Mathematics
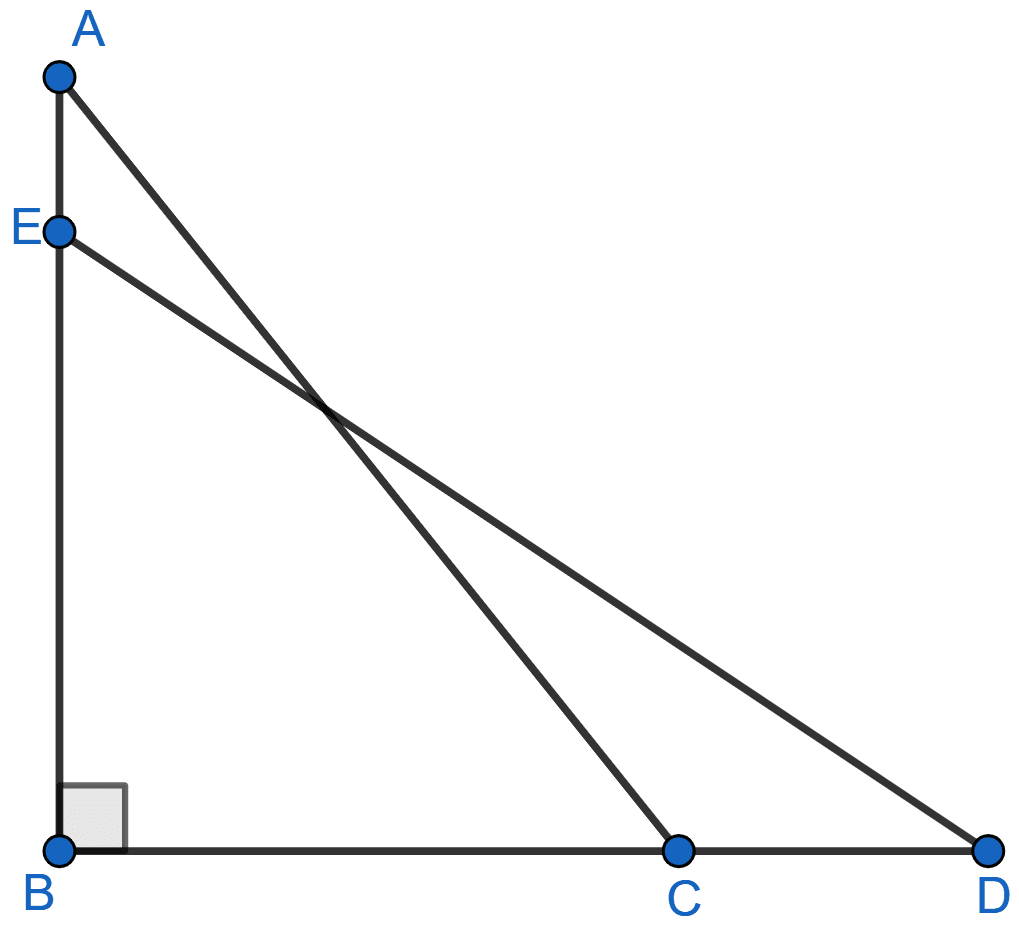
In figure given below, BC = 5 cm, ∠B = 90°, AB = 5AE, CD = 2AE and AC = ED. Calculate the lengths of EA, CD, AB and AC.
Pythagoras Theorem
116 Likes
Answer
In right angle △ABC,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ AC2 = (5AE)2 + 52
⇒ AC2 = 25AE2 + 25
⇒ AC2 = 25(AE2 + 1) …….(i)
From figure,
EB = AB - AE = 5AE - AE = 4AE.
In right angle △BED,
⇒ ED2 = EB2 + BD2
⇒ ED2 = (4AE)2 + (5 + 2AE)2
⇒ ED2 = 16AE2 + 25 + 4AE2 + 20AE
⇒ ED2 = 20AE2 + 20AE + 25 …….(ii)
Given, AC = ED.
∴ From (i) and (ii) we get,
⇒ 25(AE2 + 1) = 20AE2 + 20AE + 25
⇒ 25AE2 + 25 = 20AE2 + 20AE + 25
⇒ 25AE2 - 20AE2 - 20AE + 25 - 25 = 0
⇒ 5AE2 - 20AE = 0
⇒ 5AE(AE - 4) = 0
⇒ 5AE = 0 or AE - 4 = 0
⇒ AE = 0 or AE = 4 cm.
Since, side cannot be 0 so AE ≠ 0.
AE = 4 cm,
CD = 2AE = 8 cm,
AB = 5AE = 20 cm,
Substituting value of AE in (i) we get,
⇒ AC2 = 25(AE2 + 1)
⇒ AC2 = 25(42 + 1)
⇒ AC2 = 25(16 + 1) = 25 × 17 = 425
⇒ AC = cm.
Hence, EA = 4 cm, CD = 8 cm, AB = 20 cm and AC = cm.
Answered By
61 Likes
Related Questions
In figure given below, ∠PSR = 90°, PQ = 10 cm, QS = 6 cm and RQ = 9 cm. Calculate the length of PR.

In figure given below, ∠D = 90°, AB = 16 cm, BC = 12 cm and CA = 6 cm. Find CD.

In figure given below, ABC is a right triangle right angled at C. If D is mid-point of BC, prove that AB2 = 4AD2 - 3AC2.
In △ABC, AB = AC = x, BC = 10 cm and the area of △ABC is 60 cm2. Find x.