Mathematics
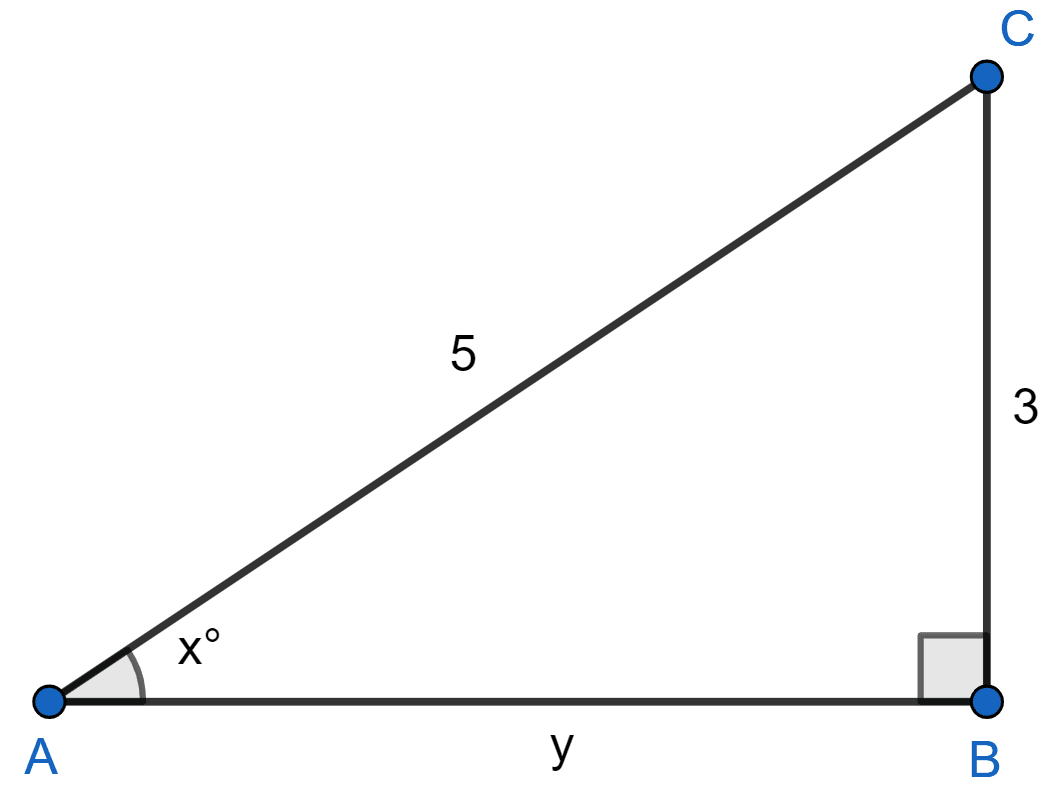
In the figure (2) given below, ∆ABC is right-angled at B. If AB = y units, BC = 3 units and CA = 5 units, find
(i) sin x°
(ii) y.
Trigonometrical Ratios
22 Likes
Answer
(i) By formula,
sin x° =
= .
Hence, sin x° = .
(ii) In right-angled ∆ABC
Using pythagoras theorem
⇒ AC2 = BC2 + AB2
⇒ AB2 = AC2 - BC2
⇒ y2 = 52 - 32
⇒ y2 = 25 - 9
⇒ y2 = 16
⇒ y =
⇒ y = 4.
Hence, y = 4 units.
Answered By
10 Likes
Related Questions
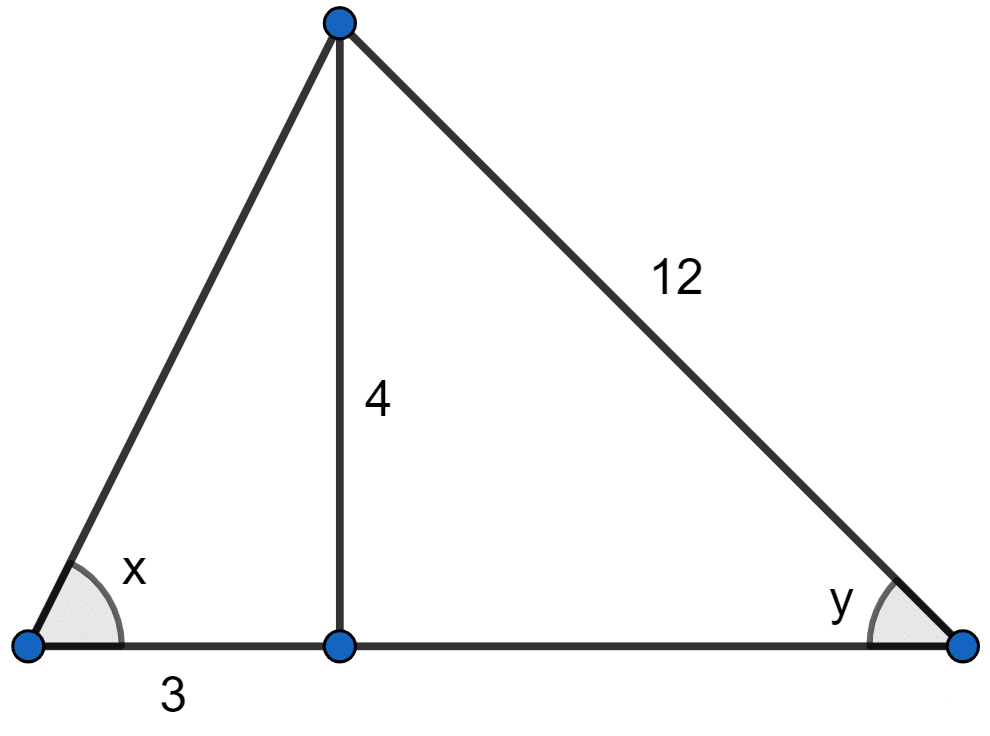
From the figure (2) given below, find the value of :
(i) sin x
(ii) cot x
(iii) cot2 x - cosec2 x
(iv) sec y
(v) tan2 y -
From the figure (1) given below, find the values of :
(i) 2 sin y - cos y
(ii) 2 sin x - cos x
(iii) 1 - sin x + cos y
(iv) 2 cos x - 3 sin y + 4 tan x

In a right-angled triangle, it is given that angle A is an acute angle and that tan A = . Find the values of :
(i) cos A
(ii) cosec A - cot A.
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 90°. If AB = 7 cm and BC - AC = 1 cm, find :
(i) sin C
(ii) tan B