Physics
A ray of green light enters a liquid from air, as shown in the figure. The angle 1 is 45° and angle 2 is 30°.
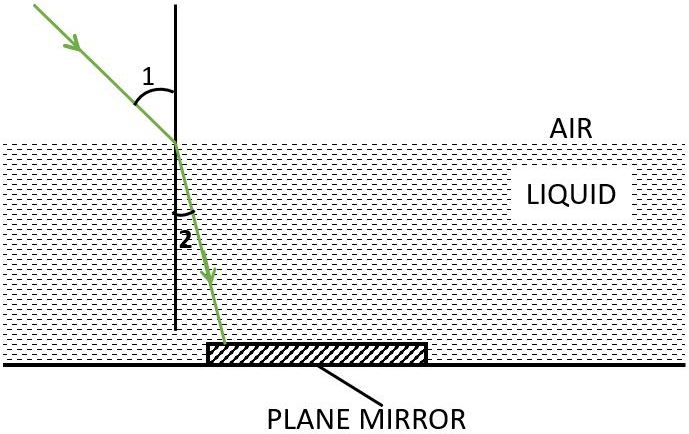
(a) Find the refractive index of liquid.
(b) Show in the diagram the path of the ray after it strikes the mirror and re-enters in air. Mark in the diagram the angles wherever necessary.
(c) Redraw the diagram if plane mirror becomes normal to the refracted ray inside the liquid. State the principle used.
Refraction Plane Surfaces
106 Likes
Answer
(a) Refractive index of the liquid is given by Snell's law and is shown as below,
airμliquid =
airμliquid =
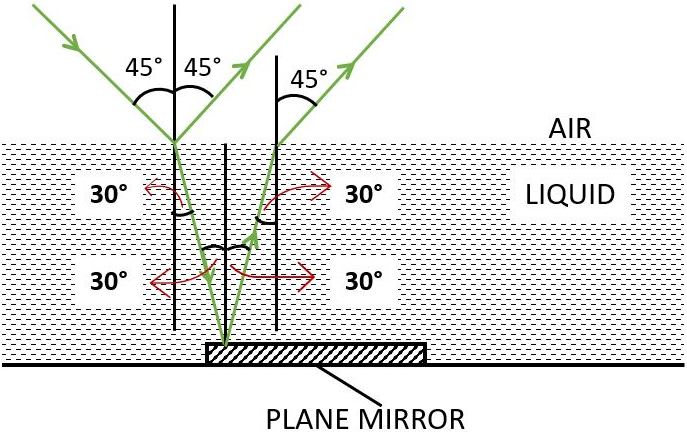
(b) Below labelled diagram shows the path of the ray after it strikes the mirror and re-enters in air:
(c) Below labelled diagram shows the path of the ray when it strikes the plane mirror normally inside the liquid:
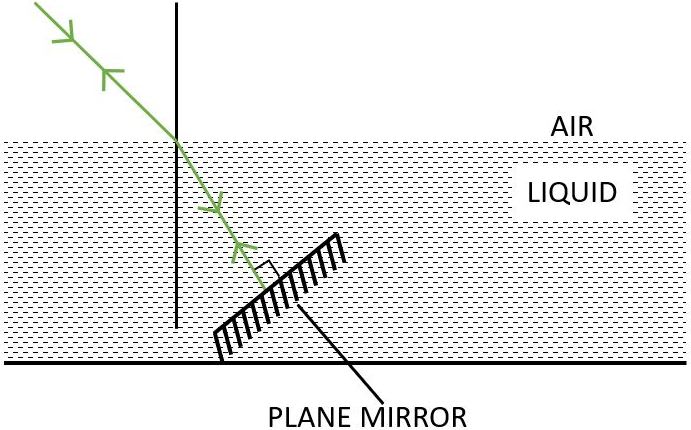
The principle of reversibility is used.
Answered By
73 Likes
Related Questions
A ray of light strikes the surface at a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is (i) 0°, (ii) 45°. In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
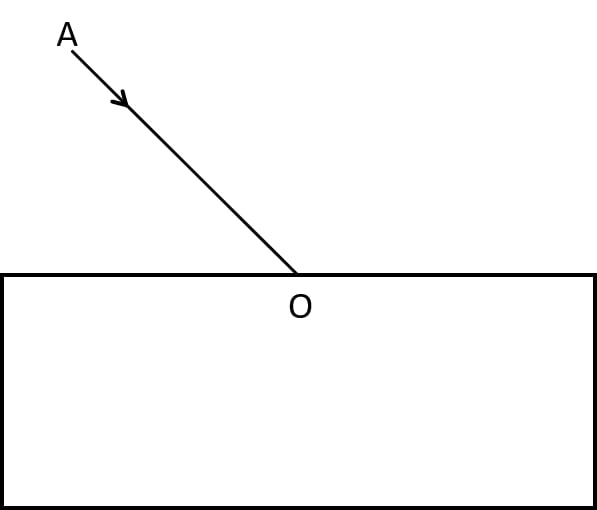
(a) Complete the path of the ray until it emerges out of the slab.
(b) In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to angles i and r?
(c) Mark angle of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
(d) Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
(e) Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
The speed of light in air is 3 x 108 m s-1. Calculate the speed of light in glass. The refractive index of glass is 1.5.
The speed of light in diamond is 125,000 km s-1. What is the refractive index? (Speed of light in air = 3 x 108 m s-1).