(a) Name any two basic principles of Object-oriented Programming.
Answer
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
(b) Write a difference between unary and binary operator.
Answer
unary operators operate on a single operand whereas binary operators operate on two operands.
(c) Name the keyword which:
- indicates that a method has no return type.
- makes the variable as a class variable
Answer
- void
- static
(d) Write the memory capacity (storage size) of short and float data type in bytes.
Answer
- short — 2 bytes
- float — 4 bytes
(e) Identify and name the following tokens:
- public
- 'a'
- ==
- { }
Answer
- Keyword
- Literal
- Operator
- Separator
(a) Differentiate between if else if and switch-case statements
Answer
| if else if | switch-case |
|---|---|
| if else if can test for any Boolean expression like less than, greater than, equal to, not equal to, etc. | switch-case can only test if the expression is equal to any of its case constants. |
| if else if can use different expression involving unrelated variables in its different condition expressions. | switch-case statement tests the same expression against a set of constant values. |
(b) Give the output of the following code:
String P = "20", Q ="19";
int a = Integer.parseInt(P);
int b = Integer.valueOf(Q);
System.out.println(a+""+b);Answer
Output of the above code is:
2019
Both Integer.parseInt() and Integer.valueOf() methods convert a string into integer. Integer.parseInt() returns an int value that gets assigned to a. Integer.valueOf() returns an Integer object (i.e. the wrapper class of int). Due to auto-boxing, Integer object is converted to int and gets assigned to b. So a becomes 20 and b becomes 19. 2019 is printed as the output.
(c) What are the various types of errors in Java?
Answer
There are 3 types of errors in Java:
- Syntax Error
- Runtime Error
- Logical Error
(d) State the data type and value of res after the following is executed:
char ch = '9';
res= Character.isDigit(ch);Answer
Data type of res is boolean as return type of method Character.isDigit() is boolean. Its value is true as '9' is a digit.
(e) What is the difference between the linear search and the binary search technique?
Answer
| Linear search | Binary search |
|---|---|
| Linear search works on sorted and unsorted arrays. | Binary search works on only sorted arrays. |
| In Linear search, each element of the array is checked against the target value until the element is found or end of the array is reached. | In Binary search, array is successively divided into 2 halves and the target element is searched either in the first half or in the second half. |
| Linear Search is slower. | Binary Search is faster. |
(a) Write a Java expression for the following:
|x2 + 2xy|
Answer
Math.abs(x * x + 2 * x * y)
(b) Write the return data type of the following functions:
- startsWith()
- random()
Answer
- boolean
- double
(c) If the value of basic=1500, what will be the value of tax after the following statement is executed?
tax = basic > 1200 ? 200 :100;Answer
Value of tax will be 200. As basic is 1500, the condition of ternary operator — basic > 1200 is true. 200 is returned as the result of ternary operator and it gets assigned to tax.
(d) Give the output of following code and mention how many times the loop will execute?
int i;
for( i=5; i>=1; i--)
{
if(i%2 == 1)
continue;
System.out.print(i+" ");
}Answer
Output of the above code is:
4 2
Loop executes 5 times. The below table shows the dry run of the loop:
| i | Output | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1st Iteration — As i % 2 gives 1 so condition is true and continue statement is executed. Nothing is printed in this iteration. | |
| 4 | 4 | 2nd Iteration — i % 2 is 0 so condition is false. Print statement prints 4 (current value of i) in this iteration. |
| 3 | 4 | 3rd Iteration — i % 2 is 1 so continue statement is executed and nothing is printed in this iteration. |
| 2 | 4 2 | 4th Iteration — i % 2 is 0. Print statement prints 2 (current value of i) in this iteration. |
| 1 | 4 2 | 5th Iteration — i % 2 is 1 so continue statement is executed and nothing is printed in this iteration. |
| 0 | 4 2 | As condition of loop (i >= 1) becomes false so loops exits and 6th iteration does not happen. |
(e) State a difference between call by value and call by reference.
Answer
In call by value, actual parameters are copied to formal parameters. Any changes to formal parameters are not reflected onto the actual parameters. In call by reference, formal parameters refer to actual parameters. The changes to formal parameters are reflected onto the actual parameters.
(f) Give the output of the following:
Math.sqrt(Math.max(9,16))
Answer
The output is 4.0.
First Math.max(9,16) is evaluated. It returns 16, the greater of its arguments. Math.sqrt(Math.max(9,16)) becomes Math.sqrt(16). It returns the square root of 16 which is 4.0.
(g) Write the output for the following:
String s1 = "phoenix"; String s2 ="island";
System.out.println(s1.substring(0).concat(s2.substring(2)));
System.out.println(s2.toUpperCase());Answer
The output of above code is:
phoenixland
ISLAND
s1.substring(0) results in phoenix. s2.substring(2) results in land. concat method joins both of them resulting in phoenixland. s2.toUpperCase() converts island to uppercase.
(h) Evaluate the following expression if the value of x=2, y=3 and z=1.
v=x + --z + y++ + y
Answer
v = x + --z + y++ + y
⇒ v = 2 + 0 + 3 + 4
⇒ v = 9
(i) String x[] = {"Artificial intelligence", "IOT", "Machine learning", "Big data"};
Give the output of the following statements:
- System.out.println(x[3]);
- System.out.println(x.length);
Answer
- Big data
- 4
(j) What is meant by a package? Give an example.
Answer
A package is a named collection of Java classes that are grouped on the basis of their functionality. For example, java.util.
Design a class name ShowRoom with the following description:
Instance variables / Data members:
String name — To store the name of the customer
long mobno — To store the mobile number of the customer
double cost — To store the cost of the items purchased
double dis — To store the discount amount
double amount — To store the amount to be paid after discount
Member methods:
ShowRoom() — default constructor to initialize data members
void input() — To input customer name, mobile number, cost
void calculate() — To calculate discount on the cost of purchased items, based on following criteria
| Cost | Discount (in percentage) |
|---|---|
| Less than or equal to ₹10000 | 5% |
| More than ₹10000 and less than or equal to ₹20000 | 10% |
| More than ₹20000 and less than or equal to ₹35000 | 15% |
| More than ₹35000 | 20% |
void display() — To display customer name, mobile number, amount to be paid after discount.
Write a main method to create an object of the class and call the above member methods.
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ShowRoom
{
private String name;
private long mobno;
private double cost;
private double dis;
private double amount;
public ShowRoom()
{
name = "";
mobno = 0;
cost = 0.0;
dis = 0.0;
amount = 0.0;
}
public void input() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter customer name: ");
name = in.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter customer mobile no: ");
mobno = in.nextLong();
System.out.print("Enter cost: ");
cost = in.nextDouble();
}
public void calculate() {
int disPercent = 0;
if (cost <= 10000)
disPercent = 5;
else if (cost <= 20000)
disPercent = 10;
else if (cost <= 35000)
disPercent = 15;
else
disPercent = 20;
dis = cost * disPercent / 100.0;
amount = cost - dis;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Customer Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Mobile Number: " + mobno);
System.out.println("Amout after discount: " + amount);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
ShowRoom obj = new ShowRoom();
obj.input();
obj.calculate();
obj.display();
}
}
Using the switch-case statement, write a menu driven program to do the following:
(a) To generate and print Letters from A to Z and their Unicode
| Letters | Unicode |
|---|---|
| A | 65 |
| B | 66 |
| . | . |
| . | . |
| . | . |
| Z | 90 |
(b) Display the following pattern using iteration (looping) statement:
1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KnowledgeBoat
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 1 for letters and Unicode");
System.out.println("Enter 2 to display the pattern");
System.out.print("Enter your choice: ");
int ch = in.nextInt();
switch(ch) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Letters\tUnicode");
for (int i = 65; i <= 90; i++)
System.out.println((char)i + "\t" + i);
break;
case 2:
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
System.out.print(j + " ");
System.out.println();
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong choice");
break;
}
}
}

Write a program to input 15 integer elements in an array and sort them in ascending order using the bubble sort technique.
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatBubbleSort
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = 15;
int arr[] = new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array:");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = in.nextInt();
}
//Bubble Sort
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int t = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = t;
}
}
}
System.out.println("Sorted Array:");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Design a class to overload a function series( ) as follows:
(a) void series (int x, int n) – To display the sum of the series given below:
x1 + x2 + x3 + .......... xn terms
(b) void series (int p) – To display the following series:
0, 7, 26, 63 .......... p terms
(c) void series () – To display the sum of the series given below:
1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4 + .......... 1/10
Answer
public class KboatOverloadSeries
{
void series(int x, int n) {
long sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += Math.pow(x, i);
}
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
}
void series(int p) {
for (int i = 1; i <= p; i++) {
int term = (int)(Math.pow(i, 3) - 1);
System.out.print(term + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
void series() {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 2; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += 1.0 / i;
}
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
}
}


Write a program to input a sentence and convert it into uppercase and count and display the total number of words starting with a letter 'A'.
Example:
Sample Input: ADVANCEMENT AND APPLICATION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ARE EVER CHANGING.
Sample Output: Total number of words starting with letter 'A' = 4
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class WordsWithLetterA
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a string: ");
String str = in.nextLine();
str = " " + str; //Add space in the begining of str
int c = 0;
int len = str.length();
str = str.toUpperCase();
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
if (str.charAt(i) == ' ' && str.charAt(i + 1) == 'A')
c++;
}
System.out.println("Total number of words starting with letter 'A' = " + c);
}
}
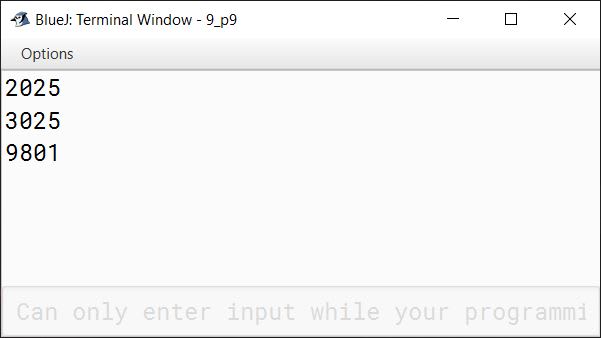
A tech number has even number of digits. If the number is split in two equal halves, then the square of sum of these halves is equal to the number itself. Write a program to generate and print all four digits tech numbers.
Example:
Consider the number 3025
Square of sum of the halves of 3025 = (30 + 25)2
= (55)2
= 3025 is a tech number.
Answer
public class TechNumbers
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
for (int i = 1000; i <= 9999; i++) {
int secondHalf = i % 100;
int firstHalf = i / 100;
int sum = firstHalf + secondHalf;
if (i == sum * sum)
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}