Mathematics
Without using set square or protractor, construct the quadrilateral ABCD in which ∠BAD = 45°, AD = AB = 6 cm, BC = 3.6 cm and CD = 5 cm.
(i) Measure ∠BCD.
(ii) Locate the point P on BD which is equidistant from BC and CD.
Locus
15 Likes
Answer
Draw AB = 6 cm as base. Construct 90° from point A and bisect the angle and cut off AD = 6cm, such that ∠BAD = 45°.
From D cut an arc of 5 cm and from B cut an arc of 3.6 cm. C will be their point of intersection. Join the points forming quadrilateral ABCD.
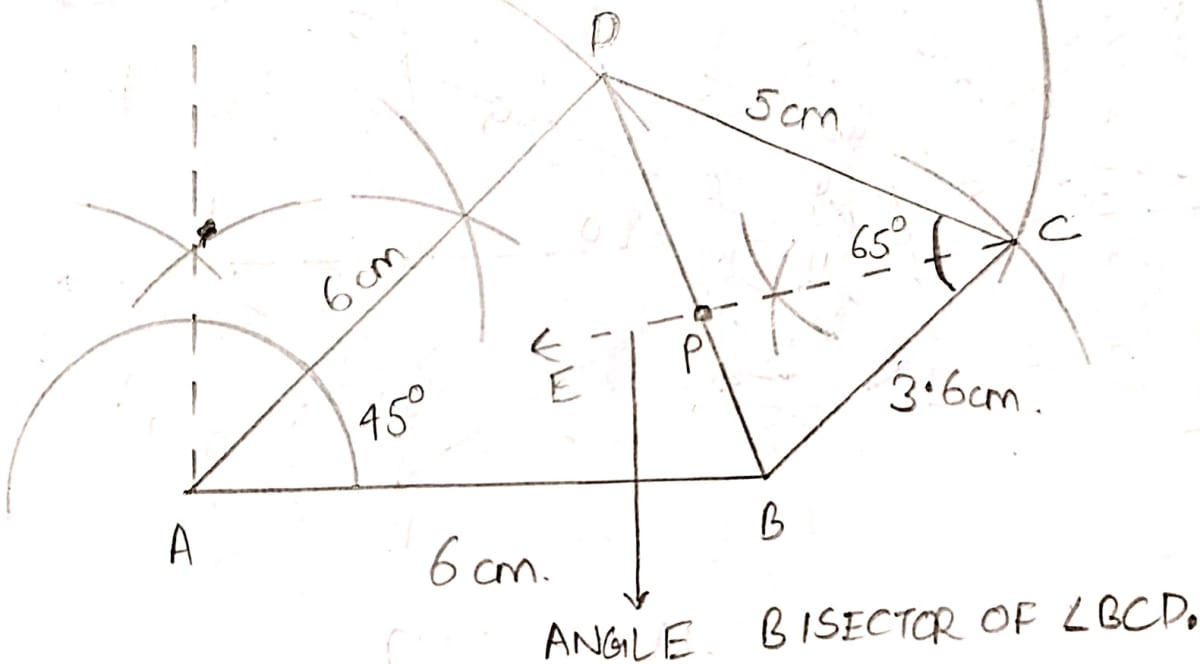
(i) Measuring angle BCD from the figure we get,
∠BCD = 65°.
(ii) We know that locus of points equidistant from two lines is the angle bisector of angle between them.
From the figure,
CE is the angular bisector of ∠BCD, hence it will be equidistant from CD and BC.
CE meets BD at point P as marked in the figure.
Answered By
10 Likes
Related Questions
Points A, B and C represent position of three towers such that AB = 60 m, BC = 73 m and CA = 52 m. Taking a scale of 10 m to 1 cm, make an accurate drawing of △ABC. Find by drawing, the location of a point which is equidistant from A, B and C, and its actual distance from any of the towers.
Draw two intersecting lines to include an angle of 30°. Use ruler and compasses to locate points which are equidistant from these lines and also 2 cm away from their point of intersection. How many such point exist ?
Without using set square or protractor, construct rhombus ABCD with sides of length 4 cm and diagonal AC of length 5 cm. Measure ∠ABC. Find the point R on AD such that RB = RC. Measure the length of AR.
Without using set square or protractor construct :
(i) Triangle ABC, in which AB = 5.5 cm, BC = 3.2 cm and CA = 4.8 cm.
(ii) Draw the locus of a point which moves so that it is always 2.5 cm from B.
(iii) Draw the locus of a point which moves so that it is equidistant from the sides BC and CA.
(iv) Mark the point of intersection of the loci with the letter P and measure PC.