Which of the following is not an example of a machine used as a force multiplier?
- A jack used to lift a car.
- A single fixed pulley used to lift a bucket of water from a well.
- A bar used to lift a heavy stone.
- A wheel barrow used to carry a load.
Answer
A single fixed Pulley used to lift a bucket of water from a well.
Reason — When a single fixed pulley is used to lift a bucket of water from a well, it only changes the direction of the force required to lift the bucket.
For an ideal machine:
- Output energy = Input energy
- Output energy > Input energy
- Output energy < Input energy
- Work output > Work input
Answer
Output energy = Input energy
Reason — In an ideal machine, the output energy is equal to the input energy. Ideal machines do not account for any energy losses due to friction, inefficiencies, or other factors.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- For a machine, velocity ratio does not change.
- Due to friction, mechanical advantage of a machine increases.
- For an ideal machine, work output is equal to the work input.
- For an ideal machine, mechanical advantage is numerically equal to the velocity ratio
Answer
Due to friction, mechanical advantage of a machine increases.
Reason — Friction reduces the mechanical advantage of a machine because frictional forces oppose motion, which means they can decrease the efficiency of a machine by dissipating energy as heat. This results in a decrease in the mechanical advantage of the machine.
Unit of velocity ratio is:
- Nm
- Joule
- Newton
- No unit
Answer
No unit
Reason — As velocity ratio is a ratio between similar quantities (distances) so it has no unit.
The correct relationship between the mechanical advantage (M.A.), velocity ratio (V.R.) and efficiency (η) is:
- M.A. = η x V.R.
- V.R. = η x M.A.
- η = M.A. x V.R.
- None of these
Answer
M.A. = η x V.R.
Reason — The mechanical advantage of a machine is equal to the product of its efficiency and velocity ratio.
Which of the following relations is wrong?
- Work input = Effort x Displacement of effort
- Work output = Load x Displacement of load
- Efficiency = Work input / Work output
- Mechanical advantage = Velocity ratio x Efficiency
Answer
Efficiency = Work input / Work output
Reason — Efficiency is the ratio of useful work output to the total work input.
If the effort needed is less than the load, then mechanical advantage of the machine is:
- Greater than 1
- Less than 1
- Equal to one
- None of these
Answer
Greater than 1
Reason — Mechanical advantage (M.A.) is defined as the ratio of the load force to the effort force. When the effort force required is less than the load force, the mechanical advantage is greater than one, indicating that the machine amplifies the input force to overcome the load.
Select the incorrect statement:
- A machine always has efficiency less than 100%.
- The mechanical advantage of a machine can be less than 1.
- A machine can have mechanical advantage greater than the velocity ratio.
- A machine can be used as a speed multiplier.
Answer
A machine can have mechanical advantage greater than the velocity ratio.
Reason — In actual practice, mechanical advantage for all practical machines is always less than its velocity ratio (i.e., MA < VR) or the output work is always less than the input work, so the efficiency is less than 1 (i.e., η < 1 ) due to some loss of input energy against the force of friction etc.
The lever for which mechanical advantage is less than 1 has:
- Fulcrum at the mid-point between load and effort.
- Load between effort and fulcrum.
- Effort between fulcrum and load.
- Load and effort acting at the same point.
Answer
Effort between fulcrum and load.
Reason — In class III lever, i.e., when effort is between fulcrum and load the mechanical advantage is less than 1.
Class II levers are designed to have:
- M.A. = V.R.
- M.A. > V.R.
- M.A. > 1
- M.A. < 1
Answer
M.A. > 1
Reason — Mechanical advantage (M.A.) is defined as the ratio of effort arm to load arm. In class II levers, as effort arm is always longer than the load arm hence M.A. > 1.
The Lever shown in the figure is:

- Class I lever
- Class II Lever
- Class III Lever
- None of these
Answer
Class I lever
Reason — As fulcrum is between load and effort hence the figure shows class I lever.
Which class of levers have effort and load on the same side of fulcrum
- Class I lever
- Class II Lever
- Class III Lever
- Class II or class III Lever
Answer
Class II or class III Lever
Reason — In class II or class III levers, effort and load are on the same side of fulcrum .
(a) What do you understand by a simple machine?
(b) State the principle of an ideal machine.
Answer
(a) A machine is a device by which we can either overcome a large resistive force (or load) at some point by applying a small force (or effort) at a convenient point and in a desired direction or by which we can obtain a gain in speed.
(b) An ideal machine is that in which there is no loss of energy in any manner. Here, the work output is equal to the work input, i.e. its efficiency is 100%.
Name a machine for each of the following use —
(a) to multiply the force,
(b) to change the point of application of force,
(c) to change the direction of force,
(d) to obtain the gain in speed.
Answer
(a) In order to multiply the force — a bar is used to lift a heavy stone.
(b) In order to change the point of application of force — The rear wheel of a cycle is rotated by applying the effort on the pedal attached to the toothed wheel which is joined to the rear wheel with the help of a chain.
(c) In order to change the direction of force — to lift a bucket full of water from the well, a single fixed pulley is used by applying the effort in the downward direction instead of applying it upwards when the bucket is lifted up without the use of pulley.
(d) In order to obtain gain in speed — A knife. The blade of a knife moves longer by a small displacement of its handle.
How is mechanical advantage related to the velocity ratio for
(i) an ideal machine,
(ii) a practical machine?
Answer
(i) For an ideal machine (free from friction etc.), work output is equal to the work input, so the efficiency is equal to 1 ( or 100% ) and the mechanical advantage is numerically equal to the velocity ratio. So,
For an ideal machine, M.A. = V.R.
(ii) In the case of a practical machine, the mechanical advantage is always less than its velocity ratio or the output work is always less than the input work as some of the input energy is lost due to the force of friction etc. So,
For a practical machine, M.A. < V.R.
A machine works as a
(i) force multiplier,
(ii) speed multiplier.
In each case state whether the velocity ratio is more than or less than 1.
Answer
(i) When a machine works as a force multiplier then the displacement of the load is less than the displacement of effort. Hence, the velocity ratio is more than 1.
(ii) When a machine works as a speed multiplier then the displacement of load is more than displacement of effort. Hence, the velocity ratio is less than 1.
How is mechanical advantage related to the velocity ratio for an actual machine? State whether the efficiency of such a machine is equal to 1, less than 1 or more than 1.
Answer
For an actual machine, the mechanical advantage is always less than its velocity ratio or the output work is always less than the input work.
The efficiency of such a machine is always less than 1 as some part of input energy is lost against the force of friction.
Write down a relation expressing the mechanical advantage of a lever.
Answer
The expression of the mechanical advantage of a lever is:
Give one example each of a class I lever where mechanical advantage is
(a) more than 1 and
(b) less than 1
Answer
(a) For a class I lever, the mechanical advantage is more than 1 in the case of shears used for cutting the thin metal sheets.
(b) For a class I lever, the mechanical advantage is less than 1 in case of a pair of scissors whose blades are longer than its handles.
Classify the following into levers as class I, class II or class III:
(a) A door
(b) A catapult
(c) Claw hammer
(d) A wheel barrow
(e) A fishing rod
(f) Sugar tongs
Answer
(a) A door — Class II
(b) A catapult — Class I
(c) Claw hammer — Class I
(d) A wheel barrow — Class II
(e) A fishing rod — Class III
(f) sugar tongs — Class III
What type of lever is formed by the human body while
(a) raising a load on the palm, and
(b) raising the weight of body on toes?
Answer
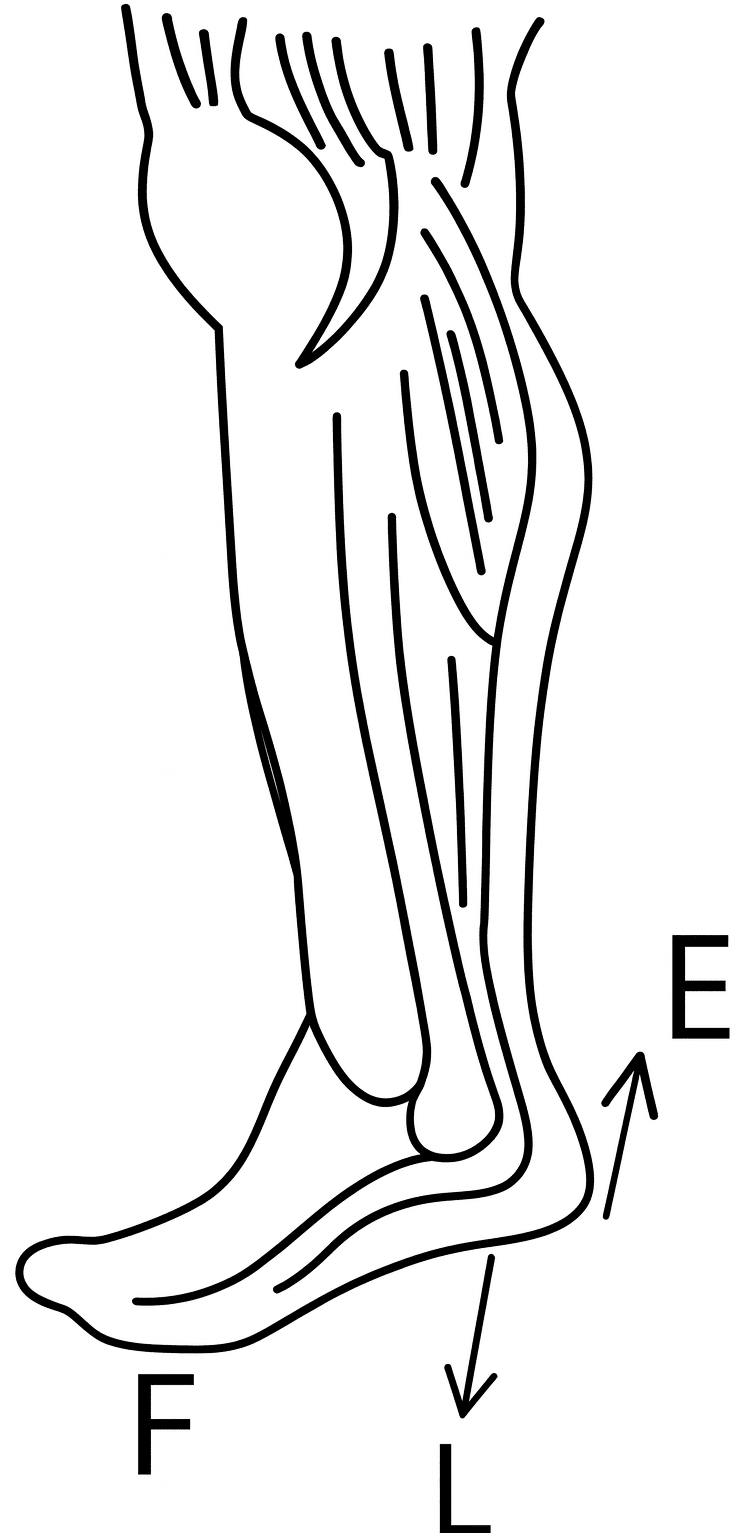
(a) When a human body raises a load on the palm then it is an example of a Class III lever. The elbow joint acts as fulcrum F at one end, biceps exerts the effort in the middle and load L on the palm is at the other end.
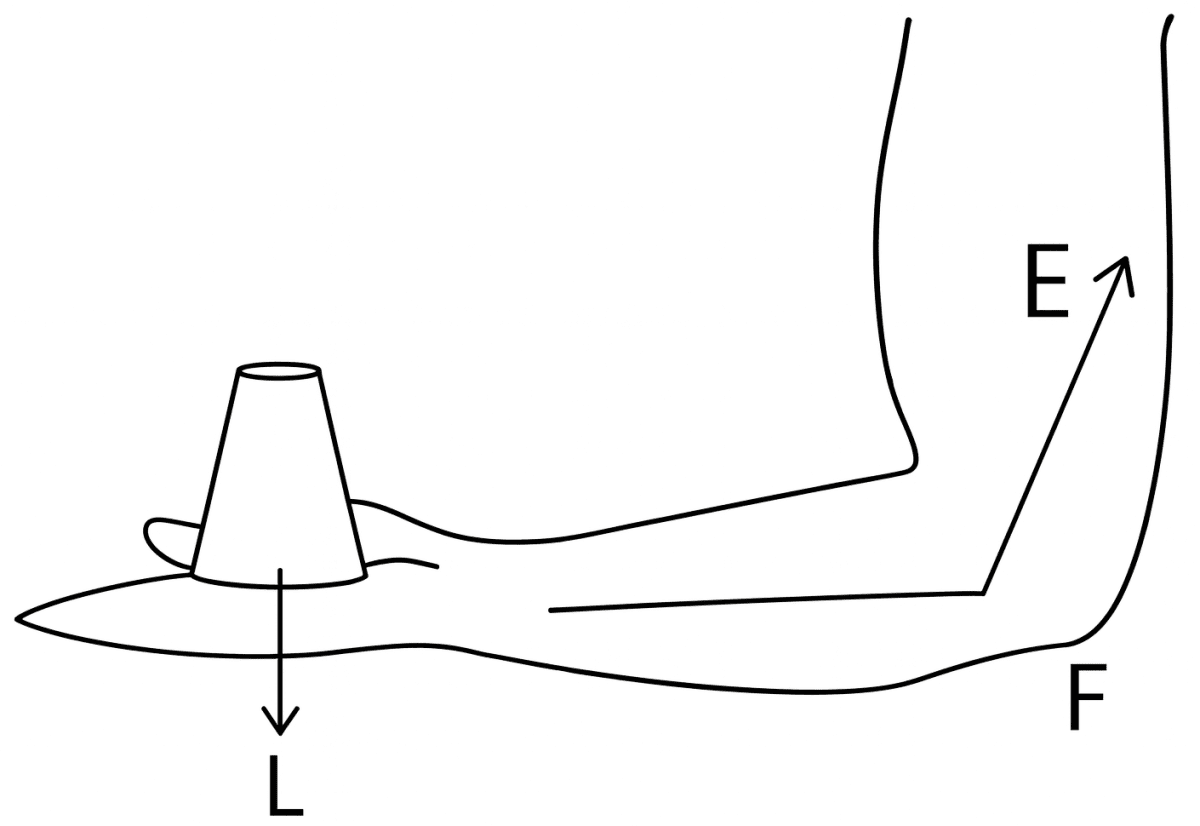
(b) When raising the weight of body on toes then it is a Class II lever. The fulcrum F is at toes at one end, the load L (i.e. weight of the body) is in the middle and the effort E by muscles is at the other end.
Give an example of each class of lever in a human body.
Answer
The examples of each class of lever in a human body are:
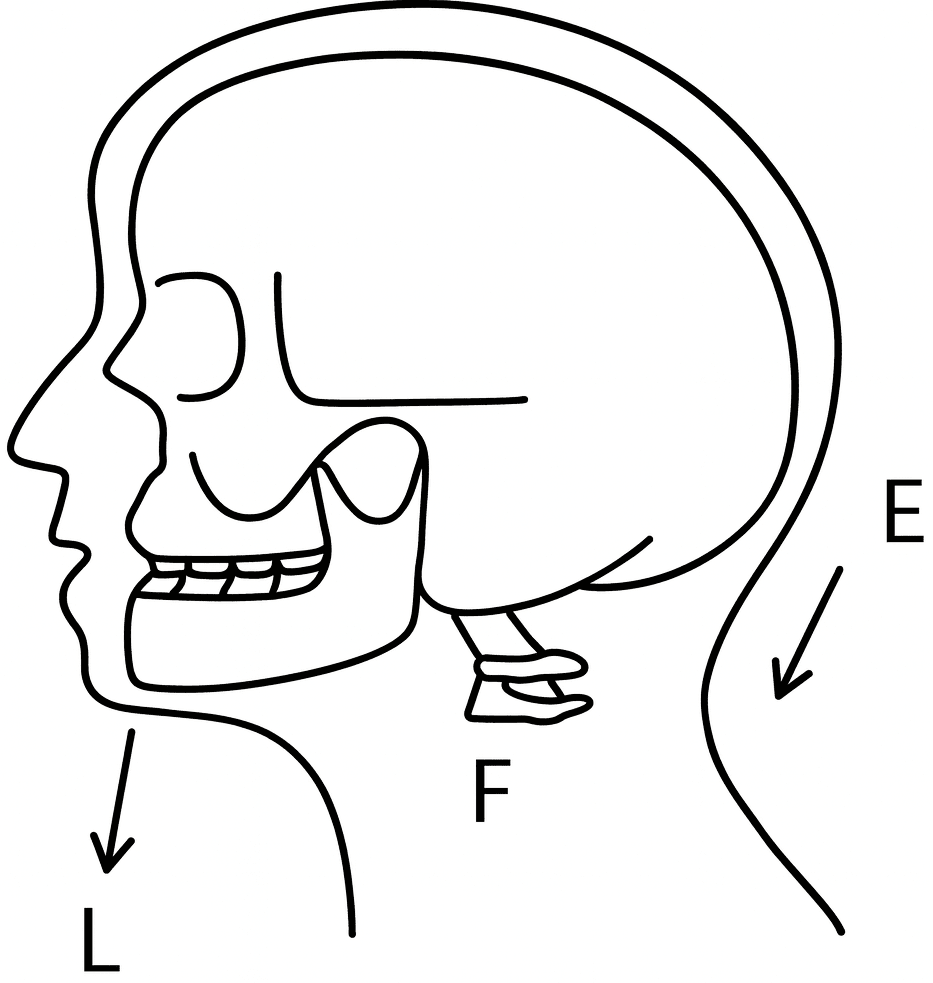
(i) The action of nodding of the head is a Class I lever. In this case the spine acts as the fulcrum F, load L is at its front part while effort E is at its rear part.
(ii) The action of raising the weight of the body on toes is an example of Class II lever. In this case, the fulcrum F is at toes at one end, the load L (i.e. the weight of the body) is in the middle and effort E by muscles is at the other end.

(iii) The action of raising a load by forearm is an example of Class III lever. In this case the elbow joint acts as fulcrum F at one end, biceps exerts the effort E in the middle and a load L on the palm is at the other end.

Complete the following sentences:
(a) Mechanical advantage = ............... × velocity ratio
(b) In class II lever, effort arm is ............... than the load arm.
(c) A pair of scissors is a ............... multiplier.
Answer
(a) Mechanical advantage = efficiency × velocity ratio
(b) In Class II lever, effort arm is longer than the load arm.
(c) A pair of scissors is speed multiplier
State four ways in which machines are useful to us?
Answer
Machines are useful to us in —
(a) Changing the point of application of effort to a convenient point.
(b) Lifting a heavy load by applying a less effort.
(c) Changing the direction of effort to a convenient direction.
(d) For obtaining a gain in speed.
What is the purpose of a jack in lifting a car by it?
Answer
A jack is a mechanical lifting device used to lift heavy loads.
A jack works as a force multiplier, as with a little effort on the jack we are able to lift heavy load like a car. It acts as a force multiplier.
What do you understand by an ideal machine? How does it differ from a practical machine?
Answer
An ideal machine is that where there is no loss of energy i.e. the work output is equal to the work input. An ideal machine is 100% efficient.
In a practical machine output energy is always less than the input energy i.e. there is some loss of energy during the operation which is not the case in an ideal machine.
Explain the term mechanical advantage. State its unit.
Answer
The ratio of the load to the effort is called mechanical advantage of the machine.
As mechanical advantage is a ratio of similar quantities so it has no unit.
Define the term velocity ratio. State its unit.
Answer
Velocity ratio is defined as the ratio of the velocity of effort to the velocity of the load.
As velocity ratio is a ratio of two similar quantities, so it has no unit.
Define the term efficiency of a machine. Give two reasons for a machine not to be 100% efficient?
Answer
The efficiency of a machine is defined as the ratio of the work done on load by the machine to the work done on the machine by the effort.
It has no unit as it is the ratio of two similar quantities.
A machine is not always 100% efficient due to —
(a) friction
(b) weight of moving parts of machine of a given design.
Due to the above reasons, the velocity ratio of the machine does not change but it's mechanical advantage decreases so its efficiency decreases.
When does a machine act as
(a) a force multiplier
(b) a speed multiplier?
Can a machine act as a force multiplier and speed multiplier simultaneously?
Answer
(a) A machine acts as a force multiplier when the effort arm is longer than the load arm. The mechanical advantage in such cases is greater than 1.
(b) A machine acts as a speed multiplier when the effort arm is shorter than the load arm. The mechanical advantage in such cases is less than 1.
No, it is not possible for a machine to act as a force multiplier and speed multiplier simultaneously.
For a machine used as a force multiplier, effort < load while for a machine used to obtain a gain in speed, effort > load. Hence, it is not possible for a single machine to act as both, simultaneously.
(a) State the relationship between mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency.
(b) Name the term that will not change for a machine of a given design.
Answer
(a) The mechanical advantage of a machine is equal to the product of its efficiency and velocity ratio.
M.A. = V.R. x η
(b) The term that does not change for a machine of a given design is its velocity ratio.
State one reason why mechanical advantage is less than the velocity ratio for an actual machine.
Answer
The mechanical advantage of an actual machine is always less than the velocity ratio as there is a loss of energy due to friction.
What is a lever? State its principle.
Answer
A lever is a rigid, straight (or bent) bar which is capable of turning about a fixed axis.
A lever works on the principle of moments, according to which in the equilibrium position of levers, moment of load about the fulcrum must be equal to the moment of effort about the fulcrum and the two moments must be in opposite directions.
Name the three classes of levers and state how are they distinguished. Give two examples of each class.
Answer
The three classes of levers are —
(i) Class I levers — In this type of the levers, the fulcrum F is in between the effort E and the load L.
Example — a seesaw, a pair of scissors
(ii) Class II levers — In these type of levers, the fulcrum F and the effort E are at the two ends of the lever and the load L is somewhere in between the effort E and the fulcrum F.
Example — a nutcracker, a bottle opener.
(iii) Class III levers — In these type of levers, the fulcrum F and the load L are at the two ends of the lever and the effort E is somewhere in between the fulcrum F and the load L.
Example — sugar tongs, foot treadle.
Both a pair of scissors and a pair of pliers belong to the same class of levers. Name the class of lever. Which one has the mechanical advantage less than 1?
Answer
A pair of scissors and a pair of pliers both belong to class I lever.
As the blades of the scissors are longer than its handles, so the effort arm is shorter than the load arm. Hence, the mechanical advantage of a pair of scissors is less than 1.
Figure shows a lemon crusher.

(a) In the diagram, mark the position of the directions of load L and effort E.
(b) Name the class of lever.
Answer
(a) Labelled diagram of lemon crusher is shown below:

(b) It is a class II lever.
The diagram below shows a rod lifting a stone.

(a) Mark position of fulcrum F and draw arrows to show the directions of load L and effort E.
(b) What class of lever is the rod?
(c) Give one more example of the same class of lever stated in part (b).
Answer
(a) Below diagram shows the position of fulcrum F and the directions of load L and effort E:

(b) The rod is a Class II lever as the load is between fulcrum and effort.
(c) A nut cracker is also an example of a Class II lever.
State the kind of lever which always has the mechanical advantage less than 1. Draw a labelled diagram of such a lever.
Answer
The Class III levers have mechanical advantage always less than 1.

Explain why mechanical advantage of class III lever is always less than 1.
Answer
The fulcrum F and the load L are at the two ends of the lever and the effort E is somewhere in between the fulcrum F and the load L.
The effort and the load are on the same side of fulcrum but in opposite directions and the effort arm is always smaller than the load arm. Therefore, the mechanical advantage of class III lever is always less than 1.
Classes III levers have mechanical advantage less than 1. Why are they then used?
Answer
Class III levers have mechanical advantage less than 1 so as effort arm is always less than the load arm, so we do not get gain in force, but we get gain in speed, i.e. a larger displacement of load is obtained by a smaller displacement of effort.
State the class of levers and the relative positions of load (L), effort (E) and fulcrum (F) in
(a) a bottle opener, and
(b) sugar tongs.
Answer

(a) A bottle opener is an example of Class II lever, as the fulcrum F and the effort E are at the two ends of the lever and the load is in between the fulcrum F and the effort E.
(b) Sugar tongs is an example of Class III lever, as the fulcrum F and the load L are at the two ends of the lever and the effort E is in between the fulcrum F and the load L.
Indicate the positions of load L, effort E and fulcrum F in the forearm shown below. Name the class of lever.

Answer
The positions of load L, effort E and fulcrum F in the forearm are shown below:

It is a Class III lever.
Derive a relationship between mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of a machine.
Answer
Suppose a machine overcomes a load L by the application of effort E.
Let,
the displacement of effort = dE and
the displacement of the load = dL in time t.
But we know that,
and
Substituting the above two values in the formula for efficiency we get
Hence, the mechanical advantage of a machine is equal to the product of its efficiency and velocity ratio.
Explain why scissors for cutting cloth may have blades longer than the handles, but shears for cutting metals have short blades and long handles.
Answer
A pair of scissors which is used to cut a piece of cloth has blades longer than the handles i.e. it has effort arm shorter than load arm so that the blades move longer on the cloth when the handles are moved a little.
Shears used for cutting metals have short blades and long handles i.e., it's effort arm is longer than the load arm and acts as a force multiplier which helps us to overcome large resistive force by a small effort.
Figure shows a uniform metre rule of weight W supported on a fulcrum at the 60 cm mark by applying the effort E at the 90 cm mark.

(a) State with reasons whether the weight W of the rule is greater than, less than or equal to the effort E.
(b) Find the mechanical advantage in an ideal case.
Answer
(a) The weight W of the scale is greater than E.
The effort arm is 30 cm and the load arm is 10 cm. In order to balance the scale — weight (W) of scale has to be more than effort (E).
(b) Given,
Load arm = 10 cm
Effort arm = 30 cm
As we know that,
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
Which type of lever has a mechanical advantage always more than 1? Give reason with one example. What change can be made in this lever to increase its mechanical advantage?
Answer
The Class II levers have mechanical advantage always greater than 1 and the reason for this is that, the load and effort are on same side of the fulcrum but in opposite directions and the effort arm is always greater than the load arm.
Therefore, mechanical advantage is always greater than 1.
This type of levers act as a force multiplier so less effort is needed to overcome a large load.
Example — a nut cracker
In order to increase the mechanical advantage, we can increase the length of effort arm.
Draw a diagram of a lever which is always used as a force multiplier. How is the effort arm related to the load arm in such a lever?
Answer
A Class II lever acts as a force multiplier as the mechanical advantage is always greater than 1 and the effort arm is longer than the load arm.

Explain why mechanical advantage of a class II type of lever is always more than 1.
Answer
In Class II levers, the fulcrum F and the effort E are at the two ends of the lever and the load L is somewhere in between the effort E and the fulcrum F.
So, the load and the effort are on the same side of the fulcrum but in opposite directions and the effort arm is always longer than the load arm.
Therefore, the mechanical advantage is always greater than 1.
Draw a labelled diagram of a class II lever. Give one example for such a lever.
Answer
Draw a labelled diagram of a Class II lever. Give one example of such a lever.
Answer
The figure below represents a Class II lever.

A nut cracker is an example of a class II lever.
What is the use of a lever if its mechanical advantage is
(a) more than 1,
(b) equal to 1, and
(c) less than 1?
Answer
(a) When the mechanical advantage is more the 1, the lever serves as force multiplier i.e. it enables us to overcome a large resistive force (load) by a small effort.
(b) When the mechanical advantage is equal to 1, the lever has effort arm and load arm of equal lengths like in a physical balance with both arms equal in length.
(c) When the mechanical advantage is less than 1, the levers are used to obtain the gain in speed. This means that the displacement of load is more as compared to the displacement of effort.
Draw a labelled sketch of a class III lever. Give one example of this kind of lever.
Answer

Sugar tongs is an example of class III lever.
Draw diagrams to illustrate the position of fulcrum, load and effort, in each of the following:
(a) A seesaw
(b) A common balance
(c) A nutcracker
(d) Forceps
Answer
(a) A seesaw

(b) A common balance

(c) A nutcracker

(d) Forceps.

A crowbar of length 120 cm has its fulcrum situated at a distance of 20 cm from the load. Calculate the mechanical advantage of the crowbar.
Answer
Given,
Total length of a crowbar = 120 cm
Effort arm = 120 – 20 = 100 cm
Load arm = 20 cm
We know that,
A pair of scissors has its blades 15 cm long, while its handles are 7.5 cm long. What is its mechanical advantage?
Answer
Given,
Load arm = 15 cm
Effort arm = 7.5 cm
A force of 5kgf is required to cut a metal sheet. A pair of shears used for cutting the metal sheet has its blades 5 cm long, while its handles are 10 cm long. What effort is needed to cut the sheet?
Answer
Given,
Load arm = 5 cm
Effort arm = 10 cm
We also know that,
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
The diagram below shows a lever in use.

(a) To which class of lever does it belong?
(b) If AB =1 m, AF= 0.4 m, find its mechanical advantage.
(c) Calculate the value of E.
Answer
(a) The diagram represents a Class I lever.
(b) Given,
AB = 1m
AF = Load arm =0.4 m
BF = Effort arm = 0.6 m
(c) We know that,
Given,
Load = 15 kgf
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
A man uses a crowbar of length 1.5 m to raise a load of 75 kgf by putting a sharp edge below the bar at a distance 1 m from his hand.
(a) Draw a diagram of the arrangement showing the fulcrum (F), load (L) and effort (E) with their directions.
(b) State the kind of lever.
(c) Calculate — (i) load arm, (ii) effort arm, (iii) mechanical advantage, and (iv) the effort needed.
Answer
(a) Below is the diagram of the crowbar showing the fulcrum (F), load (L) and effort (E) with their directions:

(b) Crowbar belongs to class I lever.
(c)
Given,
(i) Total length = 1.5 m
Effort arm = 1 m
(ii) Effort arm = 1 m
(iii)
(iv) Given,
Load = 75 kgf
We know that,
Substituting the values in formula we get,
A pair of scissors is used to cut a piece of cloth by keeping it at a distance of 8.0 cm from its rivet and applying an effort of 10 kgf by fingers at a distance 2.0 cm from the rivet.
(a) Find: (i) the mechanical advantage of scissors and (ii) the load offered by the cloth.
(b) How does the pair of scissors act - as a force multiplier or as a speed multiplier?
Answer
(a)
(i) We know that,
Given,
Load arm = 8.0 cm
Effort arm = 2 cm
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
(ii) We know,
Given,
Effort = 10 kgf
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
(b) As the mechanical advantage is less than 1 i.e. M.A. < 1. Hence, the pair of scissors acts as a speed multiplier as there is larger displacement of load than displacement of effort.
A 4 m long rod of negligible weight is supported at a point 125 cm from its one end and a load of 18 kgf is suspended at a point 60 cm from the support on the shorter arm.
(a) If a weight W is placed at a distance of 250 cm from the support on the longer arm to balance the rod, find W.
(b) If a weight 5 kgf is kept to balance the rod, find its position.
(c) To which class of lever does it belong?
Answer
(a) The principle of moments states that —
Moment of the load about the fulcrum = Moment of the effort about the fulcrum
Given,
Load = 18kgf and 18 kgf load is placed at 60 cm from the support.
Effort = W and W kgf weight is placed at 250 cm from the support.
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
∴ W = 4.32 kgf
(b) The principle of moments states that —
Moment of the load about the fulcrum = Moment of the effort about the fulcrum
Given,
Load = 18kgf and 18 kgf load is placed at 60 cm from the support.
W = 5 kgf and 5 kgf weight is placed at d cm from the support.
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
∴ d = 216 cm
(c) It belongs to class I lever as fulcrum is in between the effort and the load.
A lever of length 9 cm has its load arm 5 cm long and the effort arm is 9 cm long.
(a) To which class does it belong?
(b) Draw diagram of the lever showing the position of fulcrum F and directions of both the load L and effort E.
(c) What is the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency is 100%?
(d) What will be the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency becomes 50%?
Answer
(a) It belongs to Class II lever as length of the lever is equal to the effort arm and the effort arm is also more than the load arm.
(b) Below is the diagram of the lever with position of fulcrum F and directions of both the load L and effort E labelled:

(c) We know that,
Given,
Load arm = 5 cm
Effort arm = 9 cm
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
Relation between mechanical advantage, efficiency and velocity ratio is
Given, η = 100% = 1
So,
Therefore, Mechanical advantage = Velocity ratio = 1.8
(d) When efficiency reduces to 50%, its mechanical advantage reduces however, its velocity ratio remains the same. So,
M.A. = 0.5 x 1.8 = 0.9
V.R. = 1.8
The diagram below shows a lever in use.

(a) To which class of lever does it belong?
(b) Without changing the dimensions of the lever, if the load is shifted towards the fulcrum what happens to the mechanical advantage of the lever?
Answer
(a) The diagram shown belongs to class II lever as Load is in between Fulcrum and Effort.
(b) The mechanical advantage of the lever increases when load is shifted towards the fulcrum, as less effort is required to lift the load.
The figure below shows a wheel barrow of mass 15 kg carrying a load of 30 kgf with its centre of gravity at A. The points B and C are the centre of wheel and tip of the handle such that the horizontal distance AB = 20 cm and AC = 40 cm.

Find:
(a) the load arm,
(b) the effort arm,
(c) the mechanical advantage, and
(d) the minimum effort required to keep the leg just off the ground.
Answer
(a) Load arm AF = 20 cm
(b) Effort arm CF = 60 cm
(c) We know that,
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
(d) We know that,
Given,
Load = 30 kgf + 15 kgf = 45 kgf
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
Ramesh went for fishing with his fishing rod. Identify the class of lever for a fishing rod. If a fish exerts a load of 10 N and the distance between fulcrum and fish is 1.5 m, and the effort applied is 0.5 m from the fulcrum, what is the force required by the fisher to pull the fish?
Answer
A fishing rod is an example of a Class III lever.
Here,
Fulcrum : at the handle (where the rod pivots)
Effort : applied by the fisher's hand along the rod
Load : the fish at the end of the rod
In Class III levers : Fulcrum — Effort — Load
The principle of moments states that —
Moment of the load about the fulcrum = Moment of the effort about the fulcrum
∴ Effort × Effort Arm = Load × Load Arm .......... (i)
Given :
Load (L) = 10 N
Load arm (distance between fulcrum and fish) = 1.5 m
Effort arm (distance between fulcrum and applied effort) = 0.5 m
From (i)
Effort x 0.5 = 10 x 1.5
⇒ Effort = = 30 N
The diagram below shows the use of a lever.

(a) State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
(b) To which class of lever does it belong? Give an example of this class of lever.
(c) If FA = 10 cm, AB = 490 cm,
calculate:
(i) the mechanical advantage, and
(ii) the minimum effort required to lift the load (= 50N).
Answer
(a) The principle of moments states that —
Moment of the load about the fulcrum = Moment of the effort about the fulcrum
(b) The above diagram belongs to Class III lever. The example of Class III lever is a sugar tongs.
(c)
(i) We know that,
Given,
Load arm = 490 cm + 10 cm = 500 cm
Effort arm = 10 cm
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
(ii) We know that,
Given,
Load = 50 kgf
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
A fire tongs has its arms 20 cm long. It is used to lift a coal of weight 1.5 kgf by applying an effort at a distance 15 cm from the fulcrum.
Find:
(i) the mechanical advantage of fire tongs and
(ii) the effort needed.
Answer
(i) We know that,
Given,
Load arm = 20 cm
Effort arm = 15 cm
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
(ii) We know that,
Given,
Load = 1.5 kgf
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
The pulley system is used in a machine:
- for gain in energy
- as a force multiplier
- as a force multiplier and for a gain in energy
- none of these
Answer
as a force multiplier
Reason — Pulleys are commonly used as force multipliers in machines. They allow a person to lift or move heavy objects with less effort by distributing the force required over multiple ropes and pulleys.
A single fixed pulley is used because it:
- has a mechanical advantage greater than 1
- has a velocity ratio less than 1
- gives 100% efficiency
- helps to apply the effort in a convenient direction.
Answer
helps to apply the effort in a convenient direction.
Reason — A single fixed pulley changes the direction of the force needed to lift an object. However, it doesn't provide a mechanical advantage greater than 1 or a velocity ratio less than 1, nor does it guarantee 100% efficiency.
The figure given below shows a fixed pulley used by a boy to lift a load of 200 N through a vertical height of 5 m in 10 s. The velocity ratio of the pulley is
- 0
- 1
- 2
- none

Answer
1
Reason — The velocity ratio of a single fixed pulley is 1. If the point of application of effort E moves a distance d, then the load L also moves the same distance d upwards.
i.e. if dE = dL = d then V.R. = 1
The mechanical advantage of an ideal single movable pulley is:
- 1
- 2
- less than 2
- less than 1.
Answer
2
Reason — The mechanical advantage in the ideal case is 2 as the load can be lifted by applying the effort equal to half the load i.e., the single movable pulley acts as a force multiplier.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- The velocity ratio of a single fixed pulley is always 1.
- The velocity ratio of a single movable pulley is always 2.
- The velocity ratio of a combination of n movable pulleys with a fixed pulley is always 2n.
- The velocity ratio of a block and tackle system is always equal to the number of strands of the tackle supporting load.
Answer
All the given options are correct.
Reason — The velocity ratio of a single fixed pulley is always 1 and that of a single movable pulley is always 2.
The velocity ratio of a combination of n movable pulleys with a fixed pulley is always 2n whereas the velocity ratio of a block and tackle system is always equal to the number of strands of the tackle supporting load.
If there are n movable pulleys with one fixed pulley, the mechanical advantage is given by :
- 2n
- 2n+1
- 2n-1
- 2n+2
Answer
2n
Reason — In general, if there are n movable pulleys with one fixed pulley, the mechanical advantage is then 2n.
Which of the following differences between a single fixed pulley and a single movable pulley is incorrect?
| Single fixed pulley | Single movable pulley |
|---|---|
| (1) It is fixed to a rigid support | (i) It is not fixed to a rigid support. |
| (2) The load moves in a direction opposite to the effort. | (ii) The load moves in the direction of effort. |
| (3) Its ideal mechanical advantage is 1. | (iii) Its ideal mechanical advantage is 1. |
| (4) Its ideal velocity ratio is 2. | (iv) Its ideal velocity ratio is 1. |
| (5) The axis of rotation does not move in space. | (v) The axis of rotation also moves. |
- (5)
- (2) and (5)
- (3) and (5)
- (3) and (4)
Answer
(3) and (4)
Reason — The correct differences are:
| Single fixed pulley | Single movable pulley |
|---|---|
| (1) It is fixed to a rigid support | (i) It is not fixed to a rigid support. |
| (2) The load moves in a direction opposite to the effort. | The load moves in the direction of effort. |
| (3) Its ideal mechanical advantage is 1. | (iii) Its ideal mechanical advantage is 2. |
| (4) Its ideal velocity ratio is 1. | (iv) Its ideal velocity ratio is 2. |
| (5) The axis of rotation does not move in space. | (v) The axis of rotation also moves. |
The relationship between mechanical advantage (M.A.) and velocity ratio (V.R.) for a practical machine is:
- M.A.= V.R.
- M.A.> V.R.
- M.A.< V.R.
- None of these
Answer
M.A.< V.R.
Reason — In actual practice there is some friction between the parts of the machine or deformation of parts, which causes the mechanical advantage to be less than the velocity ratio.
A boy uses a single fixed pulley to lift a load of 50 kgf to some height. Another boy uses a single movable pulley to lift the same load to the same height. The ratio of the two effort is:
- 1:2
- 2:1
- 1:1
- none of these
Answer
2:1
Reason — We know that in case of a single fixed pulley, the effort applied is equal to the load.
Hence,
In the case of a single movable pulley the effort needed to lift a load is equal to half the load.
Hence, the ratio of efforts applied by the respective pulley is
Therefore, Ef : Em = 2 : 1
How many strands are supporting the load in case of block and tackle system of 5 pulleys?
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Answer
5
Reason — In a block and tackle system of 5 pulleys, 5 strands will be supporting the load.
How many strands are supporting the load in case of block and tackle system of 4 pulleys when effort is in downward direction?
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 6
Answer
4
Reason — The number of strands supporting the load in case of block and tackle system of 4 pulleys will be 4.
For a system of n pulleys, the weight of the lower block along with pulleys is w, then its efficiency is given by:
Answer
Reason — For a system of n pulleys, let w be the total weight of the lower block along with the pulleys in it. In the balanced position,
E = T and L + w = nT
or L = nT - w = nE - w
M.A. =
Thus, the mechanical advantage is less than the ideal value n.
The velocity ratio does not change, it remains n, i.e., V.R. = n
Hence, efficiency .
Assertion (A): The mechanical advantage of class III levers is always less than 1.
Reason (R): This is because the effort arm is always greater than the load arm.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
- assertion is false but reason is true
- assertion is true but reason is false.
Answer
assertion is true but reason is false.
Explanation
Assertion (A) is true. Class III levers always have a mechanical advantage less than 1, indicating that the load force is greater than the effort force.
Reason (R) is false. In class III levers, the load arm is always longer than the effort arm. Therefore, the statement that the effort arm is always greater than the load arm is incorrect.
What is the ideal mechanical advantage of a single fixed pulley? Can it be used as a force multiplier?
Answer
In case of an ideal single fixed pulley the effort needed is equal to the load itself and so the mechanical advantage is equal to 1.
As the amount of effort required is equal to the load itself so a single fixed pulley cannot be used as a force multiplier.
What is the velocity ratio of a single fixed pulley?
Answer
The velocity ratio of a single fixed pulley is 1. If the point of application of effort E moves a distance d, then the load L also moves the same distance d upwards.
i.e. if dE = dL = d then V.R. = 1
In a single movable pulley, if the effort moves by a distance x upwards, by what height is the load raised?
Answer
In a single movable pulley, if the effort moves by a distance x upward, the load is raised to a height of as the segment of string on both sides of the pulley moves up by a distance .
Name a machine which is used to:
(a) multiply force
(b) multiply speed, and
(c) change the direction of force applied.
Answer
(a) Multiply force — a movable pulley is used
(b) Multiply speed — Class III lever
(c) Change the direction of force applied — single fixed pulley
State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) The velocity ratio of a single fixed pulley is always more than 1.
(b) The velocity ratio of a single movable pulley is always 2.
(c) The velocity ratio of a combination of n movable pulleys with a fixed pulley is always 2n.
(d) The velocity ratio of a block and tackle system is always equal to the number of strands of the tackle supporting the load.
Answer
(a) False
Reason — The velocity ratio of a single fixed pulley is always equal to 1, not more than 1.
(b) True
Reason — The velocity ratio of a single movable pulley is always 2.
(c) True
Reason — In a combination of n movable pulleys with a fixed pulley, each movable pulley contributes a velocity ratio of 2 because the rope supporting the load passes through two sections of the rope for each movable pulley. Therefore, if there are n movable pulleys, the total velocity ratio is 2n.
(d) True
Reason — In a block and tackle system, the velocity ratio is equal to the number of strands of the tackle supporting the load. Each strand of rope supports the load, and as the rope is pulled, each strand contributes to lifting the load. Therefore, the velocity ratio, which is the ratio of the distance moved by the effort to the distance moved by the load, is equal to the number of strands supporting the load.
What is a fixed pulley? State its one use.
Answer
A pulley, which has its axis of rotation stationary in position is called a fixed pulley.
A fixed pulley is used to change the direction of effort to be applied. It is used for lifting small load such as a water bucket.
Name the pulley which has no gain in mechanical advantage. Explain, why is such a pulley then used?
Answer
The pulley that has no gain in mechanical advantage is a single fixed pulley.
A single fixed pulley is used only to change the direction of effort to be applied i.e. with its use the effort can be applied in a more convenient direction.
It is difficult to apply the effort upwards to lift a load up directly, but it becomes easier with the help of a fixed pulley, because the effort can be applied in the downward direction to raise the load up. Further to apply the effort downwards one can conveniently make use of his own weight also for the effort.
What is a single movable pulley? What is its mechanical advantage in the ideal case?
Answer
A pulley whose axis of rotation is movable is called a single movable pulley. The mechanical advantage in the ideal case is 2 as the load can be lifted by applying the effort equal to half the load. A single, movable pulley acts as a force multiplier.
Give two reasons why the efficiency of a single movable pulley is not 100%.
Answer
The efficiency of a single movable pulley system is not 100% because of the following reasons:
- There is friction in the pulley bearings or at the axle.
- The weight of the pulley and string is not zero.
What is the velocity ratio of a single movable pulley? How does the friction in the pulley bearing affect it?
Answer
In the case of a single movable pulley the velocity ratio is always 2. The friction in the pulley bearing has no effect.
In a single movable pulley, if the effort moves by a distance x upwards, by what height is the load raised?
Answer
When the free end of string is pulled up by the effort through a distance x, the load is raised up through a distance x/2. The reason is that the segment of string on both sides of the pulley moves up by a distance x/2 i.e., if dE = x, then dL = x/2.
Give reasons for the following —
(a) In a single movable pulley, the velocity ratio is always more than the mechanical advantage.
(b) The efficiency of a movable pulley is always less than 100%.
(c) In case of a block and tackle system, the mechanical advantage increases with the increase in the number of pulleys.
(d) The lower block of a block and tackle pulley system must be of negligible weight.
Answer
(a) For an actual single movable pulley, due to (i) friction in the pulley bearings or at the axle and (ii) the weight of the pulley and string, the effort needed to lift up a load L will be more than , so the mechanical advantage will be less than 2. But the velocity ratio will remain as 2. Hence, for a single movable pulley, the velocity ratio is always more than the mechanical advantage.
(b) As some effort is wasted in overcoming the friction between the strings and the grooves of the pulley as a result the efficiency of a movable pulley is always less than 100%.
(c) In the case of a block and tackle system, the mechanical advantage increases with the increase in the number of pulleys.
∴ M.A. = Total number of pulleys in both the blocks
(d) The lower block of a block and tackle pulley system must be of negligible weight as efficiency is reduced due to the weight of the lower block of the pulley.
where, w is the total weight of the lower block along with the pulleys in it.
Name the type of a single pulley that has an ideal mechanical advantage equal to 2. Draw a labelled diagram of the pulley mentioned by you.
Answer
The single movable pulley acts as a force multiplier and has a mechanical advantage equal to 2. Below is the labelled diagram of a single movable pulley:

In which direction does the force need to be applied, when a single pulley is used with a mechanical advantage greater than 1? How can you change the direction of force applied without altering its mechanical advantage? Draw a labelled diagram of the system.
Answer
In the case of a single pulley with a mechanical advantage greater than 1, the force needs to be applied in an upward direction which is very inconvenient.
In order to change the direction of force applied without altering its mechanical advantage, we have to use a single movable pulley along with a fixed pulley.
The load is attached to the axle of movable pulley A and the effort is applied in the downward direction at the free end of the string passing over the fixed pulley B. One can also use his own weight as effort which will be quite convenient.

Draw a labelled diagram of an arrangement of two pulleys, one fixed and other movable. In the diagram, mark the directions of all forces acting on it. What is the ideal mechanical advantage of the system? How can it be achieved?
Answer
Below is the diagram of an arrangement of two pulleys, one fixed and other moveable:

The ideal mechanical advantage of a single movable pulley with a fixed pulley system is 2. The ideal mechanical advantage of 2 can be achieved by assuming there is no friction in the pulley bearings, between the string and surface of the rim of the pulley and that string and the pulley are massless.
The diagram alongside shows a pulley arrangement.

(a) Name the pulleys A and B.
(b) In the diagram, mark the direction of tension on each strand of string.
(c) What is the purpose of the pulley B?
(d) If the tension is T, deduce the relation between (i) T and E, and (ii) E and L.
(e) What is the velocity ratio of the arrangement?
(f) Assuming that the efficiency of the system is 100%, what is the mechanical advantage?
Answer
(a) A → Movable pulley, B → Fixed pulley
(b) Tension on each strand of string is as shown in the diagram below:

(c) The purpose of fixed pulley B is to change the direction of effort to be applied from upward to downward.
(d)(i) When tension in the string is T then the effort E balances the tension T. So, E = T.
(d)(ii) When the load is balanced by the tension T in two segments of the string and the effort E balances the tension T at the free end, so
L = T + T = 2 T and
E = T,
Hence, 2E = L.
(e) When distance moved by effort is d then distance moved by load is d/2 so the velocity ratio becomes 2.
(f) If the efficiency of the system is 100%, then effort applied is equal to half the load. Hence, it acts as a force multiplier and the mechanical advantage is 2.
State four differences between a single fixed pulley and a single movable pulley.
Answer
| Single fixed pulley | Single movable pulley |
|---|---|
| It is fixed to a rigid support. | It is not fixed to a rigid support. |
| Its ideal mechanical advantage is 1. | Its ideal mechanical advantage is 2 |
| Its velocity ratio is 1. | Its velocity ratio is 2. |
| The weight of pulley itself does not affect its mechanical advantage. | The weight of pulley itself reduces its mechanical advantage. |
| It is used to change the direction of effort from upwards to downwards. | It is used as a force multiplier. |
The diagram alongside shows an arrangement of three pulleys A, B and C. The load is marked as L and the effort as E.

(a) Name the pulleys A, B and C.
(b) Mark in the diagram the direction of load (L), effort (E) and tension T1 and T2 in the two strings.
(c) How are the magnitudes of L and E related to the tension T1?
(d) Calculate the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio of the arrangement.
(e) What assumptions have you made in parts (c) and (d)?
Answer
(a) Pulleys A and B are movable pulleys while pulley C is a fixed pulley.
(b) The direction of load (L), effort (E) and tension T1 and T2 in the two strings are marked in the below diagram:

(c) The relation between magnitudes of L and E to the tension T1 is as follows:
The magnitude of effort E = T1
The magnitude of load L = 22 T1 = 4T1.
(d) The mechanical advantage is 22 = 4 as there are two movable pulleys and we know,
M.A. = 2n where, n is the number of movable pulleys.
The velocity ratio = 22 = 4 as there are two movable pulleys and we know,
V.R. = 2n where, n is the number of movable pulleys.
(e) The assumptions made are:
- The pulleys A and B are weightless
- There is no friction between the bearings of the pulleys or the axle.
Draw a diagram of combination of three movable pulleys and one fixed pulley to lift up a load. In the diagram, show the directions of load, effort and tension in each strand. Find:
(i) the mechanical advantage,
(ii) velocity ratio and
(iii) the efficiency of the combination in the ideal situation.
Answer
The diagram is shown below:
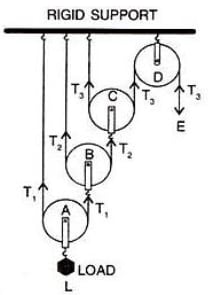
(i) In equilibrium,
Effort E = T3 (1)
Tension T1 in the string passing over the pulley A is given as 2T1 = L
T1 = (2)
Tension T2 in the string passing over the pulley B is given as
2T2 = T1
T2=
Substituting value of T1 from equation 2,
T2 = (3)
Tension T3 in the string passing over the pulley C is given as
2T3 = T2
T3 =
Substituting value of T2 from equation 3,
T3 = (4)
In equilibrium, T3 = E
From equation 4,
Load L = 23 x T3 (5)
(ii) As we know, one end of each string passing over a movable pulley is fixed, so the other end of string moves up twice the distance moved by the axle of the movable pulley.
If the load L attached to the pulley A moves a distance d,
then dL = d
Now, the string connected to the axle of pulley B, moves up by a distance,
2 times d = 2d.
Then the string connected to the axle of the pulley C, moves up by a distance,
2 times 2d = 22d
Then the end of the string passing over the fixed pulley D, moves up by a distance,
2 times 22d = 23d.
Hence, dE = 23d.
As we know,
(iii) Substituting the values in the formula we get,
Draw a diagram of a block and tackle system of pulleys having a velocity ratio of 5. In your diagram indicate clearly the points of application and the directions of the load L and effort E. Also mark the tension T in each strand.
Answer
The diagram of a block and tackle system of pulleys having a velocity ratio of 5 with directions of the load L, effort E and tension T in each strand is shown below:

A woman draws water from a well using a fixed pulley. The mass of the bucket and water together is 6 kg. The force applied by the women is 70 N. Calculate the mechanical advantage. (Take g = 10 m s-2).
Answer
Given,
Load = m x g = 6 x 10 = 60 N
Effort = 70 N
As we know that,
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
A fixed pulley is driven by a 100 kg mass falling at a rate of 8.0 m in 4.0 s. It lifts a load of 75.0 kgf.
Calculate —
(a) The power input to the pulley taking the force of gravity on 1 kg as 10 N.
(b) the efficiency of the pulley, and
(c) the height to which the load is raised in 4.0 s.
Answer
(a) As we know,
and
Given,
Substituting the values in the formula for power we get,
(b) We know,
Given,
We know,
Substituting the values for M.A. we get,
When the effort moves by a distance d downwards, the load moves by the same distance upwards. So we get,
V.R. = 1
Substituting the values of M.A. and V.R. in the formula for efficiency we get,
Hence, efficiency = 75 %
(c) As the load moves same distance upwards as much as effort moves downwards. So, the height achieved by the load is 8 m.
A single fixed pulley and a movable pulley both are separately used to lift a load of 50 kgf to the same height. Compare the efforts applied in an ideal situation.
Answer
We know that in case of a single fixed pulley, the effort applied is equal to the load.
Hence,
In the case of a movable pulley the effort needed to lift a load is equal to half the load.
Hence, the ratio of efforts applied by the respective pulley is
Therefore, Ef : Em = 2 : 1
In a block and tackle system consisting of 3 pulleys, a load of 75 kgf is raised with an effort of 25 kgf.
Find —
(i) the mechanical advantage,
(ii) the velocity ratio, and
(iii) the efficiency.
Answer
(i) Given,
Effort = 25 kgf
Load = 75 kgf
As we know that,
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
(ii) As we know,
V.R. = n = 3
(iii) Also,
Therefore, efficiency = 100%
A block and tackle system has 5 pulleys. If an effort of 1000 N is needed in the downward direction to raise a load of 4500 N,
Calculate —
(a)The mechanical advantage,
(b)The velocity ratio and,
(c)The efficiency of the system.
Answer
(a) Given,
Effort = 1000 N
Load = 4500 N
Number of pulleys = n = 5
As we know that,
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
(b) As we know,
V.R. = n = 5
(c) And,
Therefore, efficiency = 90%
In figure draw a tackle to lift the load by applying the force in the downward direction.

(a) Mark in the diagram the direction of load L and effort E.
(b) If the load is raised by 1 m, through what distance will the effort move?
(c) State the number of strands of tackle supporting the load.
(d) What is the mechanical advantage of the system?
Answer
(a) The below diagram shows the tackle along with the direction of load L and effort E marked:

(b) As we know that in a system of 5 pulleys, if the load moves up through a distance 1 m, each segment of the string is loosened by a length 1m so the effort end moves through a distance 5 times 1m i.e. 5m
(c) Five strands of tackle are supporting the load.
(d) As we know,
Load = 5m
Effort = 1m
Substituting the values in the formula for M.A. we get,
A pulley system has a velocity ratio 3. Draw a diagram showing the point of application and direction of load (L), effort (E) and tension (T).
It lifts a load of 150 N by an effort of 60 N. Calculate its mechanical advantage. Is the pulley system ideal? Give reason.
Answer

Given,
Effort = 60 N
Load = 150 N
As we know,
Substituting the values in the formula for M.A. we get,
Therefore, Mechanical advantage = 2.5
For an ideal case the M.A. should be equal n, where n is the number of pulleys of the pulley system.
In this case as the mechanical advantage is less than 3 ( i.e. the number of pulleys ) so the pulley system is not ideal.
Figure shows a system of four pulleys. The upper two pulleys are fixed and the lower two are movable.

(a) Draw a string around the pulleys. Also show the point of application and direction in which the effort E is applied.
(b) What is the velocity ratio of the system?
(c) How are load and effort of the pulley system related?
(d) What assumption do you make in arriving at your answer in part (c)?
Answer
(a) The diagram below shows the point of application and direction of the effort E:

(b) As we know that in a system of 4 pulleys, if the load moves up through a distance d, each segment of the string is loosened by a length d so the effort end moves through a distance 4 times d.
(c) As we know,
As M.A. = n = 4
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
(d) Assumptions made are —
(i) There is no friction in the pulley bearings.
(ii) Weight of lower pulleys is negligible.
(iii) The effort is applied downwards.
Figure shows a block and tackle system of pulleys used to lift a load.

(a) How many strands of tackle are supporting the load?
(b) Draw arrows to represent tension T in each strand.
(c) What is the mechanical advantage of the system?
(d) When load is pulled up by a distance 1 m, how far does the effort end move?
(e) How much effort is needed to lift a load of 100 N?
(f) What will be its V.R. if the weight of the movable block is doubled?
Answer
(a) There are 4 strands of tackle supporting the load.
(b) Tension T in each strand is as shown in the diagram below:

(c) As we know,
Load = 4T
Effort = T
Substituting the values in the formula for M.A. we get,
Hence, M.A. = 4
(d) In a system of 4 pulleys, if the load moves up through a distance 1m, each segment of the string is loosened by a length 1m so the effort end moves through a distance 4 times 1m. Hence, we get 4m as the distance moved by the effort arm.
(e) As we know,
M.A = 4
Load = 100 N
Substituting the values in the formula for M.A. we get,
(f) V.R = n (number of pulleys) = 4
A block and tackle system has the velocity ratio 3. Draw a labelled diagram of the system indicating the points of application and the directions of load L and effort E. A man can exert a pull of 200 kgf.
(a) What is the maximum load he can raise with this pulley system if its efficiency is 60%?
(b) If the effort end moves a distance 60 cm, what distance does the load move?
Answer
Given,
V.R = n (number of pulleys) = 3
Hence, number of pulleys = 3
Below is a labelled diagram of the system indicating the points of application and the directions of load L and effort E:

(a) As we know,
Given,
Effort = 200 kgf
Efficiency = 60% = 0.6
Substituting the values in the formula for efficiency we get,
As we know,
(b) The velocity ratio of system is V.R = number of pulleys = 3
As we know,
Substituting the values in the formula for V.R. we get,
You are given four pulleys and three strings. Draw a neat and labelled diagram to use them so as to obtain a maximum mechanical advantage equal to 8. In your diagram mark the directions of load L, effort E and tension in each strand.
What assumptions have you made to obtain the required mechanical advantage?
[Hint: Three movable pulleys with one fixed pulley attached to the same support]
Answer
The four pulleys can be used as three movable pulleys with one fixed pulley as shown in the diagram below:

Assumptions are —
(i) The weight of the pulleys and the string is massless.
(ii) There is no friction between the bearings of the pulley.