Mathematics
Using remainder theorem, factorise 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2 completely.
Factorisation
3 Likes
Answer
Substituting, x = 2 in 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2, we get :
⇒ 6(2)3 - 11(2)2 - 3(2) + 2
⇒ 6 × 8 - 11 × 4 - 6 + 2
⇒ 48 - 44 - 6 + 2
⇒ 6 - 6
⇒ 0.
∴ (x - 2) is a factor of 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2.
On dividing 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2 by (x - 2), we get:
∴ 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2 = (x - 2)(6x2 + x - 1)
⇒ 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2 = (x - 2)(6x2 + 3x - 2x - 1)
⇒ 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2 = (x - 2)[3x(2x + 1) - 1(2x + 1)]
⇒ 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2 = (x - 2)(3x - 1)(2x + 1).
Hence, 6x3 - 11x2 - 3x + 2 = (x - 2)(3x - 1)(2x + 1).
Answered By
2 Likes
Related Questions
If }[r] x & 6 \ y & 8 \end{bmatrix} + 3 \times \begin{bmatrix}[r] 1 & -1 \ 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix} = 3 \times \begin{bmatrix}[r] 3 & 3 \ 4 & 6 \end{bmatrix}, find the values of x and y.
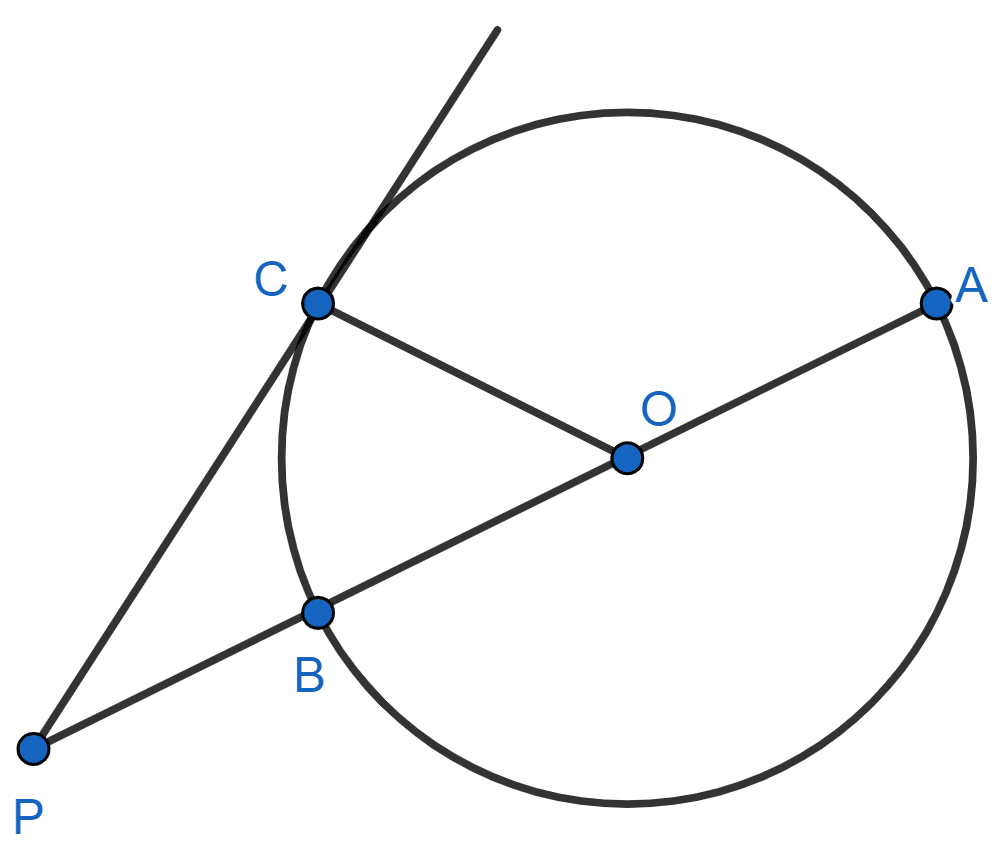
In the given figure, AB is diameter and PC is tangent to the circle with center O. If AP = 40 cm, CP = 20 cm, find the radius of the circle.
In rhombus ABCD, the co-ordinates of point A and C are (2, -6) and (-4, 8) respectively. Find the equation of the diagonal BD.
Prove that :
= 2 cosec A.