Computer Applications
Define a class to accept a number and check whether it is an FDS Number or not. A number is called an FDS Number if the sum of the factorials of its digits equals the number itself.
Example 1:
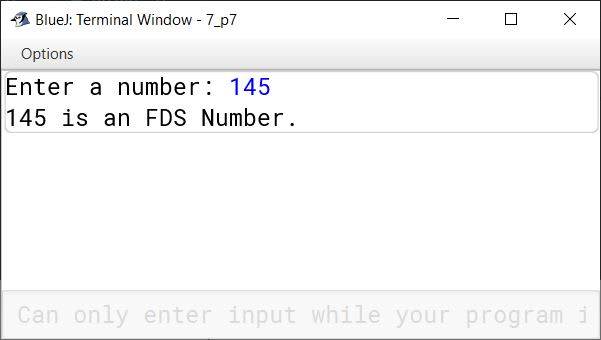
Input: 145
Output: FDS Number [1! + 4! + 5! = 1 + 24 + 120 = 145]
Example 2:
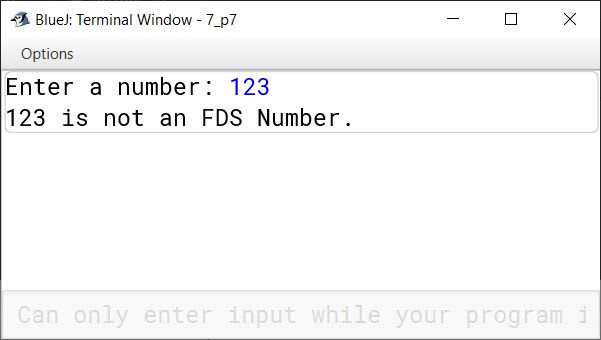
Input: 123
Output: Not an FDS Number [1! + 2! + 3! = 1 + 2 + 6 ≠ 123]
import java.util.Scanner;
class KboatFDSNum {
static int fact(int d) {
int f = 1;
_______(1)_________ {
_______(2)_________
}
_______(3)_________
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int num = in.nextInt();
int t = num, sum = 0;
_______(4)_________ {
_______(5)_________
_______(6)_________
_______(7)_________
}
_______(8)_________ {
_______(9)_________
} else {
_______(10)_________
}
}
}
Java Iterative Stmts
1 Like
Answer
for (int i = 1; i <= d; i++)f *= i;return f;while (t > 0)int d = t % 10;sum += fact(d);t /= 10;if (sum == num)System.out.println(num + " is an FDS Number.");System.out.println(num + " is not an FDS Number.");
Explanation
import java.util.Scanner;
class KboatFDSNum {
static int fact(int d) {
int f = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= d; i++) {
f *= i;
}
return f;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int num = in.nextInt();
int t = num, sum = 0;
while (t > 0) {
int d = t % 10;
sum += fact(d);
t /= 10;
}
if (sum == num) {
System.out.println(num + " is an FDS Number.");
} else {
System.out.println(num + " is not an FDS Number.");
}
}
}
Variable Description Table
Function: fact
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
d | int | Represents the digit whose factorial is to be calculated. |
f | int | Used to store the factorial of the digit d, initialized to 1. |
Function: main
| Variable | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
in | Scanner | An instance of Scanner to read input from the user. |
num | int | The number input by the user to check if it is an FDS number. |
t | int | A temporary variable used to hold the value of num during processing. |
sum | int | Used to store the sum of factorials of digits of the number. |
d | int | Used inside the while loop to hold the current digit extracted from t. |
Program Explanation
Let's go through the Java program step by step to understand how it works:
1. Import Scanner Class:
The program begins by importing the Scanner class, which is part of the java.util package. This class is used to read user input from the keyboard.
import java.util.Scanner;
2. Class Declaration:
The class KboatFDSNum is declared. This class contains the main method and a static method for calculating factorials.
class KboatFDSNum {
3. Factorial Method (fact):
A static method fact(int d) is defined to compute the factorial of a given integer d.
- The method initializes a local variable
fto 1. - It then uses a
forloop to multiplyfby every integer from 1 tod. - Finally, it returns the computed factorial.
static int fact(int d) {
int f = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= d; i++) {
f *= i;
}
return f;
}
4. Main Method:
The main method is the entry point of the program and is responsible for the execution of the FDS Number check.
public static void main(String args[]) {
5. User Input:
An instance of the Scanner class is created to read input from the user. The program prompts the user to enter a number and stores this input in the variable num.
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
int num = in.nextInt();
6. Initialization for Checking:
Two variables t and sum are initialized. t is set to the value of num to preserve the original number, while sum is initialized to 0 to accumulate the sum of the factorials of the digits.
int t = num, sum = 0;
7. Sum of Factorials of Digits:
A while loop is used to extract each digit of the number t, compute its factorial using the fact method, and add the factorial to sum. The loop continues until all digits of the number t have been processed (t > 0).
while (t > 0) {
int d = t % 10; // Extract the last digit
sum += fact(d); // Add factorial of the digit to sum
t /= 10; // Remove the last digit from t
}
8. Check and Output Results:
After the loop, the program checks if the sum of the factorials of the digits (sum) is equal to the original number (num). If they are equal, it prints that the number is an FDS Number. Otherwise, it prints that the number is not an FDS Number.
if (sum == num) {
System.out.println(num + " is an FDS Number.");
} else {
System.out.println(num + " is not an FDS Number.");
}
Output
Answered By
2 Likes
Related Questions
How many times will the following loop execute? Write the output of the code:
for(int j = 12; j >= 2; j -= 2) { if(j % 5 == 0) continue; System.out.println(j); }Define a class to accept a number from user and check if it is an EvenPal number or not.
(The number is said to be EvenPal number when number is palindrome number (a number is palindrome if it is equal to its reverse) and sum of its digits is an even number.)
Example: 121 – is a palindrome number
Sum of the digits – 1+2+1 = 4 which is an even numberTo execute a loop 10 times, which of the following is correct?
- for (int i=11;i<=30;i+=2)
- for (int i=11;i<=30;i+=3)
- for (int i=11;i<20;i++)
- for (int i=11;i<=21;i++)
Define a class to accept a number and check whether it is a SUPERSPY number or not. A number is called SUPERSPY if the sum of the digits equals the number of the digits.
Example1:
Input: 1021 output: SUPERSPY number [SUM OF THE DIGITS = 1+0+2+1 = 4, NUMBER OF DIGITS = 4 ]Example2:
Input: 125 output: Not an SUPERSPY number [1+2+5 is not equal to 3]