Physics
With the use of Archimedes' principle, state how you will find relative density of a solid denser than water and insoluble in it. How will you modify your experiment if the solid is soluble in water?
Fluids Upthrust
54 Likes
Answer
Relative density of a solid denser than water and insoluble in it
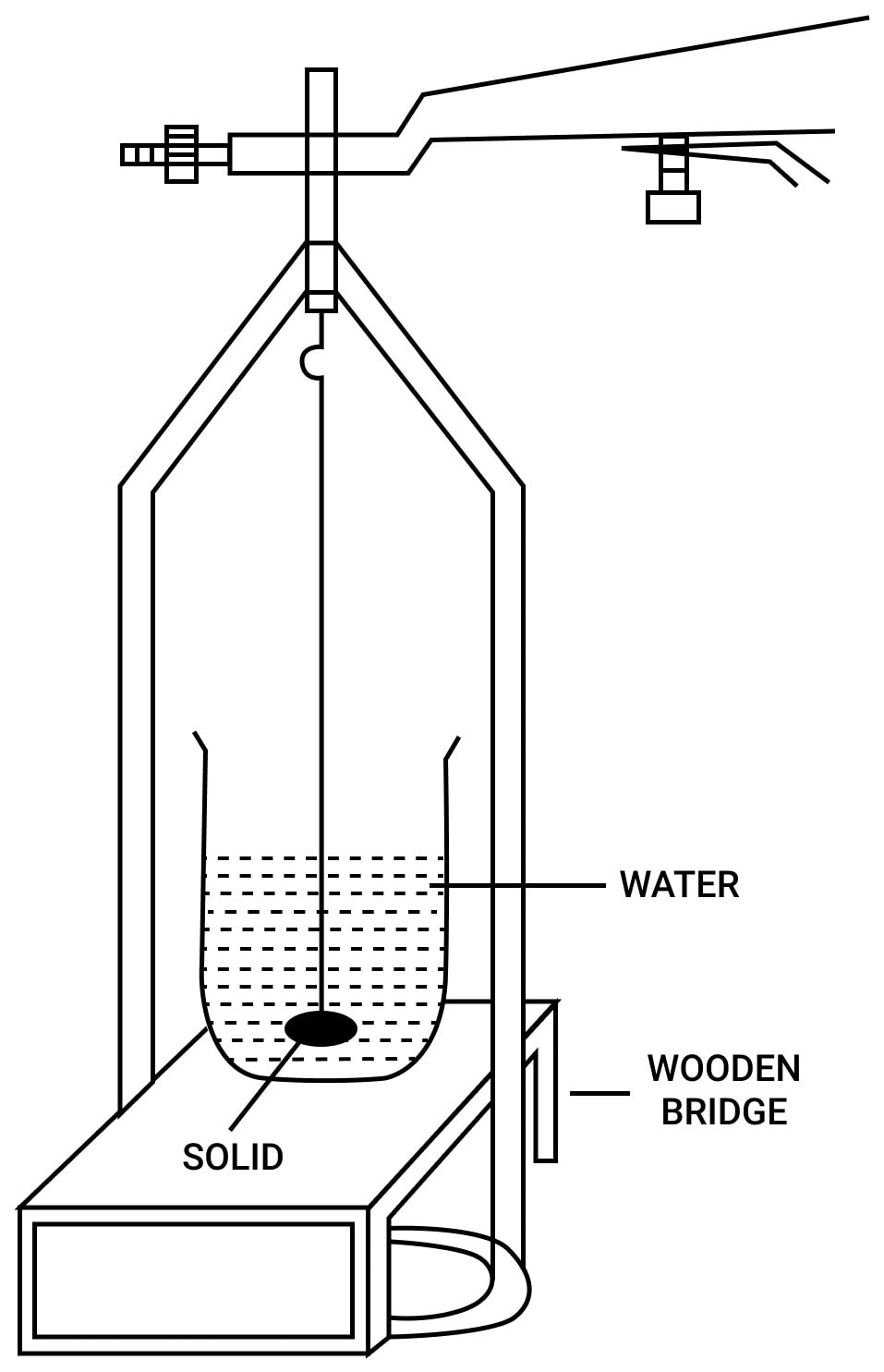
Procedure —
(i) Suspend a piece of the given solid with a thread from hook of the left pan of a physical balance and find it's weight W1.
(ii) Now balance a wooden bridge over the left pan of balance and place a beaker nearly two-third filled with water on the bridge. Take care that the bridge and beaker do not touch the pan of balance,
(iii) Immerse the solid completely in water such that it does not touch the walls and bottom of beaker and find the weight W2 of solid in water.
Observation —
Weight of solid in air = W1 gf
Weight of solid in water= W2 gf
Calculation —
Loss in weight of solid when immersed in water = (W1 - W2) gf
or
Relative density of a solid denser than water and soluble in it —
Procedure —
If solid is soluble in water, instead of water, we take a liquid of known relative density in which solid in insoluble and it sinks in that liquid. Then the process described above is repeated. Now
Answered By
26 Likes
Related Questions
Define relative density as a ratio of mass?
Differentiate between density and relative density of a substance?
Describe an experiment, using Archimedes' principle, to find the relative density of a liquid.
A body weighs W1 gf in air and when immersed in a liquid, it weighs W2 gf, while it weighs W3 gf on immersing it in water. Find: (i) volume of the body (ii) upthrust due to liquid (iii) relative density of the solid and (iv) relative density of the liquid.