Mathematics
In the figure (2) given below, ∆ABC is right-angled at B and BD is perpendicular to AC. Find :
(i) cos ∠CBD
(ii) cot ∠ABD

Trigonometrical Ratios
53 Likes
Answer
In right angle ∆ABC,
⇒ AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ AC2 = 122 + 52
⇒ AC2 = 144 + 25
⇒ AC2 = 169
⇒ AC = = 13.
Let ∠CBD = x.
∠DBA = 90° - x
In ∆DAB,
⇒ ∠DAB + ∠ADB + ∠DBA = 180° [Angle sum property of triangle]
⇒ ∠DAB + 90° + 90° - x = 180°
⇒ ∠DAB = 180° - 180° + x
⇒ ∠DAB = x.
From figure,
∠DAB = ∠CAB = x
∴ ∠CBD = ∠CAB = x
(i) cos ∠CBD = cos ∠CAB
= .
Hence, cos ∠CBD = .
(ii) In ∆BCD,
⇒ ∠DBC + ∠DCB + ∠CDB = 180° [Angle sum property of triangle]
⇒ ∠DCB + x + 90° = 180°
⇒ ∠DCB = 180° - 90° - x
⇒ ∠DCB = 90° - x.
From figure,
∠DCB = ∠ACB =90° - x
∴ ∠ABD = ∠ACB = 90° - x
∴ cot ∠ABD = cot ∠ACB
= .
Hence, cot ∠ABD = .
Answered By
41 Likes
Related Questions
If in ∆ABC, ∠C = 90° and tan A = , prove that
sin A cos B + cos A sin B = 1.
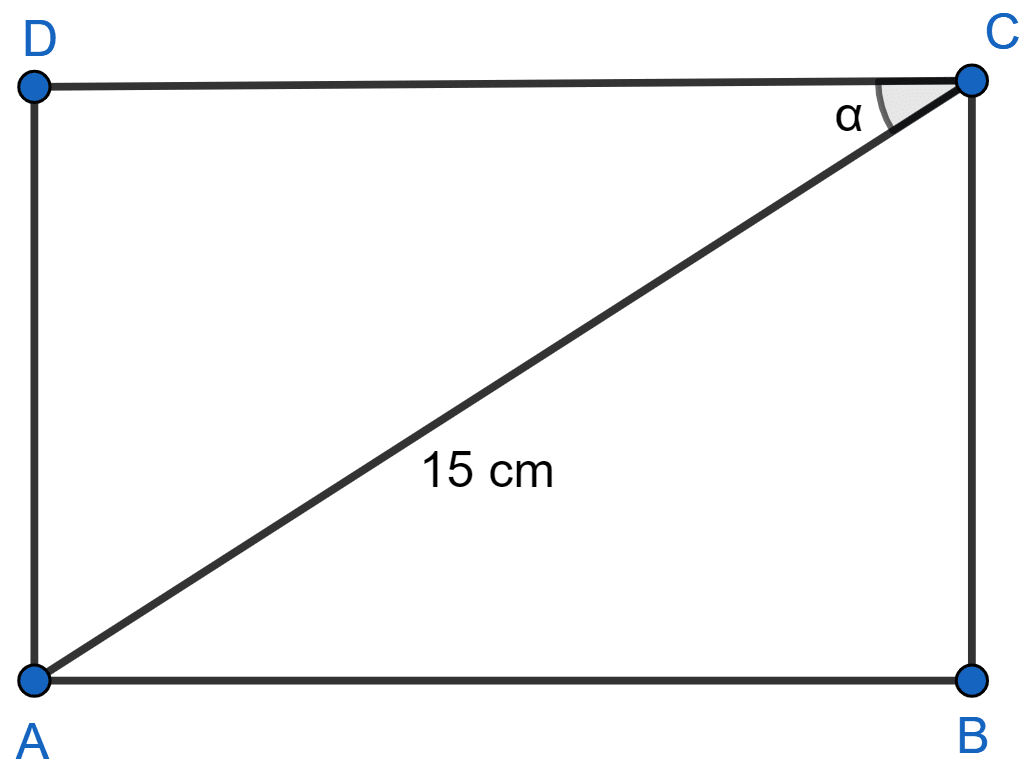
In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a rectangle. Its diagonal AC = 15 cm and ∠ACD = α. If cot α = , find the perimeter and the area of the rectangle.
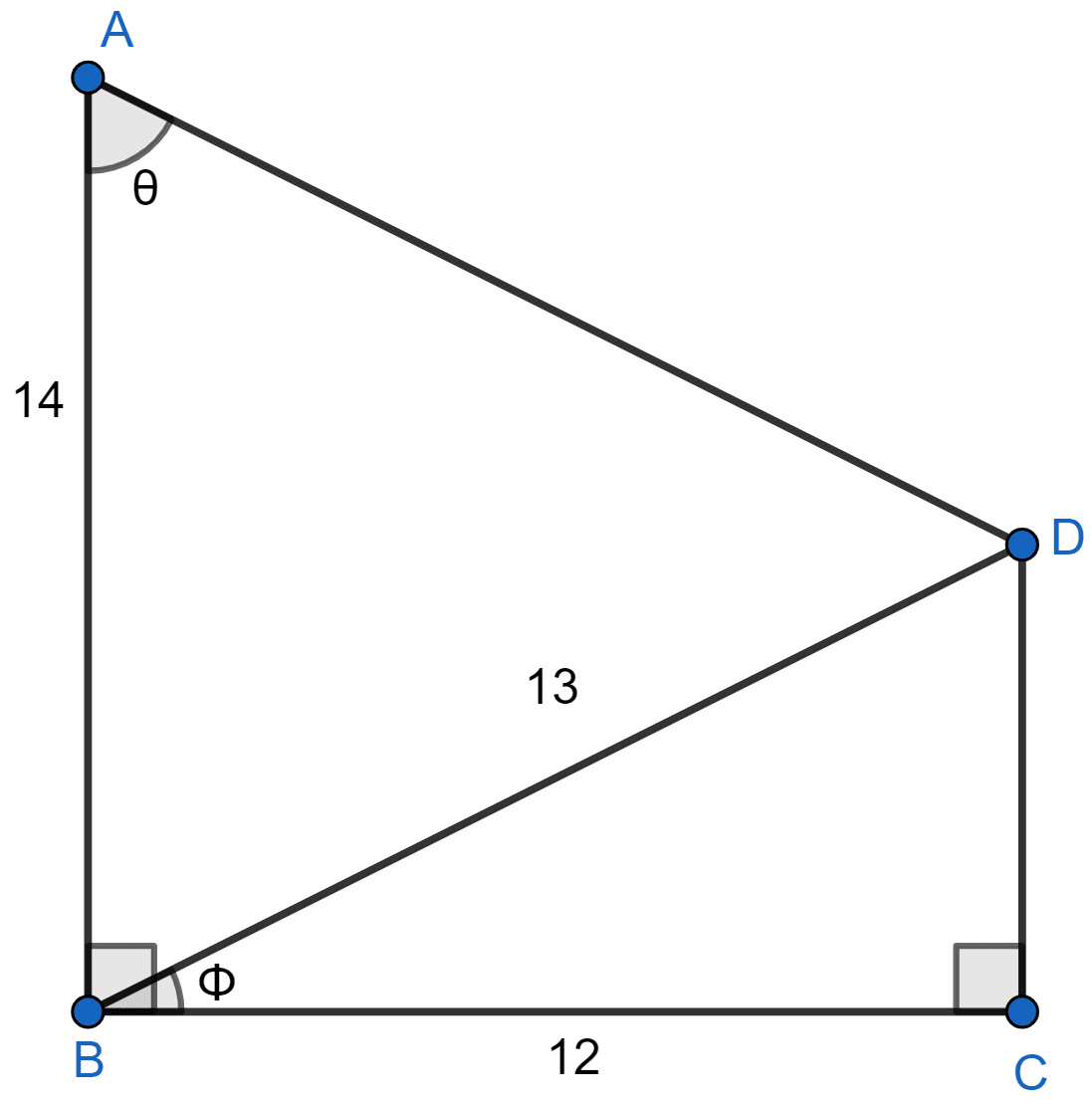
Using the measurements given in the figure alongside,
(a) Find the values of:
(i) sin Φ
(ii) tan θ.
(b) Write an expression for AD in terms of θ.
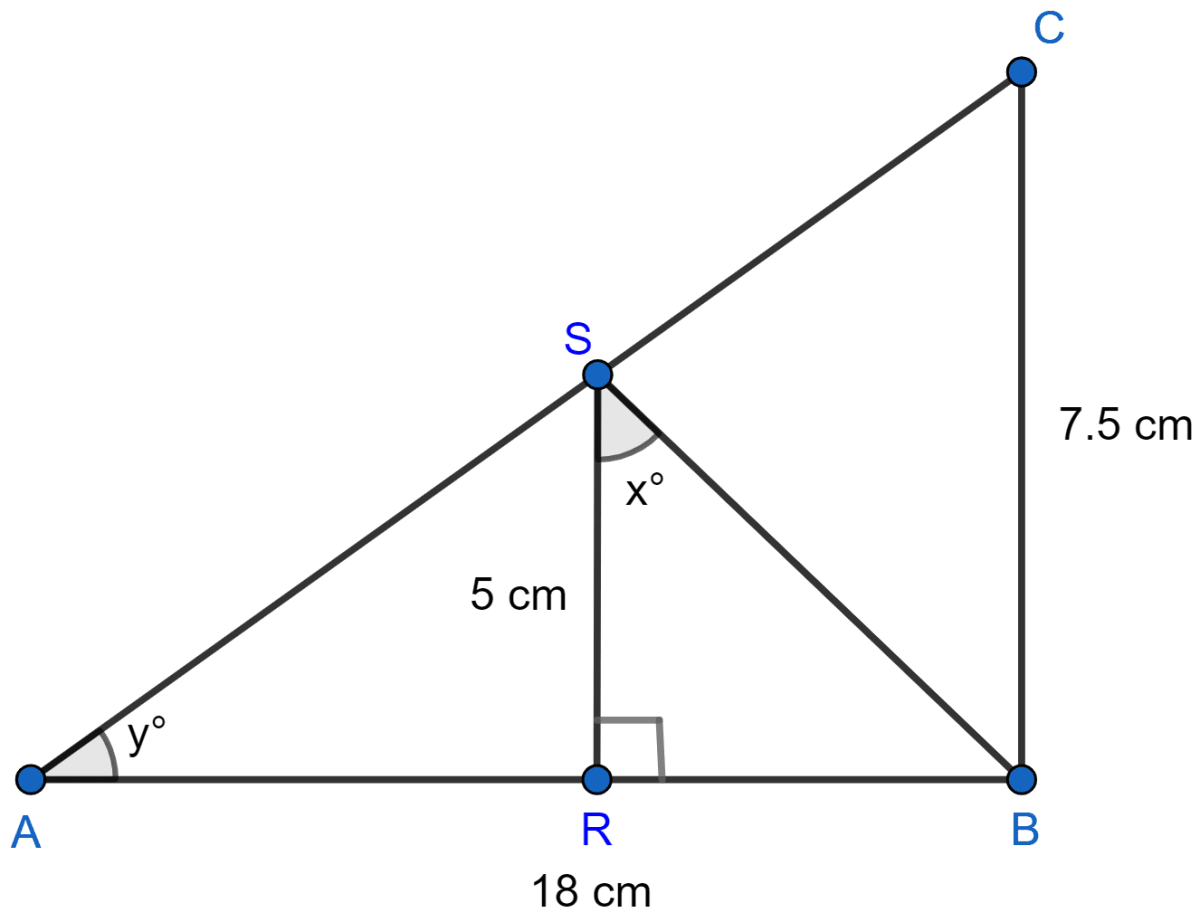
In figure (1) given below, ∆ABC is right-angled at B and ∆BRS is right-angled at R. If AB = 18 cm, BC = 7.5 cm, RS = 5 cm, ∠BSR = x° and ∠SAB = y°, then find :
(i) tan x°
(ii) sin y°.