Mathematics
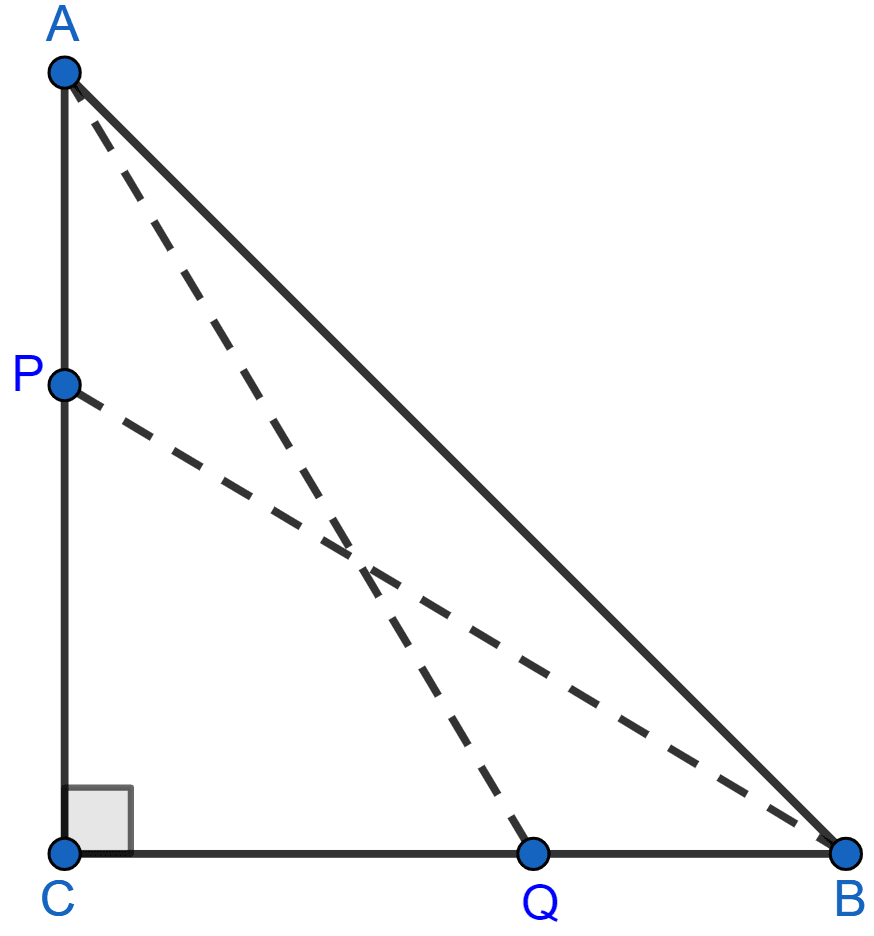
In a right angled triangle ABC, right angled at C, P and Q are the points on the sides CA and CB respectively which divide these sides in the ratio 2 : 1. Prove that
(i) 9AQ2 = 9AC2 + 4BC2
(ii) 9BP2 = 9BC2 + 4AC2
(iii) 9(AQ2 + BP2) = 13AB2
Pythagoras Theorem
12 Likes
Answer
(i) In right angle triangle ACQ,
By pythagoras theorem we get,
⇒ AQ2 = AC2 + CQ2
Multiplying both sides by 9 we get,
⇒ 9AQ2 = 9AC2 + 9CQ2
⇒ 9AQ2 = 9AC2 + (3CQ)2 …….(i)
Given, BQ : CQ = 1 : 2
Substituting above value in (i) we get,
⇒ 9AQ2 = 9AC2 + (2BC)2
⇒ 9AQ2 = 9AC2 + 4BC2.
Hence, proved that 9AQ2 = 9AC2 + 4BC2.
(ii) In right angle triangle BPC,
By pythagoras theorem we get,
⇒ BP2 = BC2 + CP2
Multiplying both sides by 9 we get,
⇒ 9BP2 = 9BC2 + 9CP2
⇒ 9BP2 = 9BC2 + (3CP)2 …….(ii)
Given, AP : PC = 1 : 2
Substituting above value in (ii) we get,
⇒ 9BP2 = 9BC2 + (2AC)2
⇒ 9BP2 = 9BC2 + 4AC2.
Hence, proved that 9BP2 = 9BC2 + 4AC2.
(iii) In right angle triangle ABC,
By pythagoras theorem we get,
⇒ AB2 = AC2 + BC2 ……(iii)
Adding resultants from part (i) and (ii) we get,
9AQ2 + 9BP2 = 9AC2 + 4BC2 + 9BC2 + 4AC2
9(AQ2 + BP2) = 13AC2 + 13BC2
9(AQ2 + BP2) = 13(AC2 + BC2)
9(AQ2 + BP2) = 13AB2 [From (iii)].
Hence, proved that 9(AQ2 + BP2) = 13AB2.
Answered By
7 Likes
Related Questions
In figure given below, triangle ABC is right angled at B. Given that AB = 9 cm, AC = 15 cm and D, E are mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively, calculate (i) the length of BC (ii) the area of △ADE.

If in △ABC, AB > AC and AD ⊥ BC, prove that AB2 - AC2 = BD2 - CD2.
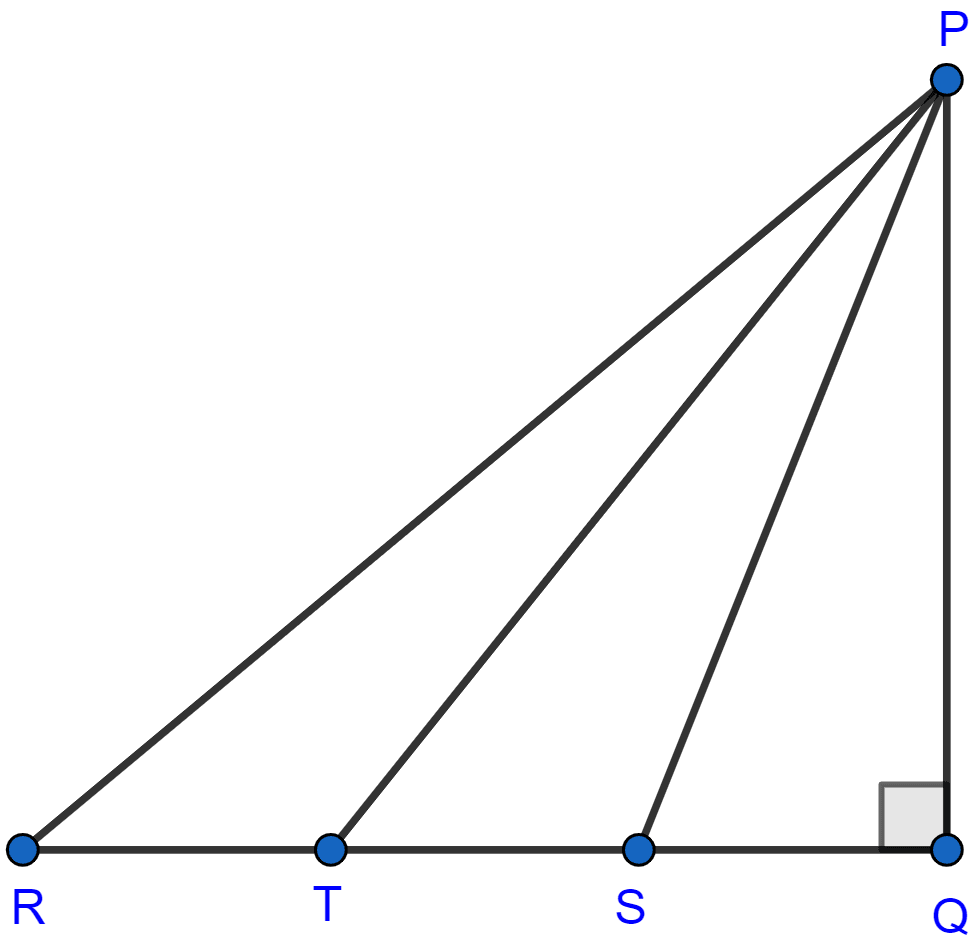
In the adjoining figure, △PQR is right angled at Q and points S and T trisect side QR. Prove that
8PT2 = 3PR2 + 5PS2.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠B = 90°. If AD2 = AB2 + BC2 + CD2, Prove that ∠ACD = 90°.