Mathematics
Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD in which ∠BCA = 90°, AB = 13 cm and ACD is an equilateral triangle of side 12 cm.
Mensuration
71 Likes
Answer
In right-angled △ABC,
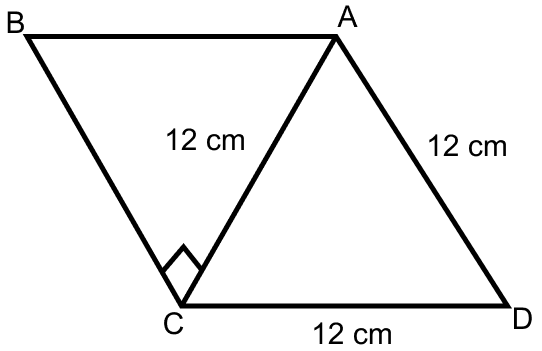
Using Pythagoras theorem,
⇒ AB2 = AC2 + BC2
Substituting the values we get,
⇒ 132 = 122 + BC2
⇒ BC2 = 132 – 122
⇒ BC2 = 169 – 144 = 25
⇒ BC = = 5 cm.
Calculating area of △BCA,
Calculating area of △ACD,
From figure,
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of △BCA + Area of △ACD
= 30 cm2 + 62.35 cm2
= 92.35 cm2.
Hence, area of quadrilateral ABCD = 92.35 cm2.
Answered By
24 Likes
Related Questions
Find the area of a quadrilateral whose diagonals are of length 18 cm and 12 cm and they intersect each other at right angles.
Find the area of the quadrilateral field ABCD whose sides AB = 40 m, BC = 28 m, CD = 15 m, AD = 9 m and ∠A = 90°.
Find the area of quadrilateral ABCD in which ∠B = 90° , AB = 6 cm, BC = 8 cm and CD = AD = 13 cm.
The perimeter of a rectangular cardboard is 96 cm; if its breadth is 18 cm, find the length and the area of the cardboard.