Mathematics
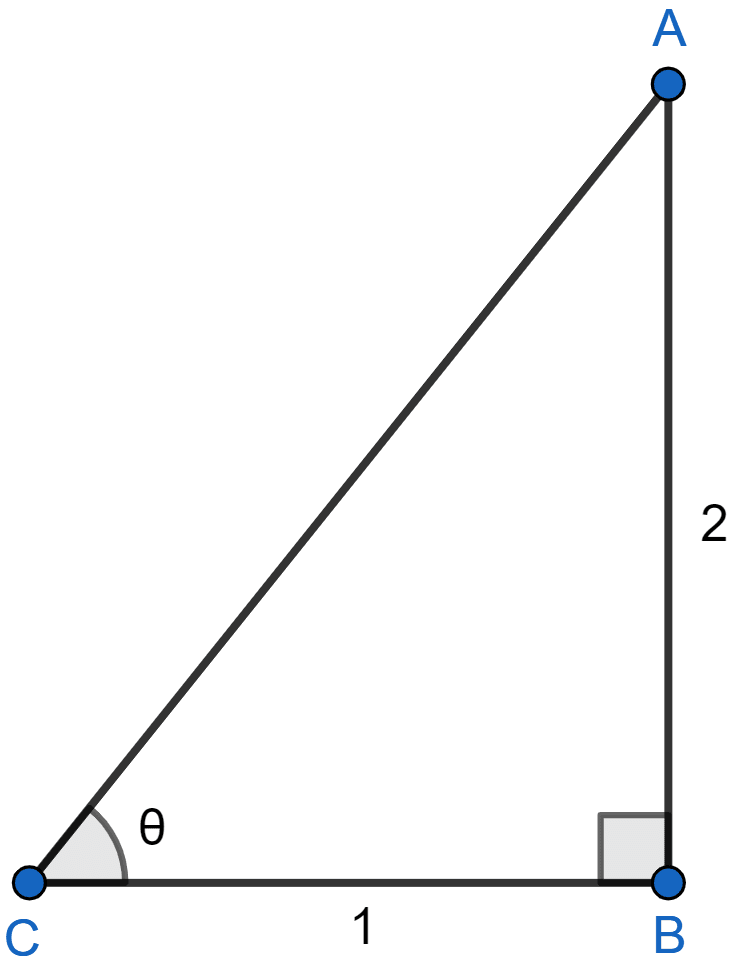
In the figure (2) given below, △ABC is right-angled at B. Given that ∠ACB = θ, side AB = 2 units and side BC = 1 unit, find the value of sin2 θ + tan2 θ.
Trigonometrical Ratios
33 Likes
Answer
In right angle triangle ABC,
⇒ AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ AC2 = (2)2 + (1)2
⇒ AC2 = 4 + 1 = 5
⇒ AC = .
Calculating sin θ, we get :
Calculating tan θ, we get :
Substituting value of sin θ and tan θ in sin2 θ + tan2 θ, we get :
Hence, sin2 θ + tan2 θ = .
Answered By
21 Likes
Related Questions
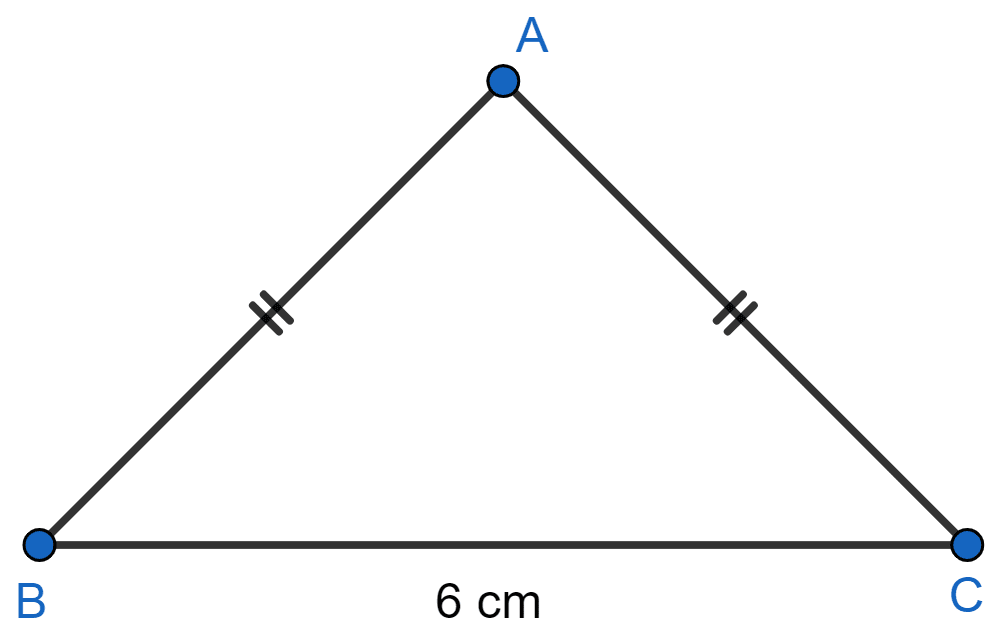
In the figure (1) given below, ∆ABC is isosceles with AB = AC = 5 cm and BC = 6 cm. Find
(i) sin C
(ii) tan B
(iii) tan C - cot B.
In △ABC, AB = AC = 15 cm, BC = 18 cm. Find
(i) cos ∠ABC
(ii) sin ∠ACB.
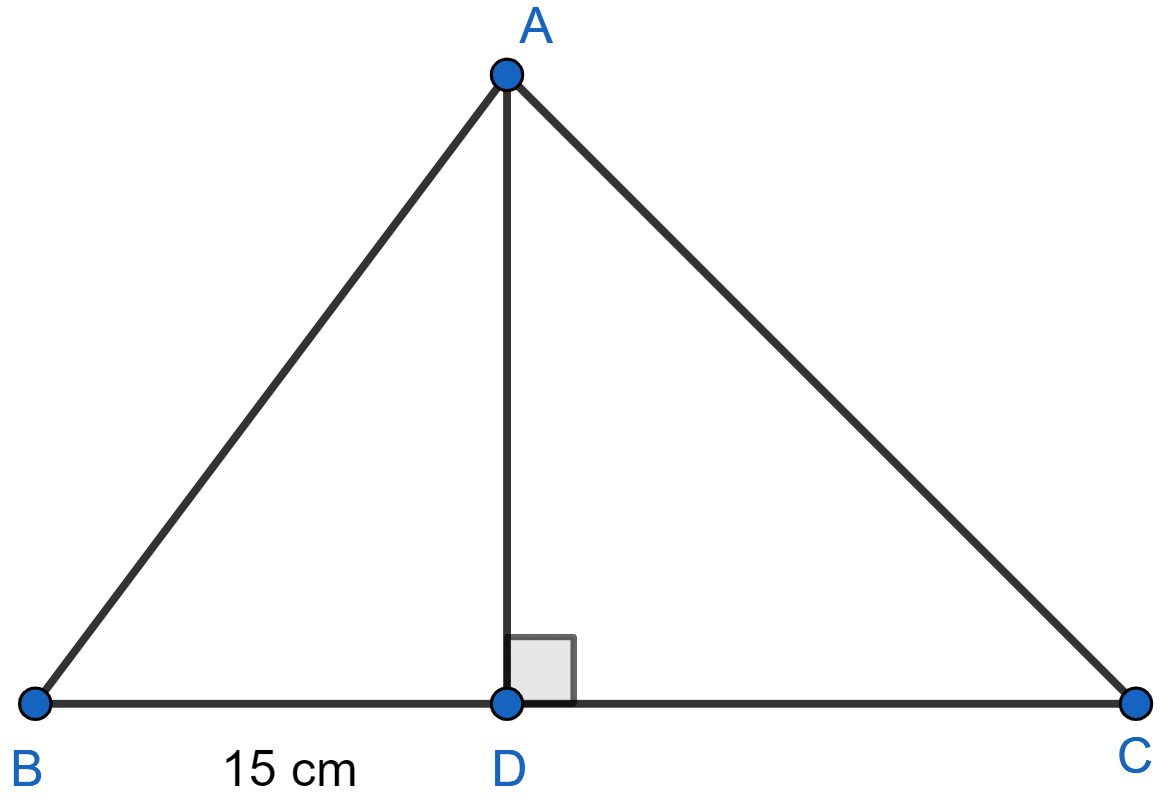
In the figure (3) given below, AD is perpendicular to BC, BD = 15 cm, sin B = and tan C = 1.
(i) Calculate the lengths of AD, AB, DC and AC.
(ii) Show that = -1.
If sin θ = and θ is acute angle, find
(i) cos θ
(ii) tan θ.