Mathematics
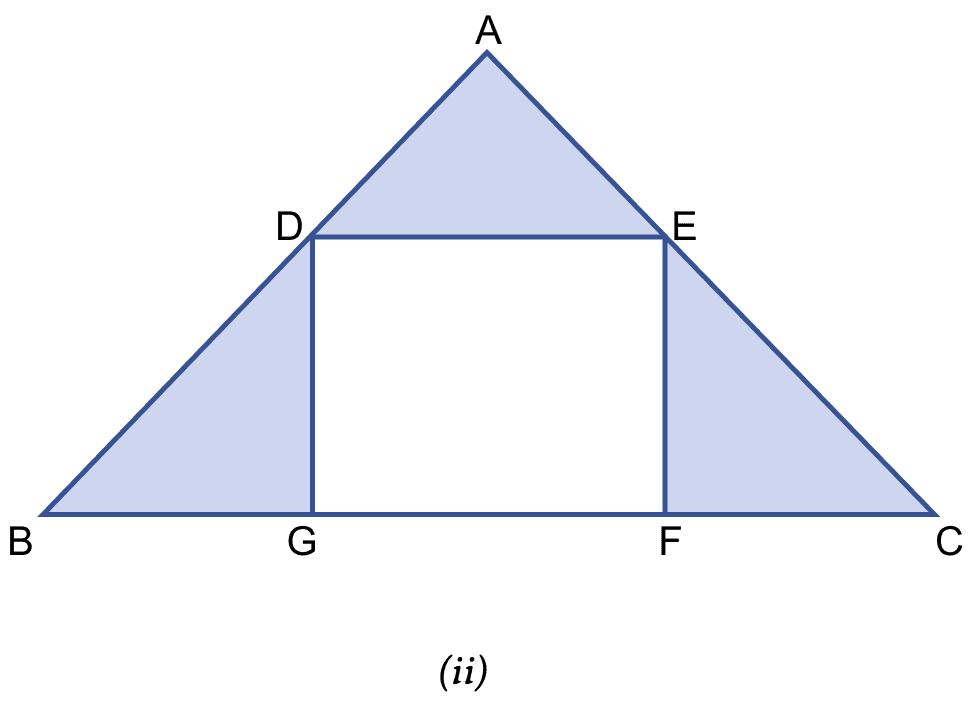
In the figure (ii) given, ABC is an isosceles right-angled triangle and DEFG is a rectangle. If AD = AE = 3 cm and DB = EC = 4 cm, find the area of the shaded region.
Mensuration
47 Likes
Answer
From figure,
In right angle triangle ADE,
Using pythagoras theorem,
⇒ DE2 = AD2 + AE2
⇒ DE2 = 32 + 32
⇒ DE2 = 9 + 9
⇒ DE2 = 18
⇒ DE = cm
Since, DEFG is a rectangle.
∴ GF = DE = cm.
In △DBG and △ECF,
DB = EC = 4 cm
DG = EF (Opposite sides of rectangle are equal)
∠DGB = ∠EFC = 90° (∵ DEFG is a rectangle)
Hence, by RHS axiom △DBG ≅ △ECF.
So, BG = FC (By C.P.C.T.)
Let BG = FC = x.
In right angle triangle ABC,
⇒ BC2 = AB2 + AC2
⇒ BC2 = 72 + 72
⇒ BC2 = 49 + 49
⇒ BC2 = 98
⇒ BC = cm
From figure,
BG + GF + FC = BC
⇒ BG + GF + FC =
⇒ x + + x =
⇒ 2x =
⇒ 2x =
⇒ x = cm.
In right angle triangle DBG,
⇒ DB2 = BG2 + DG2
⇒ 42 = 2 + DG2
⇒ 16 = 8 + DG2
⇒ DG2 = 16 - 8 = 8
⇒ DG = cm.
Area of right angle triangle DBG = x BG x DG
= x x
= x 8 = 4 cm2.
Since, △DBG ≅ △ECF.
∴ Areas of both triangle are equal.
Area of right angle triangle ADE = x AD x AE
= x 3 x 3
= = 4.5 cm2.
Area of shaded region = Area of (△ADE + △DBG + △ECF)
= 4.5 + 4 + 4 = 12.5 cm2.
Hence, area of shaded region = 12.5 cm2.
Answered By
32 Likes
Related Questions
An umbrella is made by stitching 10 triangular pieces of cloth of two different colors (shown in the adjoining figure), each piece measuring 20 cm, 50 cm and 50 cm. How much cloth of each colour is required for the umbrella?

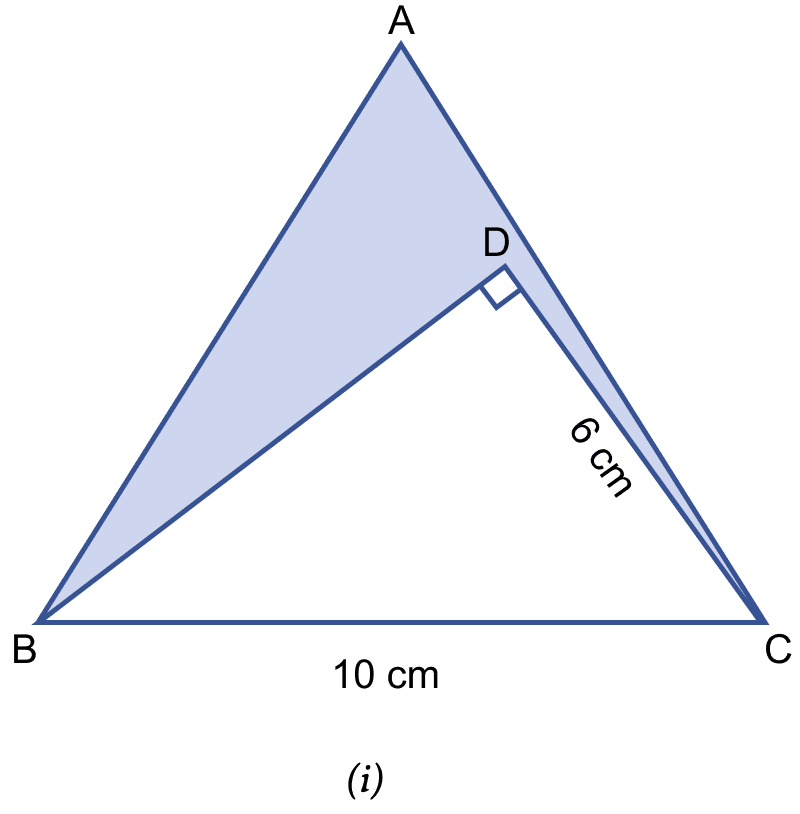
In the figure (i) given below, ABC is an equilateral triangle with each side of length 10 cm. In △BCD, ∠D = 90° and CD = 6 cm. Find the area of the shaded region. Give your answer correct to one decimal place.
Find the area of quadrilateral whose one diagonal is 20 cm long and the perpendiculars to this diagonal from other vertices are of length 9 cm and 15 cm.
Find the area of a quadrilateral whose diagonals are of length 18 cm and 12 cm and they intersect each other at right angles.