Mathematics
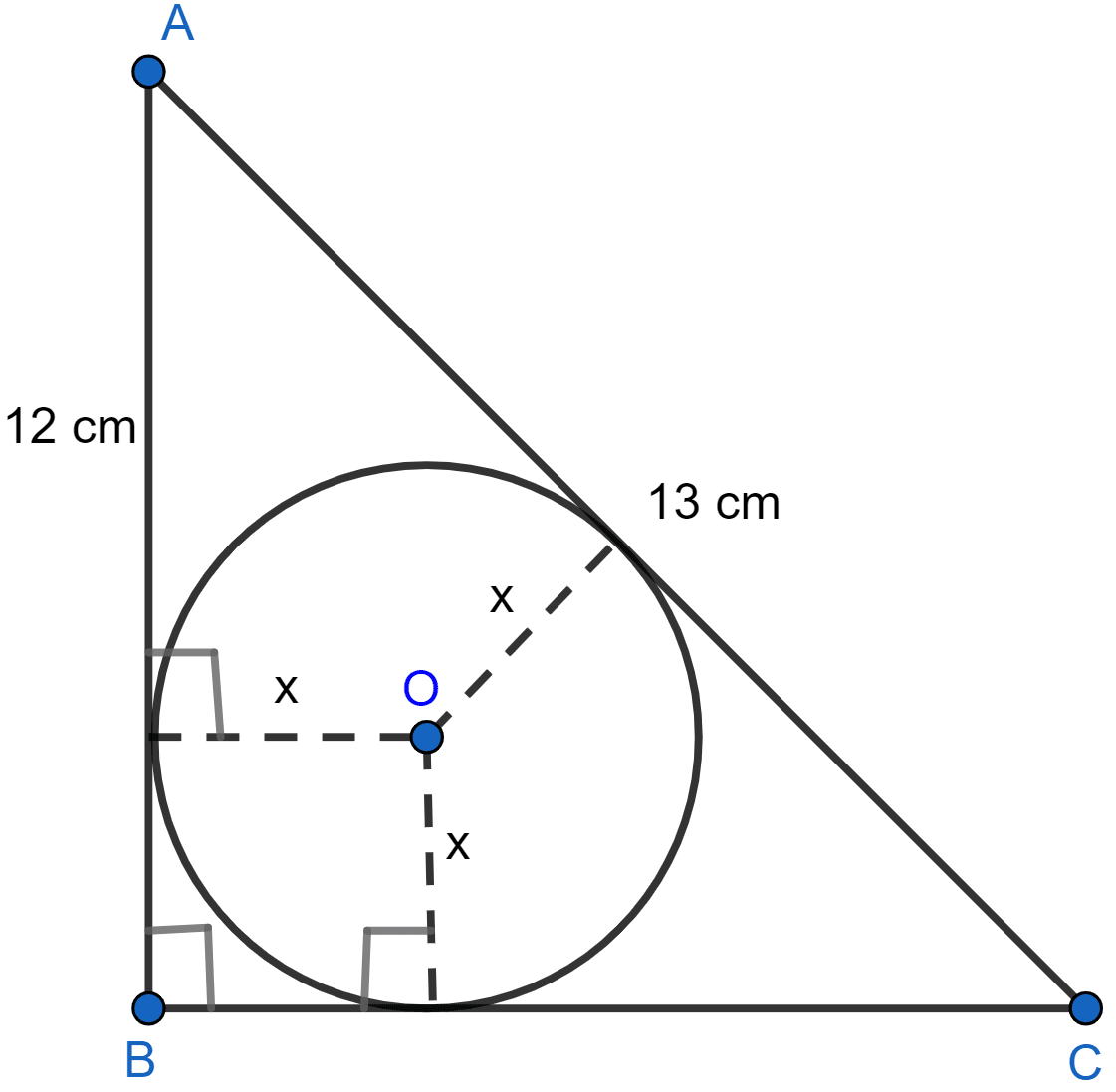
ABC is a right angled triangle with AB = 12 cm and AC = 13 cm. A circle, with center O, has been inscribed inside the triangle. Calculate the value of x, the radius of the inscribed circle.
Circles
16 Likes
Answer
Let AB touches the circle at L, AC at N and BC at M.
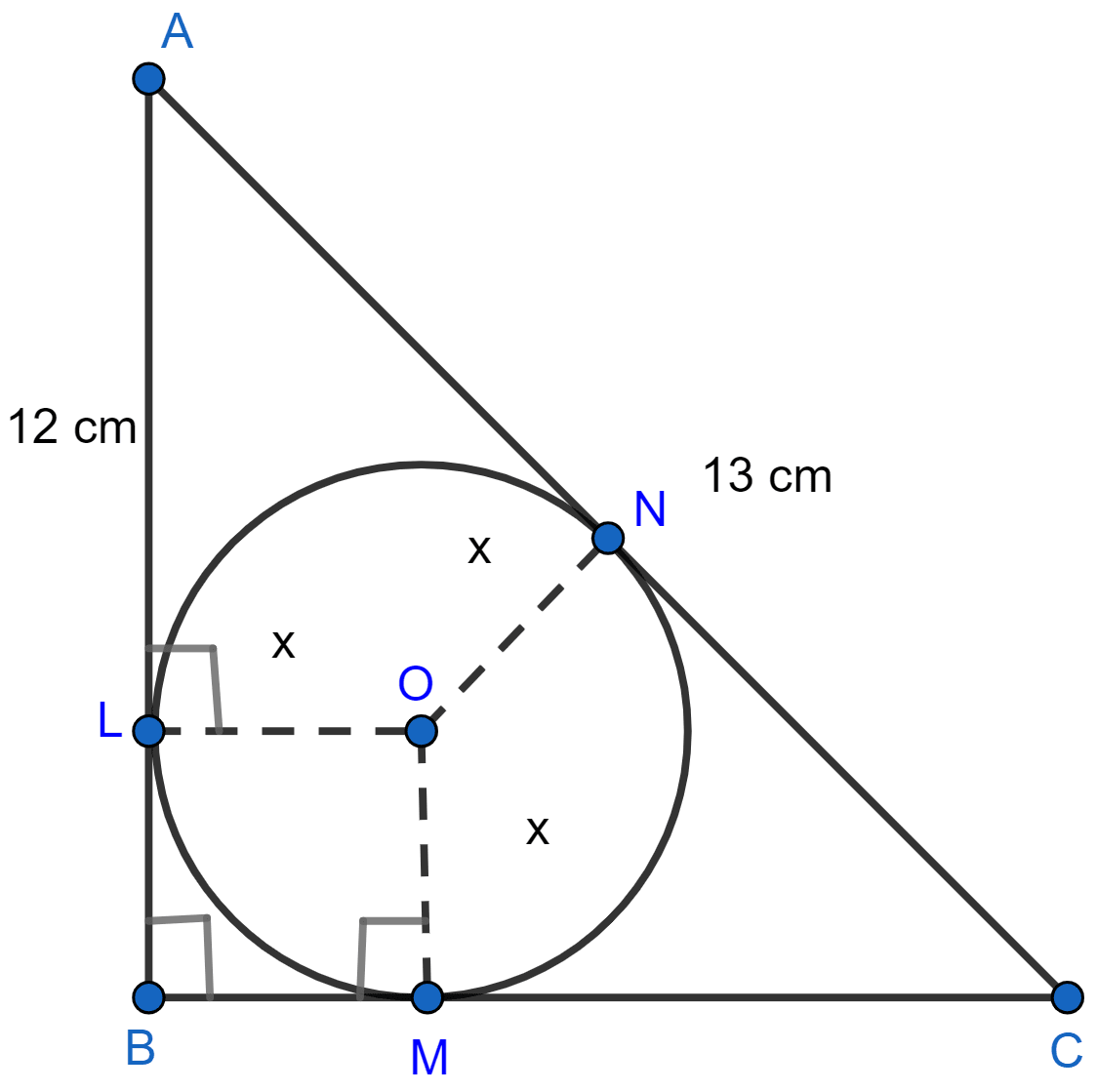
From figure,
LBMO is a square.
LB = BM = OM = OL = x.
AL = AB - LB = (12 - x) cm.
AL = AN = (12 - x) cm. [∵ Tangents from exterior point are equal in length.]
Since, ABC is a right angled triangle,
∴ AC2 = AB2 + BC2 [By pythagoras theorem]
⇒ 132 = 122 + BC2
⇒ BC2 = 132 - 122
⇒ BC2 = 169 - 144
⇒ BC2 = 25
⇒ BC =
⇒ BC = 5 cm.
From figure,
MC = BC - BM = (5 - x) cm.
Also,
CN = CM = (5 - x) cm. [∵ Tangents from exterior point are equal in length.]
Also,
⇒ AC = AN + CN
⇒ 13 = (12 - x) + (5 - x)
⇒ 13 = 17 - 2x
⇒ 2x = 17 - 13
⇒ 2x = 4
⇒ x =
⇒ x = 2 cm.
Hence, x = 2.
Answered By
5 Likes
Related Questions
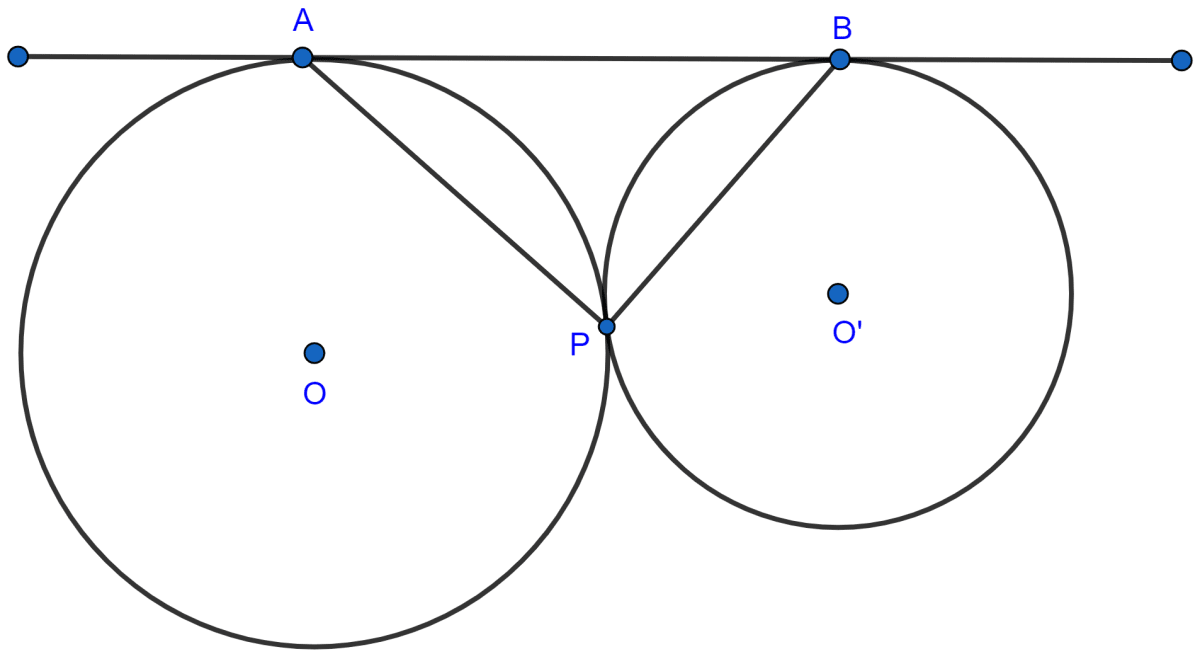
In the given figure, two circles touch each other externally at point P. AB is the direct common tangent of these circles. Prove that :
(i) tangent at point P bisects AB.
(ii) angle APB = 90°.
Tangents AP and AQ are drawn to a circle, with center O, from an exterior point A. Prove that :
∠PAQ = 2∠OPQ
In a triangle ABC, the incircle (center O) touches BC, CA and AB at points P, Q and R respectively. Calculate :
(i) ∠QOR
(ii) ∠QPR;
given that ∠A = 60°.
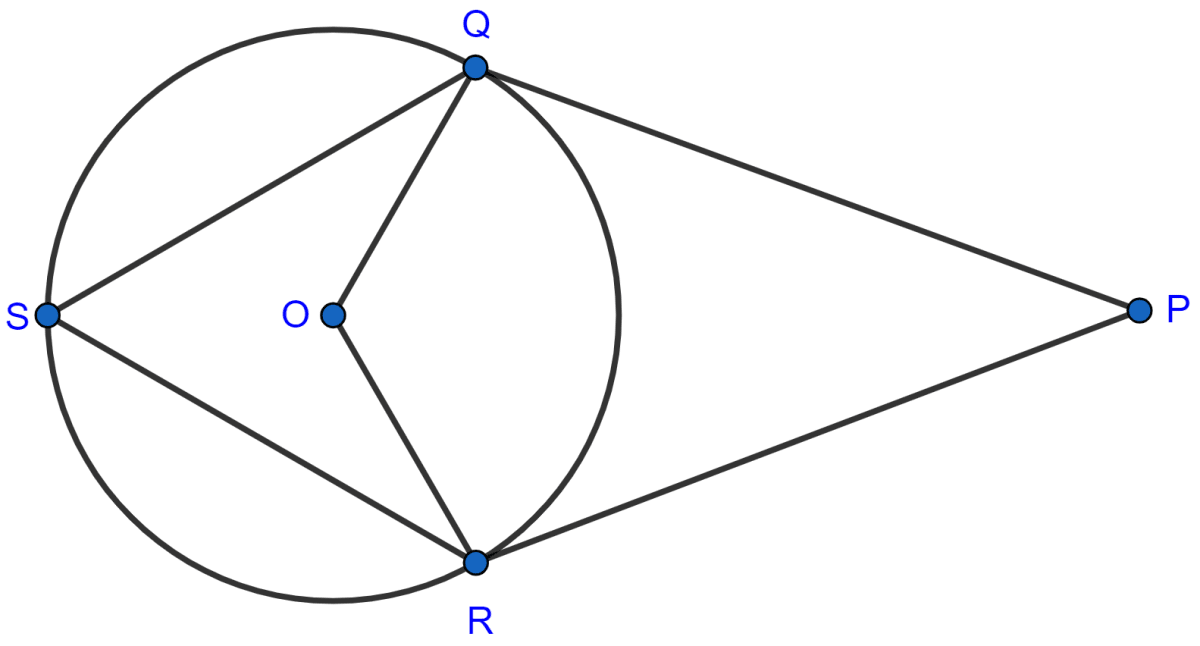
In the following figure, PQ and PR are tangents to the circle, with center O. If ∠QPR = 60°, calculate :
(i) ∠QOR,
(ii) ∠OQR,
(iii) ∠QSR.