Mathematics
In the adjoining figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠BAO = 60°, then ∠ADC is equal to
30°
45°
60°
120°

Circles
6 Likes
Answer
In the figure,
OA = OB (Radius of the circle.)
So, △OAB is an isosceles triangle with ∠OBA = ∠BAO (∵ angles opposite to equal sides are equal.)
∠OBA = 60°.
In a triangle the exterior angle is equal to the sum of opposite interior angle.
∴ ∠AOC = ∠BAO + ∠OBA = 60° + 60° = 120°.
Arc AC subtends ∠AOC at centre and ∠ADC at remaining part of circle.
∠AOC = 2∠ADC (∵ angle subtended at centre is double the angle subtended at remaining part of circle.)
120° = 2∠ADC
∠ADC = = 60°.
Hence, Option 3 is the correct option.
Answered By
4 Likes
Related Questions
In the adjoining figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠OAB = 40°, then ∠ACB is equal to
50°
40°
60°
70°

ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral such that AB is a diameter of the circle circumscribing it and ∠ADC = 140°, then ∠BAC is equal to
80°
50°
40°
30°
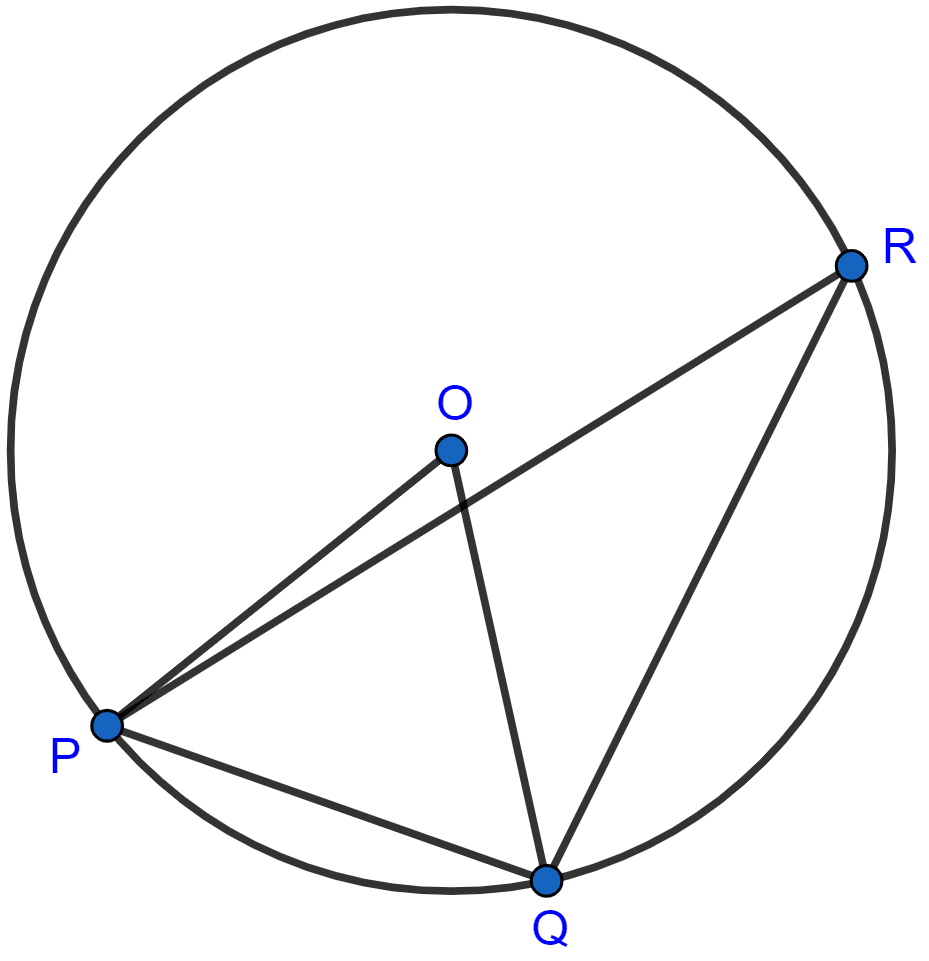
In the adjoining figure, O is the centre of the circle. If the length of the chord PQ is equal to the radius of the circle, then ∠PRQ is
60°
45°
30°
15°
In the adjoining figure, if O is the centre of the circle then the value of x is
18°
20°
24°
36°
