Mathematics
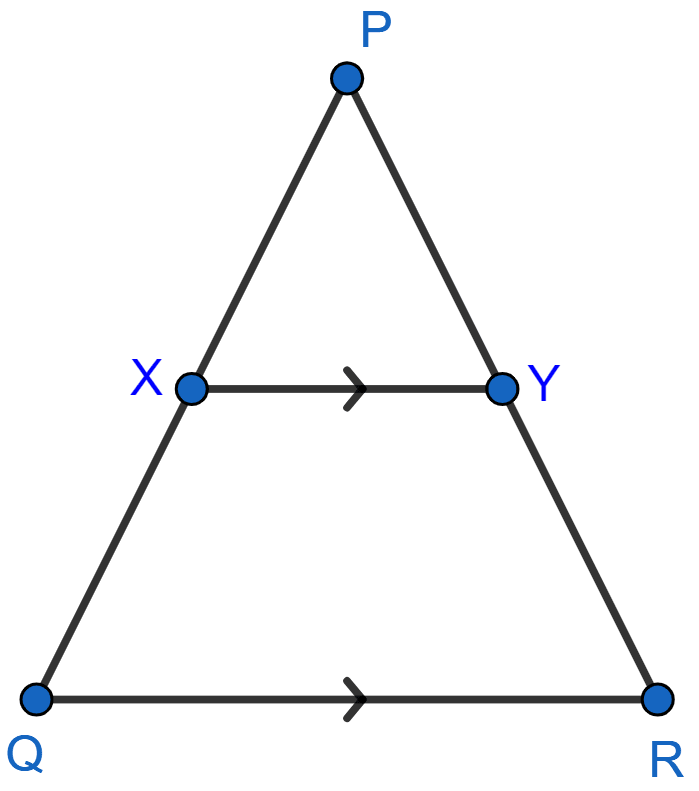
The given figure shows a triangle PQR in which XY is parallel to QR. If PX : XQ = 1 : 3 and QR = 9 cm, find the length of XY.
Further, if the area of △PXY = x cm2; find, in terms of x, the area of :
(i) triangle PQR
(ii) trapezium XQRY.
Similarity
1 Like
Answer
(i) In △PXY and △PQR,
∠PXY = ∠PQR [Corresponding angles are equal]
∠XPY = ∠QPR [Common angles]
∴ △PXY ~ △PQR [By AA]
Given,
⇒ PX : XQ = 1 : 3
⇒
Let PX = a and XQ = 3a
From figure,
⇒ PQ = PX + XQ = a + 3a = 4a.
Since, corresponding sides of similar triangle are proportional.
Hence, XY = 2.25 cm.
(i) We know that,
The ratio between the areas of two similar triangles is same as the square of the ratio between their corresponding sides.
Hence, Area of ∆PQR = 16x cm2.
(ii) From figure,
Area of trapezium XQRY = Area of ∆PQR - Area of ∆PXY
= 16x - x = 15x.
Hence, Area of trapezium XQRY = 15x cm2.
Answered By
1 Like
Related Questions
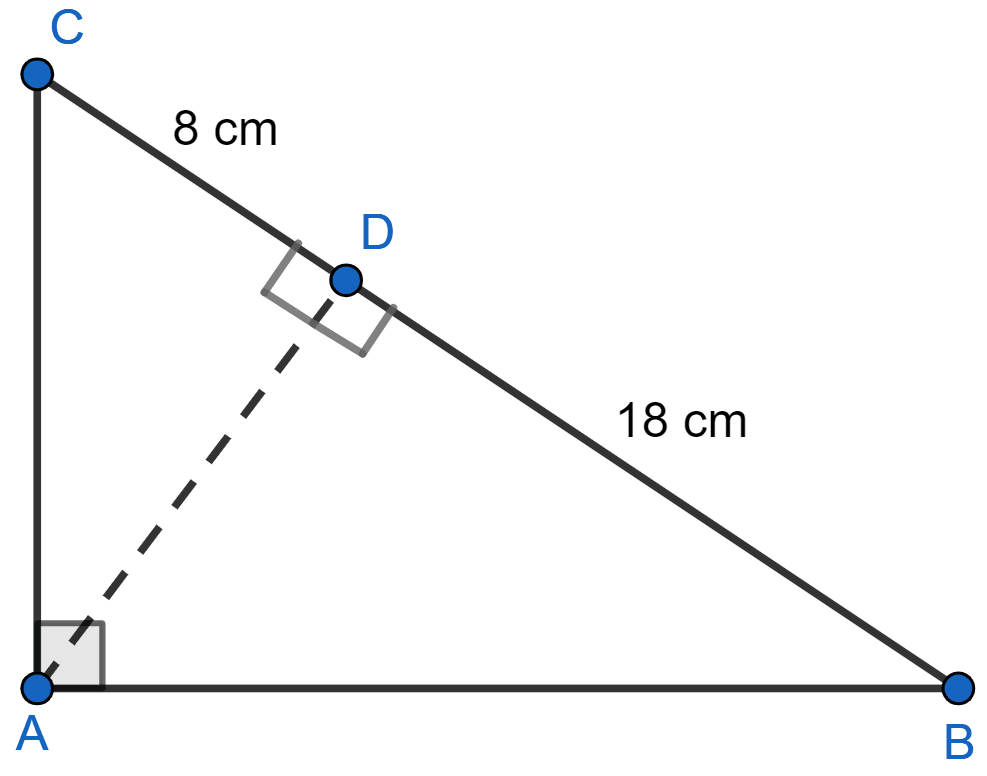
In the given figure, ABC is a right angled triangle with ∠BAC = 90°.
(i) Prove that : △ADB ~ △CDA.
(ii) If BD = 18 cm and CD = 8 cm, find AD.
(iii) Find the ratio of the area of △ADB is to area of △CDA.
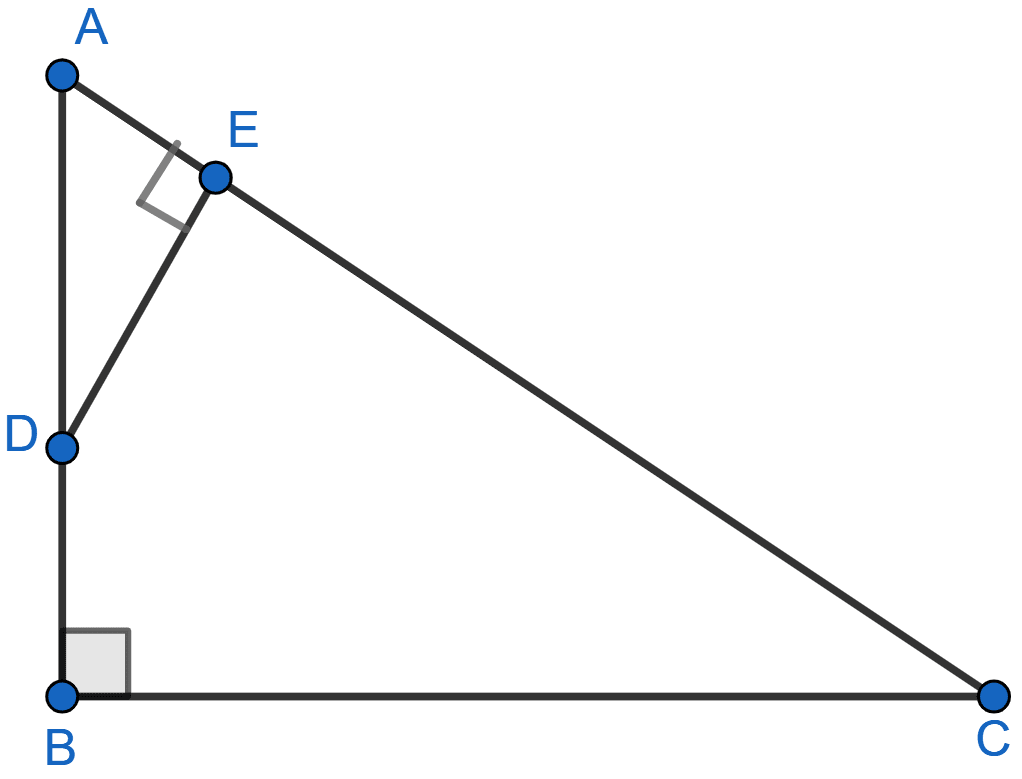
ABC is a right angled triangle with ∠ABC = 90°. D is any point on AB and DE is perpendicular to AC. Prove that :
(i) △ADE ~ △ACB
(ii) If AC = 13 cm, BC = 5 cm and AE = 4 cm. Find DE and AD.
(iii) Find, area of △ADE : area of quadrilateral BCED.
Given : AB || DE and BC || EF. Prove that :
(i)
(ii) △DFG ~ △ACG.

PQR is a triangle. S is a point on the side QR of △PQR such that ∠PSR = ∠QPR. Given QP = 8 cm, PR = 6 cm and SR = 3 cm.
(i) Prove △PQR ~ △SPR.
(ii) Find the lengths of QR and PS.
(iii)
