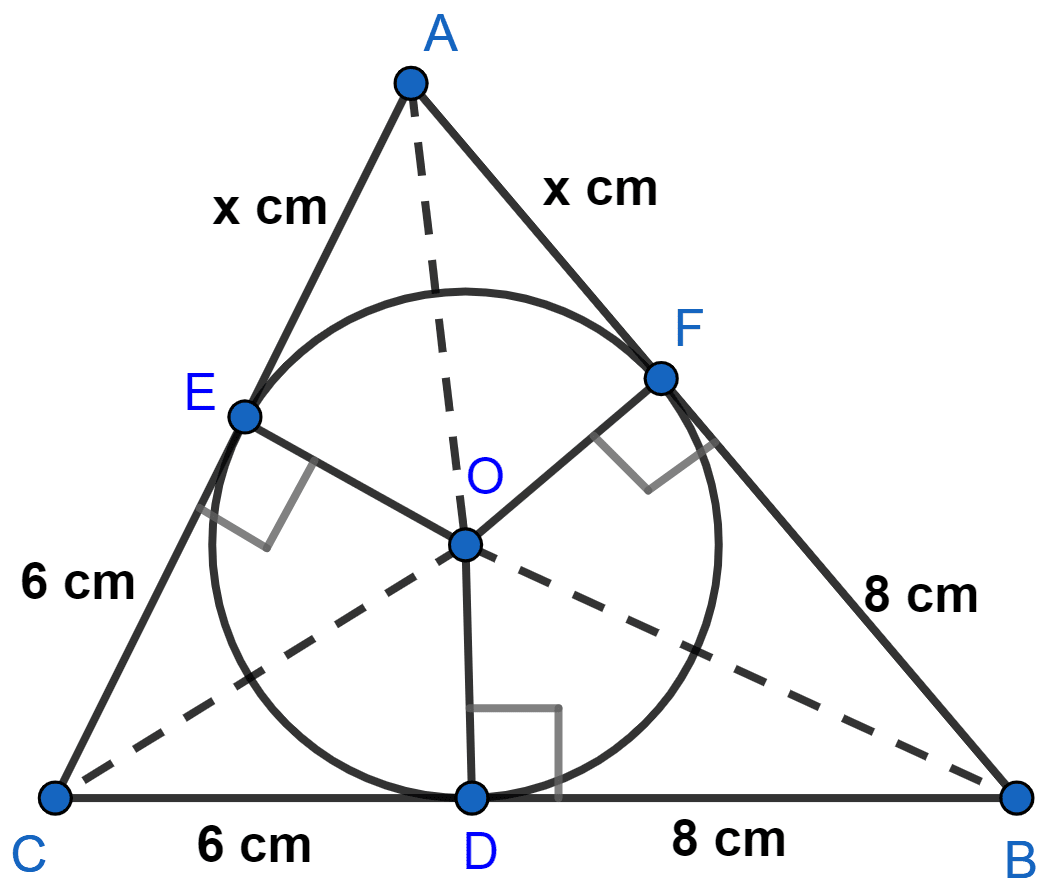
Draw OE perpendicular to AC and OF perpendicular to AB.
We know that,
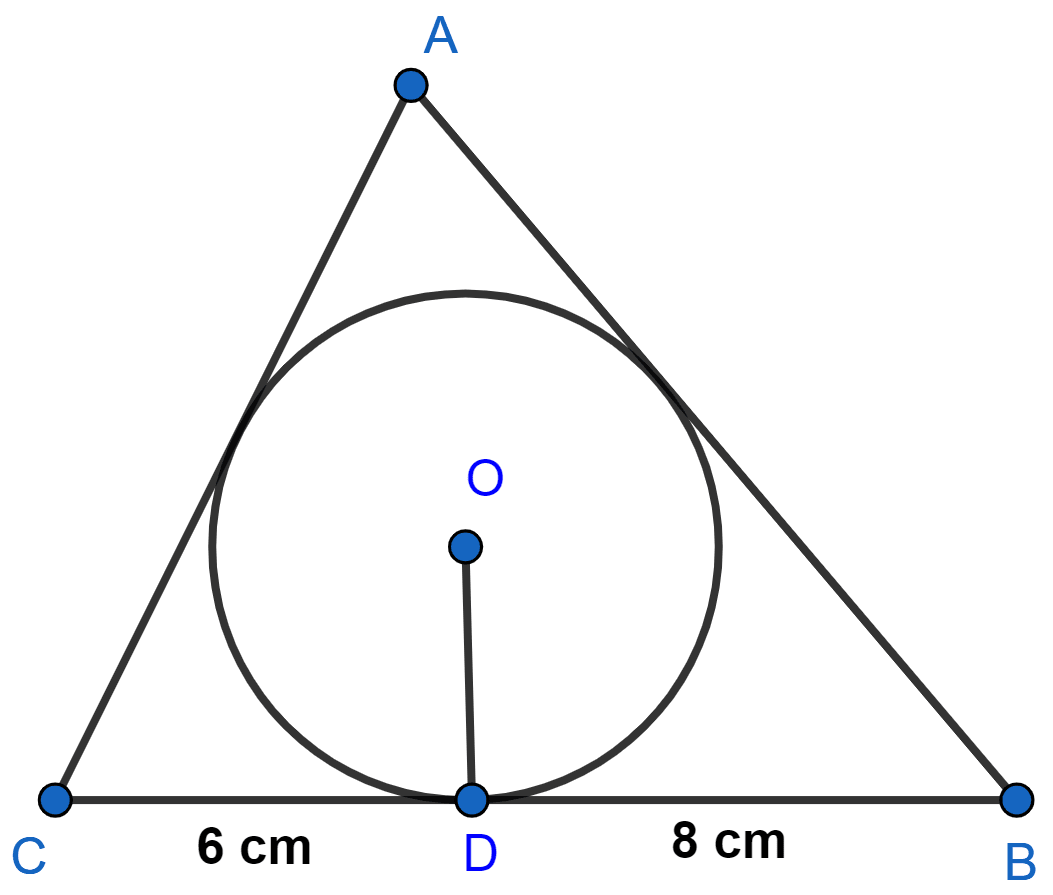
The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
CE = CD = 6 cm, BF = BD = 8 cm.
AE = AF = x cm (let)
By heron's formula,
Area = s ( s − a ) ( s − b ) ( s − c ) \sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} s ( s − a ) ( s − b ) ( s − c ) 1 2 \dfrac{1}{2} 2 1
Substituting values we get :
s = 1 2 [ ( A F + B F ) + ( B D + C D ) + ( A E + C E ) ] = 1 2 [ ( x + 8 ) + ( 8 + 6 ) + ( x + 6 ) ] = 1 2 [ 2 x + 28 ] = 1 2 × 2 [ x + 14 ] = x + 14. s = \dfrac{1}{2}[(AF + BF) + (BD + CD) + (AE + CE)] \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{2}[(x + 8) + (8 + 6) + (x + 6)] \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{2}[2x + 28] \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2[x + 14] \\[1em] = x + 14. s = 2 1 [( A F + BF ) + ( B D + C D ) + ( A E + CE )] = 2 1 [( x + 8 ) + ( 8 + 6 ) + ( x + 6 )] = 2 1 [ 2 x + 28 ] = 2 1 × 2 [ x + 14 ] = x + 14.
Substituting value of s in Heron's formula,
Area = ( x + 14 ) ( x + 14 − A B ) ( x + 14 − B C ) ( x + 14 − A C ) = ( x + 14 ) [ x + 14 − ( x + 8 ) ] [ x + 14 − 14 ] [ x + 14 − ( x + 6 ) ] = ( x + 14 ) × 6 × x × 8 = 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) cm 2 . \text{Area } = \sqrt{(x + 14)(x + 14 - AB)(x + 14 - BC)(x + 14 - AC)} \\[1em] = \sqrt{(x + 14)[x + 14 - (x + 8)][x + 14 - 14][x + 14 - (x + 6)]} \\[1em] = \sqrt{(x + 14)\times 6 \times x \times 8} \\[1em] = \sqrt{48(x^2 + 14x)} \text{ cm}^2. Area = ( x + 14 ) ( x + 14 − A B ) ( x + 14 − BC ) ( x + 14 − A C ) = ( x + 14 ) [ x + 14 − ( x + 8 )] [ x + 14 − 14 ] [ x + 14 − ( x + 6 )] = ( x + 14 ) × 6 × x × 8 = 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) cm 2 .
From figure,
Area of △ABC = Area of △AOB + Area of △BOC + Area of △AOC …………(1)
We know that,
Area of triangle = 1 2 × base × height \dfrac{1}{2} \times \text{ base } \times \text{height} 2 1 × base × height
Substituting values we get :
Area of △AOB = 1 2 × A B × O F = 1 2 × ( x + 8 ) × 4 = 2 ( x + 8 ) = ( 2 x + 16 ) cm 2 . Area of △BOC = 1 2 × B C × O D = 1 2 × 14 × 4 = 28 cm 2 . Area of △AOC = 1 2 × A C × O E = 1 2 × ( x + 6 ) × 4 = 2 ( x + 6 ) = ( 2 x + 12 ) cm 2 . \text{Area of △AOB } = \dfrac{1}{2} \times AB \times OF \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{2} \times (x + 8) \times 4 \\[1em] = 2(x + 8) \\[1em] = (2x + 16) \text{ cm}^2. \\[1em] \text{Area of △BOC } = \dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times OD \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 14 \times 4 \\[1em] = 28 \text{ cm}^2. \\[1em] \text{Area of △AOC } = \dfrac{1}{2} \times AC \times OE \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{2} \times (x + 6) \times 4 \\[1em] = 2(x + 6) \\[1em] = (2x + 12) \text{ cm}^2. \\[1em] Area of △AOB = 2 1 × A B × OF = 2 1 × ( x + 8 ) × 4 = 2 ( x + 8 ) = ( 2 x + 16 ) cm 2 . Area of △BOC = 2 1 × BC × O D = 2 1 × 14 × 4 = 28 cm 2 . Area of △AOC = 2 1 × A C × OE = 2 1 × ( x + 6 ) × 4 = 2 ( x + 6 ) = ( 2 x + 12 ) cm 2 .
Substituting values in equation (1), we get :
⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = ( 2 x + 16 ) + 28 + ( 2 x + 12 ) ⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = 4 x + 56 ⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = 4 ( x + 14 ) \Rightarrow \sqrt{48(x^2 + 14x)} = (2x + 16) + 28 + (2x + 12) \\[1em] \Rightarrow \sqrt{48(x^2 + 14x)} = 4x + 56 \\[1em] \Rightarrow \sqrt{48(x^2 + 14x)} = 4(x + 14) ⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = ( 2 x + 16 ) + 28 + ( 2 x + 12 ) ⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = 4 x + 56 ⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = 4 ( x + 14 )
Squaring both sides we get :
⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = 4 2 × ( x + 14 ) 2 ⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = 16 ( x 2 + 196 + 28 x ) ⇒ 48 16 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = x 2 + 196 + 28 x ⇒ 3 x 2 + 42 x = x 2 + 196 + 28 x ⇒ 3 x 2 − x 2 + 42 x − 28 x − 196 = 0 ⇒ 2 x 2 + 14 x − 196 = 0 ⇒ 2 ( x 2 + 7 x − 98 ) = 0 ⇒ x 2 + 7 x − 98 = 0 ⇒ x 2 + 14 x − 7 x − 98 = 0 ⇒ x ( x + 14 ) − 7 ( x + 14 ) = 0 ⇒ ( x − 7 ) ( x + 14 ) = 0 ⇒ x − 7 = 0 or x + 14 = 0 ⇒ x = 7 or x = − 14. \Rightarrow 48(x^2 + 14x) = 4^2 \times (x + 14)^2 \\[1em] \Rightarrow 48(x^2 + 14x) = 16(x^2 + 196 + 28x) \\[1em] \Rightarrow \dfrac{48}{16}(x^2 + 14x) = x^2 + 196 + 28x \\[1em] \Rightarrow 3x^2 + 42x = x^2 + 196 + 28x \\[1em] \Rightarrow 3x^2 - x^2 + 42x - 28x - 196 = 0 \\[1em] \Rightarrow 2x^2 + 14x - 196 = 0 \\[1em] \Rightarrow 2(x^2 + 7x - 98) = 0 \\[1em] \Rightarrow x^2 + 7x - 98 = 0 \\[1em] \Rightarrow x^2 + 14x - 7x - 98 = 0 \\[1em] \Rightarrow x(x + 14) - 7(x + 14) = 0 \\[1em] \Rightarrow (x - 7)(x + 14) = 0 \\[1em] \Rightarrow x - 7 = 0 \text{ or } x + 14 = 0 \\[1em] \Rightarrow x = 7 \text{ or } x = -14. ⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = 4 2 × ( x + 14 ) 2 ⇒ 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = 16 ( x 2 + 196 + 28 x ) ⇒ 16 48 ( x 2 + 14 x ) = x 2 + 196 + 28 x ⇒ 3 x 2 + 42 x = x 2 + 196 + 28 x ⇒ 3 x 2 − x 2 + 42 x − 28 x − 196 = 0 ⇒ 2 x 2 + 14 x − 196 = 0 ⇒ 2 ( x 2 + 7 x − 98 ) = 0 ⇒ x 2 + 7 x − 98 = 0 ⇒ x 2 + 14 x − 7 x − 98 = 0 ⇒ x ( x + 14 ) − 7 ( x + 14 ) = 0 ⇒ ( x − 7 ) ( x + 14 ) = 0 ⇒ x − 7 = 0 or x + 14 = 0 ⇒ x = 7 or x = − 14.
Since, side cannot be negative.
∴ x = 7 cm.
From figure,
AB = AF + BF = x + 8 = 7 + 8 = 15 cm
AC = AE + CE = x + 6 = 7 + 6 = 13 cm.
Hence, AB = 15 cm and AC = 13 cm.