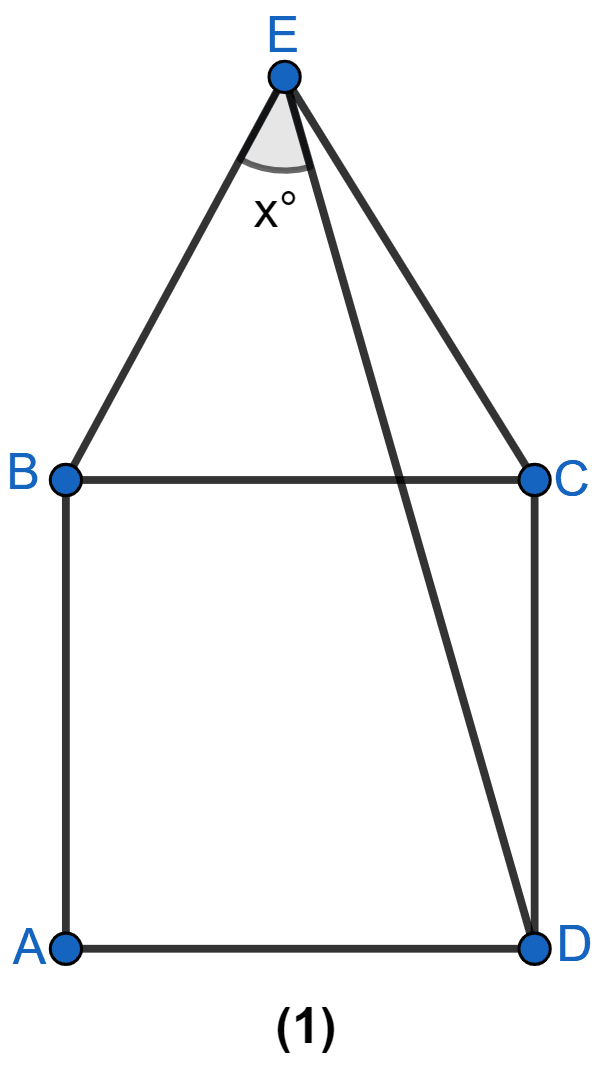
In figure (1) given below, equilateral triangle EBC surmounts square square ABCD. Find angle BED represented by x.
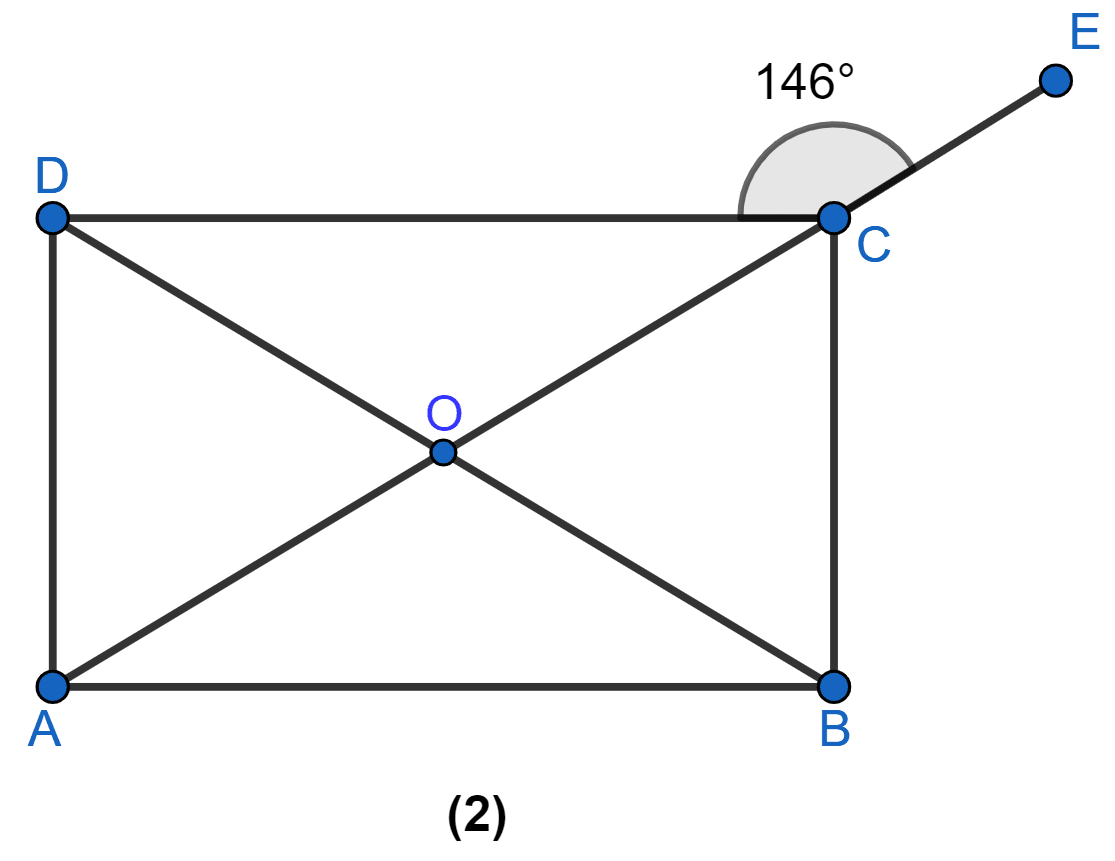
In Figure (2) given below, ABCD is a rectangle and diagonals intersect at O. AC is produced to E. If ∠ECD = 146°, find the angles of △AOB.
In figure (1) given below, ABCD is a trapezium. Find the values of x and y.

In figure (2) given below, ABCD is an isosceles trapezium. Find the values of x and y.
