Computer Applications
Write a program in Java to input a series of numbers one by one to print the count and average of those numbers which have 3 as their last digit. The process of inputting numbers should stop if the number inputted by the user is a negative number.
Java
Java Iterative Stmts
1 Like
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatNumbers
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the numbers: ");
int count = 0;
double sum = 0;
while (true) {
int n = in.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
break;
}
int ld = n % 10;
if (ld == 3) {
count++;
sum += n;
}
}
double avg = sum / count;
System.out.println("Count = " + count);
System.out.println("Average = " + avg);
}
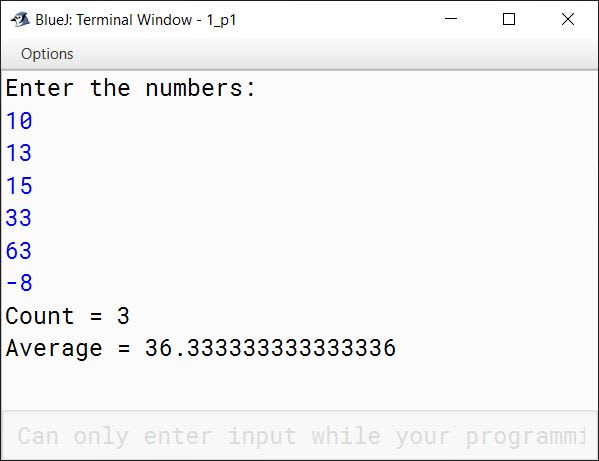
}Output
Answered By
3 Likes
Related Questions
Convert the following for loop segment to an exit-controlled loop.
for (int x = 1, y = 2; x < 11; x += 2, y += 2) { System.out.println(x + "\t" + y); }Define a class to accept a number and check whether it is an FDS Number or not. A number is called an FDS Number if the sum of the factorials of its digits equals the number itself.
Example 1:
Input: 145
Output: FDS Number [1! + 4! + 5! = 1 + 24 + 120 = 145]Example 2:
Input: 123
Output: Not an FDS Number [1! + 2! + 3! = 1 + 2 + 6 ≠ 123]import java.util.Scanner; class KboatFDSNum { static int fact(int d) { int f = 1; _______(1)_________ { _______(2)_________ } _______(3)_________ } public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter a number: "); int num = in.nextInt(); int t = num, sum = 0; _______(4)_________ { _______(5)_________ _______(6)_________ _______(7)_________ } _______(8)_________ { _______(9)_________ } else { _______(10)_________ } } }Define a class to accept a number from user and check if it is an EvenPal number or not.
(The number is said to be EvenPal number when number is palindrome number (a number is palindrome if it is equal to its reverse) and sum of its digits is an even number.)
Example: 121 – is a palindrome number
Sum of the digits – 1+2+1 = 4 which is an even numberWhich of the following are entry controlled loops?
(a) for
(b) while
(c) do..while
(d) switch
- only a
- a and b
- a and c
- c and d