Chemistry
Explain with the help of electron dot diagrams the formation of the following molecules, stating the valency of each element involved.
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Chlorine
(c) Oxygen
(d) Nitrogen
(e) Water
(f) Methane
(g) Carbon tetrachloride
(h) Ammonia
(i) Carbon dioxide
[at. nos. H = 1, C = 6, N = 7, O = 8, Cl = 17]
Answer
(a) Formation of Hydrogen molecule (H2) — The valency of hydrogen element is 1. It needs one electron to attain stable duplet structure of nearest noble gas - He [2].
Each of the 'H' atoms contribute one electron so as to have one shared pair of electrons between them. Both atoms attain stable duplet structure resulting in the formation of a single covalent bond [H-H] between them.
Electron Dot Structure:

(b) Formation of Chlorine (Cl2) — The valency of chlorine element is 1. It needs one electron to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ar [2, 8, 8].
Each of the 'Cl' atoms contribute one electron so as to have one shared pair of electrons between them. Both atoms attain stable octet structure resulting in the formation of a single covalent bond [Cl-Cl] between them.
Electron Dot Structure:

(c) Formation of Oxygen molecule (O2) — The valency of oxygen element is 2. It needs two electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8].
Each of the two 'O' atoms contribute two electrons so as to have two shared pair of electrons between them. Both atoms attain stable octet structure resulting in the formation of a double covalent bond [O=O] between them.
Electron Dot Structure:

(d) Formation of Nitrogen Molecule (N2) — The valency of nitrogen element is 3. Nitrogen needs three electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8].
Each of the two N atoms contributes three electron so as to have three shared pair of electrons between them. Both atoms attain stable octet structure, resulting in the formation of a triple covalent bond [N≡N] between them.
Electron Dot Structure:

(e) Formation of Water Molecule (H2O) — The valency of hydrogen element is 1 and that of oxygen is 2. Hydrogen needs one electrons to attain stable duplet structure of nearest noble gas - He [2] and oxygen needs two electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8]
Each of the two hydrogen atoms shares an electron pair with the oxygen atom such that hydrogen acquires a duplet configuration and oxygen an octet configuration resulting in the formation of two single covalent bonds [H-O-H] in the molecule of water.
Electron Dot Structure:

(f) Formation of Methane Molecule (CH4) — The valency of hydrogen element is 1 and that of carbon is 4. Hydrogen needs one electron to attain stable duplet structure of nearest noble gas - He [2] and carbon needs four electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8]
One carbon atom shares four electron pairs one with each of the four atoms of hydrogen such that hydrogen acquires a duplet configuration and carbon an octet configuration resulting in the formation of four single covalent bonds.
Electron Dot Structure:

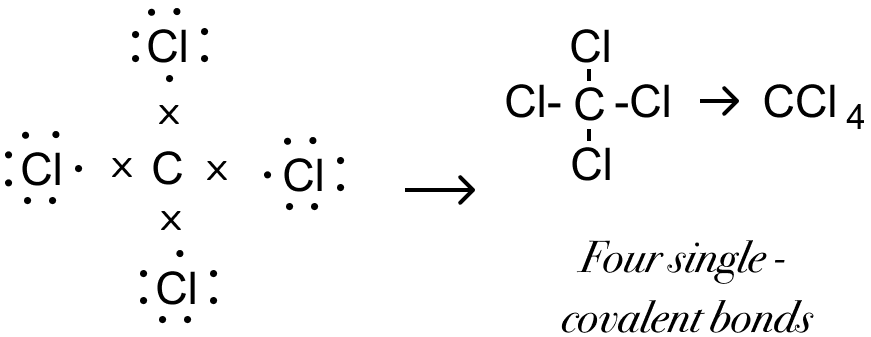
(g) Formation of Carbon tetrachloride Molecule (CCl4) — The valency of carbon element is 4 and that of chlorine is 1. Chlorine needs one electron to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ar [2,8,8] and Carbon needs four electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8]
One carbon atom shares four electron pairs one with each of the four atoms of chlorine such that chlorine and carbon attain a stable octet configuration resulting in the formation of four single covalent bonds.
Electron Dot Structure:
(h) Formation of Ammonia Molecule (NH3) — The valency of hydrogen element is 1 and that of nitrogen is 3. Hydrogen needs one electrons to attain stable duplet structure of nearest noble gas - He [2] and nitrogen needs three electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8]
One nitrogen atom shares three electron pairs one with each of the three atoms of hydrogen such that hydrogen acquires a duplet configuration and carbon attain a stable octet configuration resulting in the formation of three single covalent bonds .
Electron Dot Structure:

(i) Formation of Carbon dioxide Molecule (CO2) — The valency of carbon element is 4 and that of oxygen is 2. Carbon needs four electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8] and oxygen needs two electrons to attain stable octet structure of nearest noble gas - Ne [2,8]
One carbon atom shares two electron pairs one with each of the two atoms of oxygen such that oxygen and carbon attain a stable octet configuration resulting in the formation of two double covalent bonds.
Electron Dot Structure:

Related Questions
Define or explain the terms:
(i) Covalent or molecular bond
(ii) Covalent or molecular compound
(iii) Covalency
(iv) Shared pair of electrons.
Give two differences between the covalent compounds – methane (non-polar) and HCl (polar)
Give reasons for the following:
Molecules of hydrogen and chlorine have single covalent bonds between their atoms while oxygen has a double covalent and nitrogen a triple covalent bond respectively.
Give reasons for the following:
A molecule of methane has four single covalent bonds.