Section A
Question 1(i)
Which term is used to define the pair of valence shell electrons that are not shared with another atom?
- Lone pair electrons
- Valence electrons
- Inner-shell electrons
- Antibonding electrons
Answer
Lone pair electrons
Reason — Lone pair of electrons are valence electrons that in a covalent bond are not shared with another atom.
Question 1(ii)
Sodium atoms and sodium ions
- are chemically same
- have the same number of protons
- have an identical number of electrons
- form covalent bonds
Answer
have the same number of protons
Reason — An atom forms its respective ion by accepting or donating electrons. Hence, number of electrons between an atom and its ion will differ but both will have the same number of protons.
Question 1(iii)
In which state electrovalent compounds do not conduct electricity?
- Fused
- Ionic
- Solid
- Molten
Answer
Solid
Reason — Electrovalent compounds consists of ions but the strong electrostatic force keeps ions in fixed position in the solid state. The force is weakened in the molten state and disappears in aqueous solution state, hence free ions formed help in the conduction of electricity.
Question 1(iv)
The amount of energy released by the addition of an electron to the outermost shell of an atom in its isolated gaseous state is ...............
- electronegativity
- valency
- electron affinity
- ionisation potential
Answer
electron affinity
Reason — Electron affinity is the amount of energy released when an atom in the gaseous state accepts an electron to form an anion.
Question 1(v)
The unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo
- substitution reaction
- oxidation reaction
- addition reaction
- None of the above
Answer
addition reaction
Reason — The availability of electrons in the double or triple bonded unsaturated hydrocarbons makes them more reactive and they therefore undergo characteristic addition reactions only.
Question 1(vi)
The organic compound having a triple carbon-carbon covalent bond.
- C3H4
- C3H6
- C3H8
- C4H10
Answer
C3H4
Reason — C3H4 is an Alkyne as it follows the general formula CnH2n-2 and Alkynes contain a triple carbon-carbon covalent bond.
Question 1(vii)
When magnesium burns in air, the atoms of the metal reacts with the oxygen gas to produce magnesium oxide.
Which of the following is correct?
P. It is a combination reaction.
Q. It is a Redox reaction
R. It is a decomposition reaction
- Only P
- Only Q
- Only R
- Both Q and R
Answer
Only P
Reason — The reaction is only a combination reaction as magnesium and oxygen combine to form magnesium oxide.
2Mg + O2 ⟶ 2MgO
Question 1(viii)
Which of the following is NOT correct about electro-refining of copper?
- Cathode is pure copper rod and anode is impure copper block.
- Cathode is impure copper block and anode is pure copper rod.
- Electrolyte is copper sulphate solution, acidified with sulphuric acid.
- Anode mud may contain silver and gold as insoluble impurities.
Answer
Cathode is impure copper block and anode is pure copper rod.
Reason — In electro-refining of copper, cathode is thin strip of pure copper and anode is impure copper block.
Question 1(ix)
One atomic mass unit is how much part the mass of C-12 atoms?
Answer
Reason — Atomic mass unit is defined as th the mass of an carbon atom C-12.
Question 1(x)
A reactive metal (P) is treated with H2SO4 (dil). The gas is evolved and is collected over water. Which of the following conclusion is correct
P. The gas is hydrogen
Q. The gas is lighter than air
- Only P
- Only Q
- Both P and Q
- Neither P nor Q
Answer
Both P and Q
Reason — Hydrogen gas is evolved which is lighter than air hence both are correct.
Question 1(xi)
In which of the following solution, Zn can displace metal from the solution?

- P
- Q
- R
- S
Answer
S
Reason — In beaker S, zinc will displace iron from iron sulphate solution as zinc is above iron in the metal activity series.
Question 1(xii)
How many electrons are present in the valence shell of the element, with atomic number 18?
- 7
- 0
- 8
- 4
Answer
8
Reason — Electronic configuration of the element is 2, 8, 8. Hence, 8 electrons are present in the valence shell.
Question 1(xiii)
The table given below gives information about six elements.
| Electronic Configuration | Formula of Compound | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| W | A: 2, 1 | B: 2, 6 | A2B |
| X | B: 2, 6 | C: 2, 7 | B2C |
| Y | C: 2, 7 | D: 2, 8, 3 | DC3 |
| Z | E: 2, 8, 6 | F: 2, 8, 8, 2 | FE |
Identify the compound which is wrongly formed.
- Z
- Y
- X
- W
Answer
X
Reason — Compound B2C is wrongly formed. Valency of B is 2 and C is 1. Hence, correct formula of the compound will be BC2
Question 1(xiv)
The substance that acts as a weak electrolyte is
- NaOH
- HNO3
- H3PO4
- HBr
Answer
H3PO4
Reason — H3PO4 is a weak electrolyte.
Question 1(xv)
Ammonia gets catalytically oxidised to give
- N2 + H2O
- NO2 + H2O
- NO + H2O
- Cu
Answer
NO + H2O
Reason — Ammonia gets catalytically oxidised in presence of platinum at 800°C to give nitric oxide and water vapours.
4NH3 + 5O2 4NO↑ + 6H2O + Δ
Question 2(i)
(a) Draw the structural formula for the following.
(1) Isobutane
(2) Propanal
(3) But-2-yne
(b) Name the following organic compounds in IUPAC system.

Answer
(a) Structural formulae are shown below:
(1) Isobutane

(2) Propanal

(3) But-2-yne

(b) IUPAC names of the organic compounds are:
(1) But-1-ene
(2) 1-bromo 2, 3-dichloropropane
Question 2(ii)
Match the following Column I with Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (a) Neon | 1. CH3OH |
| (b) Vinegar | 2. Octet |
| (c) Methanol | 3. 10 electrons |
| (d) Hydrogen chloride gas | 4. CH3COOH |
| (e) O2- | 5. Upward displacement |
Answer
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (a) Neon | 2. Octet |
| (b) Vinegar | 4. CH3COOH |
| (c) Methanol | 1. CH3OH |
| (d) Hydrogen chloride gas | 5. Upward displacement |
| (e) O2- | 3. 10 electrons |
Question 2(iii)
Identify the following.
(a) Process by which impurities from metals are removed electrolytically.
(b) A gas which does not conduct electricity in the liquid state but conducts electricity when dissolved in water.
(c) An organic compound which is used as a thermometric liquid.
(d) The type of reactions alkenes undergo.
(e) A salt which on reaction with excess of ammonium hydroxide solution gives a deep blue solution
Answer
(a) Electrorefining
(b) Hydrogen chloride gas
(c) Ethanol
(d) Addition reactions
(e) Copper sulphate solution
Question 2(iv)
Complete the following by choosing the correct answers from the bracket.
(a) An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water forms ............... (hydronium/hydroxide) ions as the positively charged ions.
(b) ............... (Al/Fe) metal is used in making alloys such as duralumin and magnalium.
(c) Cold and dilute nitric acid reacts with sulphur to form ............... (nitric oxide / nitrogen dioxide).
(d) Pure water consists almost entirely of ............... (ions/molecules/particles).
(e) One carbon atom in a hydrocarbon contain the root word as ............... (meth/eth).
Answer
(a) An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water forms hydronium ions as the positively charged ions.
(b) Al metal is used in making alloys such as duralumin and magnalium.
(c) Cold and dilute nitric acid reacts with sulphur to form nitrogen dioxide.
(d) Pure water consists almost entirely of molecules.
(e) One carbon atom in a hydrocarbon contain the root word as meth.
Question 2(v)
The diagram given below shows the electrolysis of acidified water using platinum electrode. Study the diagram and answer the following.

(a) Why dil. H2SO4 is used to acidify water instead of HCl or HNO3?
(b) Write the reaction involved in the ionisation of water and sulphuric acid and name the ions that move towards the cathode and anode.
(c) Write the overall reaction for the electrolysis of acidified water and at what ratio hydrogen and oxygen are liberated at the cathode and anode.
Answer
(a) Dil. sulphuric acid is preferred to acidify water because it is a non-volatile acid, while dil. HCl or HNO3 are volatile acids and may decompose and interfere with the electrolytic reaction.
(b) H2O ⟶ H+ + OH-
H2SO4 ⟶ 2H+ + SO42-
H+ ions migrate to cathode, SO42- and OH- both ions migrate to anode.
(c) The ratio of hydrogen and oxygen liberated at cathode and anode is 2 : 1 by volume.
Overall reaction is:
2H2O 2H2 + O2
Section B
Question 3(i)
Identify the anion present in each of the following compounds.
(a) Barium chloride on reacting with compound Z will form a white precipitate.
(b) Compound Y on reaction with sulphuric acid will liberate carbon dioxide along with sodium sulphate and water.
Answer
(a) SO42- (sulphate)
Reason — White precipitate formed is of barium sulphate [BaSO4], hence anion present is SO42-.
(b) CO32- (carbonate)
Reason — Sodium carbonate will react with sulphuric acid liberate carbon dioxide along with sodium sulphate and water.
Na2CO3 + H2SO4 ⟶ CO2 + Na2SO4 + H2O
Question 3(ii)
Identify the reactant and write the balanced equation for the following.
Calcium nitrate reacts with compound Q to give calcium hydroxide and sodium nitrate.
Answer
Ca(NO3)2 + 2NaOH ⟶ Ca(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
Hence, the reactants are calcium nitrate and sodium hydroxide
Question 3(iii)
(a) State whether the following statements are True or False. Justify your answer.
(1) Fluorine is most electronegative element.
(2) The size of potassium atom is greater than the size of sodium atom.
(b) Calculate the number of moles in 9 grams of water.
Answer
(a) (1) True
Reason — Fluorine is placed in period 2 group 17 (VIIA) in the modern periodic table i.e., it occupies the upper right hand corner of the periodic table. Along a period from left to right electronegativity increases and down a group from top to bottom it decreases. Hence, Fluorine being the topmost and rightmost element in its group and period is the most electronegative element of the periodic table.
(2) True
Reason — Atomic size increases on moving down the group. As potassium lies below sodium in its group, hence, size of potassium atom is greater than the size of sodium atom.
(b) Molar mass of water [H2O] = 2(1) + 16 = 18
Number of moles = = = 0.5 moles
Hence, 0.5 moles are present in 9 gm of water.
Question 3(iv)
Fill in the blanks selecting the appropriate word from the given choice.
(a) Formation of ............... (NH4+, NH3) involves ammonia molecule and hydrogen ion.
(b) Hydroxyl ion or hydroxide ion is formed when one ............... [H+, OH-] ion is removed from water molecule.
(c) Hydrogen needs one electron to complete its ............... [singlet, duplet].
Answer
(a) Formation of NH4+ involves ammonia molecule and hydrogen ion.
(b) Hydroxyl ion or hydroxide ion is formed when one H+ ion is removed from water molecule.
(c) Hydrogen needs one electron to complete its duplet.
Question 4(i)
An organic compound containing C, H and O has 49.3% carbon, 6.84% hydrogen, 43.86% oxygen and its vapour density is 73. What will be the molecular formula of the compound?
Answer
| Element | % composition | At. wt. | Relative no. of atoms | Simplest ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 49.3 | 12 | = 4.10 | = 1.5 x 2 = 3 |
| H | 6.84 | 1 | = 6.84 | = 2.5 x 2 = 5 |
| O | 43.86 | 16 | = 2.74 | = 1 x 2 = 2 |
Simplest ratio of whole numbers = C : H : O = 3 : 5 : 2
Hence, empirical formula is C3H5O2
Empirical formula weight = 3(12)+ 5(1) + 2(16) = 36 + 5 + 32 = 73
Vapour density (V.D.) = 73
Molecular weight = 2 x V.D. = 2 x 73 = 146
∴ Molecular formula = n[E.F.] = 2[C3H5O2] = C6H10O4
Question 4(ii)
Name the functional group in the following organic compounds.
(a) C2H5CHO
(b) H3C-CH2-CH=CH-CH3
Answer
(a) C2H5CHO — aldehyde group [-CHO]
(b) H3C-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 — carbon-carbon double bond [-C=C-]
Question 4(iii)
(a) Mayank extracts aluminium by electrolytic process. Answer the following questions with respect to the electrolytic process in the extraction of aluminium.
(1) A compound which is added to lower the fusion temperature of the electrolytic bath.
(2) Explain, why powdered coke is sprinkled over the electrolytic mixture?
(b) The atomic number of an element is 16. To which group will this element belong to?
Answer
(a) Cryolite [Na3AlF6]
(b) The layer of powdered coke is sprinkled over the electrolytic mixture as :
- It prevents burning of carbon electrodes in air at the emergence point from the bath.
- It minimizes or prevents heat loss by radiation.
(c) The element belongs to group 16 [VI A].
Reason — The element Z has atomic number 16 and so the electronic configuration will be 2, 8, 6. The number of valence electrons determine the group of the element. Hence, Z will belong to group 16 [VI A] as it has 6 electrons in the valence shell.
Question 4(iv)
The following is a list of methods for the preparation of salts:
A — direct combination of two elements
B — reaction of a dilute acid with a metal
C — reaction of a dilute acid with an insoluble base
D — titration of a dilute acid with a solution of soluble base.
E — reaction of two solutions of salts to form a precipitate.
Choose from the list A to E, the best method of preparing the following salts by giving a suitable equation in each case:
- Copper (II) Sulphate
- Calcium Carbonate
- Zinc sulphate
Answer
(a) C — reaction of a dilute acid with an insoluble base
Cu(OH)2 + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ CuSO4 + 2H2O
(b) E — reaction of two solutions of salts to form a precipitate
CaCl2 + Na2CO3 ⟶ CaCO3 ↓ + 2NaCl
(c) B — reaction of a dilute acid with a metal
Zn + H2SO4 (dil.) ⟶ ZnSO4 + H2
Question 5(i)
Draw the electron dot structure for the following
(a) Hydronium ion
(b) Methane
Answer
(a) Hydronium ion
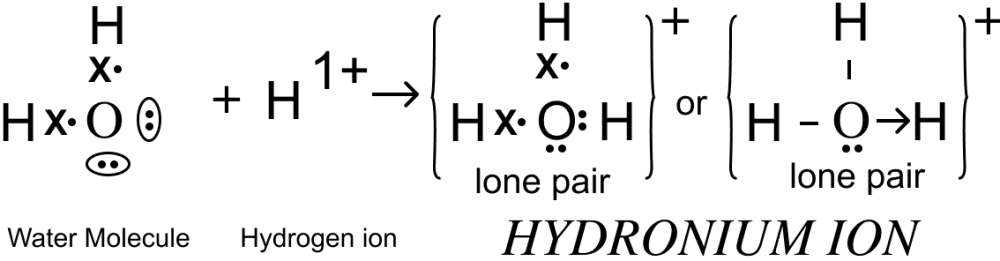
(b) Methane

Question 5(ii)
Distinguish between the following as directed.
(a) Ammonium chloride and sodium chloride on the basis of heating
(b) Ferric salt and ferrous salt by using ammonium hydroxide
Answer
(a) On strong heating, ammonium chloride sublimes to form dense white fumes which condense to white powdery substance on cooler parts of the test tube whereas no white fumes are seen on heating sodium chloride. Hence, the two can be distinguished.
NH4Cl NH3 + HCl
(b) On reaction with ammonium hydroxide, ferrous salt forms a dirty green ppt whereas ferric salt forms a reddish brown ppt. Hence, the two can be distinguished easily.
Question 5(iii)
Name the ions present in each of the following
(a) NaCl
(b) CH3COOH
(c) H2O
Answer
(a) NaCl — Na+, Cl-
(b) CH3COOH — CH3COO-, H+
(c) H2O — H+, OH-
Question 5(iv)
With reference to the first three periods of the modern periodic table, answer the questions given below.
(a) What features of the atomic structure accounts for the similarities in the chemical properties of the elements in group VII A of the periodic table?
(b) Name the element which has the highest ionisation potential.
(c) What is the atomic number and name of the element present in 3rd period and 17th group of the periodic table?
Answer
(a) All elements in group VII A have same number of valence electrons (i.e., 7), hence they have similar chemical properties.
(b) Helium (He) has highest ionisation potential, as it has fully-filled electronic configuration due to which it requires maximum energy to remove an electron from its valence shell.
(c) The element is chlorine (Cl) with atomic number 17.
Question 6(i)
The following questions are pertaining to various laboratory preparations
(a) Which property of hydrogen chloride is demonstrated by fountain experiment?
(b) Why hydrogen chloride gas is not collected over water?
(c) What is the source of nitrogen gas used in Haber's process?
Answer
(a) The high solubility of HCl gas in water is demonstrated by the Fountain experiment.
(b) Hydrogen chloride gas is not collected over water since it is highly soluble in water.
(c) Nitrogen is obtained by fractional distillation of liquid air.
Question 6(ii)
Explain the following:
(a) Zinc oxide can be reduced to zinc by using carbon monoxide, but aluminium oxide cannot be reduced by reducing a agent.
(b) During electrolysis of molten lead bromide, a graphite anode is preferred to other electrodes.
(c) Electrolysis of molten lead bromide is considered to be a redox reaction.
Answer
(a) Aluminium is placed above zinc in reactivity series. Hence, aluminium is more reactive than zinc and its oxide is stable and cannot be reduced by a reducing agent. Zinc being less reactive metal, its oxide is less stable and so it can be easily reduced by carbon monoxide.
(b) As graphite is unaffected by the reactive bromine vapours released at the anode hence, a graphite anode is preferred during the electrolysis of molten lead bromide
(c) Electrolysis of molten lead bromide involves oxidation and reduction reactions and hence is a redox reaction.
Reduction reaction at cathode:
Pb2+ + 2e- ⟶ Pb
Oxidation reaction at the anode:
Br1- - 1e2- ⟶ Br
Br + Br ⟶ Br2
Question 6(iii)
4.2 grams of magnesium carbonate is decomposed by heating according to the question.
MgCO3 ⟶ MgO + CO2
Calculate the following
(a) Volume of carbon dioxide obtained at STP.
(b) Mass of MgO formed
[Atomic weight : Mg = 24, C = 12, O = 16]
Answer
(a) Number of moles of MgCO3 = = = 0.05 moles
1 mole of MgCO3 gives 1 mole of CO2
Hence, 0.005 mole of MgCO3 gives 0.05 mole of CO2
(a) Volume of carbon dioxide at STP = no. of moles of carbon dioxide x volume in litres
= 0.05 x 22.4 = 1.12 L
Hence, volume of carbon dioxide obtained at STP = 1.12 L
(b) 84 grams of MgCO3 produce 40 grams of MgO
∴ 4.2 g will produce = x 4.2 = 2 g
Hence, mass of MgO formed = 2g
Question 7(i)
(a) Jiya was doing an experiment in which she had to dry up ammonia, but she observes that the concentrated sulphuric acid is not able to dry ammonia gas. Why is it so?
(b) Give the balanced chemical equation for the conversion of ammonia solution to an amphoteric hydroxide
Answer
(a) As sulphuric acid reacts chemically with ammonia to form ammonium sulphate hence, it is not used as a drying agent for drying ammonia.
2NH3 + H2SO4 ⟶ (NH4)2SO4
(b) AlCl3 + 3NH4OH ⟶ 3NH4Cl + Al(OH)3
Question 7(ii)
Name the gas evolved when the following reaction takes place.
(a) Dilute hydrochloric acid to zinc sulphide.
(b) Zinc sulphide ore is heated in a regular supply of air.
Answer
(a) Hydrogen sulphide [H2S] gas
(b) Sulphur dioxide gas [SO2]
Question 7(iii)
Give balanced chemical equation for the following.
(a) Preparation of ethyne from (ethylene dibromide) 1, 2-di bromoethane.
(b) Ethanoic acid from ethanol.
(c) Sodium acetate from acetic acid.
Answer
(a) Ethyne from (ethylene dibromide) 1, 2-di bromoethane.
(b) Ethanoic acid from ethanol.
(c) Sodium acetate from acetic acid.
CH3COOH + NaOH ⟶ CH3COONa + H2O
Question 7(iv)
Give one relevant observation for each of the following reactions.
(a) Zinc carbonate is heated.
(b) Excess of ammonia is passed through an aqueous solution of lead nitrate.
(c) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to nitric acid.
Answer
(a) On heating, zinc carbonate, which is a light amorphous white solid, changes to pale yellow and gives off a colourless and odourless gas that turns lime water milky. The milkiness disappears on passing excess of gas. This proves that the gas evolved is carbon dioxide.
ZnCO3 ZnO + CO2 ↑
(b) Chalky white precipitate of lead hydroxide is formed which is insoluble in excess of ammonium.
Pb(NO3)2 + 2NH4OH ⟶ 2NH4NO3 + Pb(OH)2 ↓
(c) When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to nitric acid, a colourless and odourless gas is evolved that turns lime water milky. The milkiness disappears on passing excess of gas. Hence, the gas evolved is carbon dioxide.
NaHCO3 + HNO3 ⟶ NaNO3 + H2O + CO2 ↑
Question 8(i)
The equation,
4NH3 + 5O2 ⟶ 4NO + 6H2O
represents the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. If 100 cm3 of ammonia is used, calculate the volume of oxygen required to oxidise the ammonia completely.
Answer
[By Lussac's law]
To calculate the volume of oxygen required :
Hence, volume of oxygen required = 125 cm3
Question 8(ii)
Define.
(a) Electronaffinity
(b) Electronegativity
Answer
(a) Electronaffinity — The amount of energy released while converting a neutral gaseous isolated atom into a negatively charged gaseous ion (anion) by the addition of electron is called Electron Affinity (E.A.)
(b) Electronegativity — The tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself is called its electronegativity.
Question 8(iii)
X [2, 6] and Y [2, 8, 8, 1] are two elements.
Using this information complete the following:
(a) ............... is the metallic element.
(b) Ionisation energy of X is ............... than Y.
(c) ............... is the reducing agent.
Answer
(a) Y is the metallic element.
(b) Ionisation energy of X is greater than Y.
(c) Y is the reducing agent.
Explanation
(a) Y is the metallic element as it has one valence electron.
(b) Atomic size of X is less than Y as X has 2 shells while Y has 3 shells. As, ionisation energy decreases with increase in atomic size, hence ionisation energy of X is greater than Y.
(c) Y has the tendency to lose its one valence electron and get oxidised. Hence, it acts as a reducing agent.
Question 8(iv)
Choose the correct word which refers to the process of electrolysis from A to C, to match the description 1 to 3.
A : Oxidation B : Cathode C : An electrolyte
(1) Conducts electricity in aqueous or in molten state.
(2) Loss of electron takes place at anode.
(3) A reducing electrode
Answer
(1) C : An electrolyte
(2) A : Oxidation
(3) B : Cathode