Mathematics
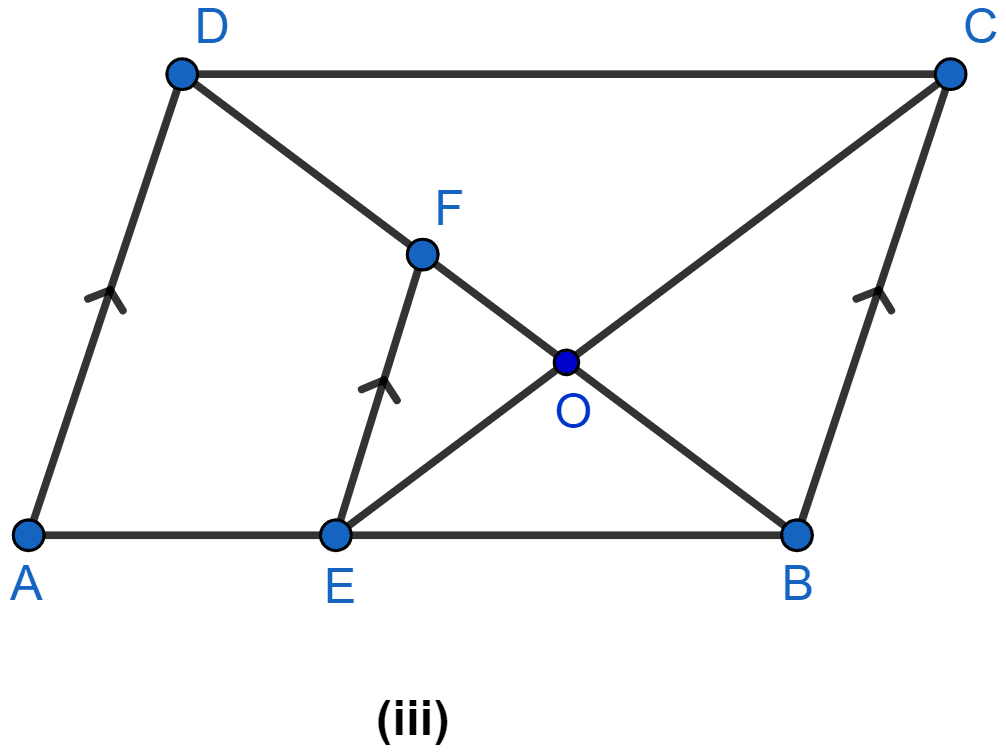
In the figure (iii) given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. E is a point on AB, CE intersects the diagonal BD at O and EF || BC. If AE : EB = 2 : 3, find
(i) EF : AD
(ii) area of △BEF : area of △ABD
(iii) area of △ABD : area of trap. AEFD
(iv) area of △FEO : area of △OBC.
Similarity
36 Likes
Answer
(i) Considering △ADB and △EFB,
∠ B = ∠ B (Common angles)
∠ DAB = ∠ FEB (Corresponding angles are equal)
Hence, by AA axiom △ADB ~ △EFB.
We know that when triangles are similar the ratio of the corresponding sides are equal,
Given, .
Since,
Hence, EF : AD = 3 : 5.
(ii) Considering △ABD and △BEF,
∠ B = ∠ B (Common angles)
∠ DAB = ∠ FEB (Corresponding angles are equal)
Hence, by AA axiom △ADB ~ △BEF.
We know that, the ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the square of their corresponding sides.
Hence, area of △BEF : area of △ABD = 9 : 25.
(iii) From (ii) we get,
⇒ 9 x Area of △ABD = 25 x Area of △BEF
⇒ 9 x Area of △ABD = 25 x (Area of △ABD - Area of trapezium AEFD)
⇒ 9 x Area of △ABD = 25 x Area of △ABD - 25 x Area of trapezium AEFD
⇒ 16 x Area of △ABD = 25 x Area of trapezium AEFD
Hence, area of △ABD : area of trapezium AEFD = 25 : 16.
(iv) Considering △FEO and △OBC,
∠ FOE = ∠ BOC (Vertically opposite angles are equal)
∠ FEO = ∠ OCB (Alternate angles are equal)
Hence, by AA axiom △FEO ~ △OBC.
We know that, the ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the square of their corresponding sides.
Since, in parallelogram opposite sides are equal so, BC = AD.
Hence, the ratio of the area of △FEO : area of △OBC = 9 : 25.
Answered By
20 Likes
Related Questions
In the figure (i) given below, DE || BC and the ratio of the areas of △ADE and trapezium DBCE is 4 : 5. Find the ratio of DE : BC.

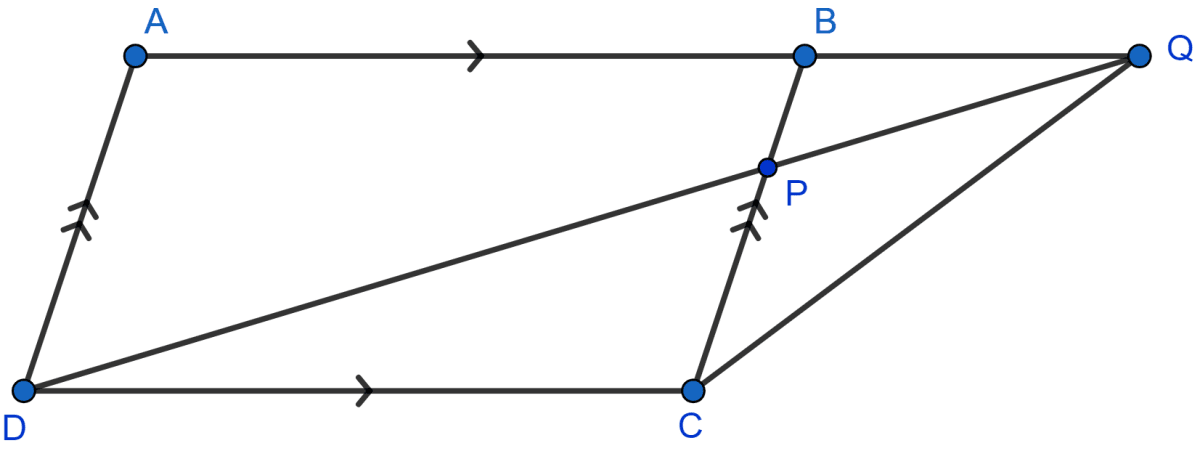
In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. P is a point on BC such that BP : PC = 1 : 2 and DP produced meets AB produced at Q.
If area of △CPQ = 20 cm2, find
(i) area of △BPQ.
(ii) area of △CDP.
(iii) area of ||gm ABCD.
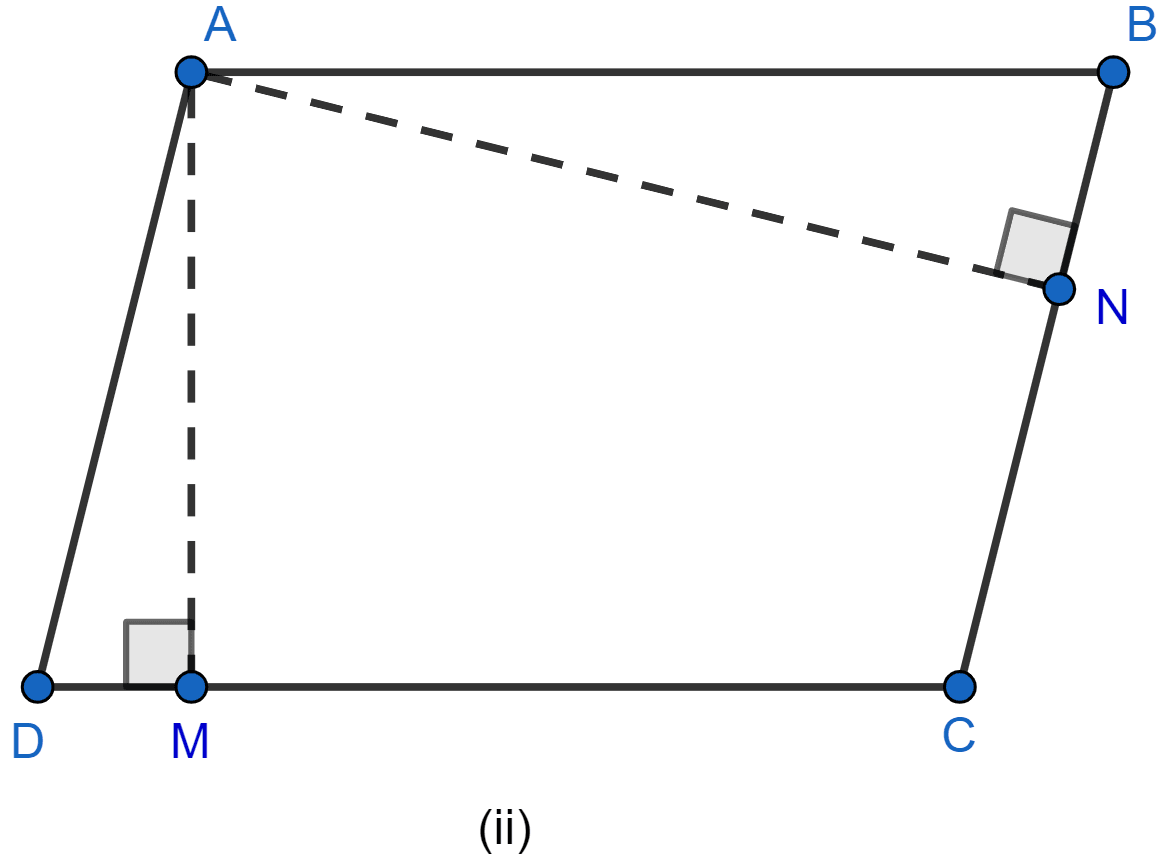
In the figure (ii) given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. AM ⊥ DC and AN ⊥ CB. If AM = 6 cm, AN = 10 cm and the area of parallelogram ABCD is 45 cm2, find
(i) AB
(ii) BC
(iii) area of △ADM : area of △ANB.
In the figure (i) given below, ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and AB = 2 CD. Determine the ratio of the areas of △AOB and △COD.
