Physics
A cell of e.m.f. 2 V and internal resistance 1.2 Ω is connected to an ammeter of resistance 0.8 Ω and two resistors of 4.5 Ω and 9 Ω as shown in figure.
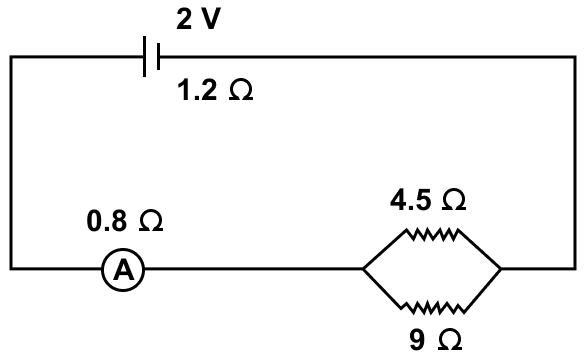
Find —
(a) the reading of the ammeter,
(b) the potential difference across the terminals of the cell, and
(c) the potential difference across the 4.5 Ω resistor.
Related Questions
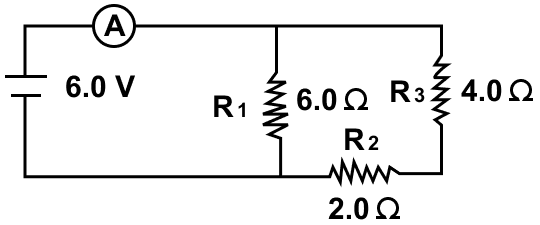
Three resistors of 6.0 Ω, 2.0 Ω and 4.0 Ω are joined to an ammeter A and a cell of e.m.f. 6.0 V as shown in figure. Calculate —
(a) the effective resistance of the circuit, and
(b) the reading of ammeter.
The diagram below in figure shows the arrangement of five different resistances connected to a battery of e.m.f. 1.8 V. Calculate —
(a) the total resistance of the circuit, and
(b) the reading of ammeter A.

The electrical energy supplied by a source is given by:
- W = QV
- W = VIt
- W = I2Rt
- All of the above
1 WH is equal to :
- 3600 J
- 360 J
- 36 J
- 3.6 J