Physics
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism? Why is it caused? State three factors on which the angle of deviation depends.
Answer
In a prism, the ray of light suffers refraction at two inclined faces. In each refraction, the ray bends towards the base of the prism. The below diagram shows the refraction of a ray of light of single colour through a prism:
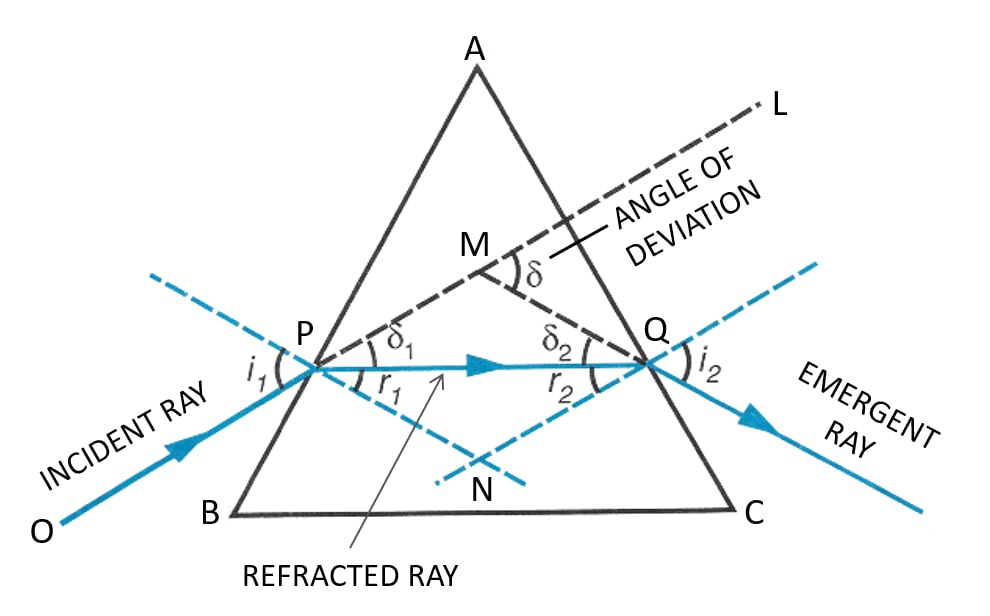
At the first face AB, the ray suffers a deviation equal to δ1. Then, at the second face AC, the ray PQ suffers a deviation δ2. Thus, the prism has produced a deviation which is the angle between the direction of incident ray and the emergent ray. This is called the angle of deviation produced by a prism.
The angle of deviation is caused as the ray passing through a prism suffers refraction at two inclined planes.
The three factors on which the angle of deviation depends are as follows:
- The angle of incidence (i)
- The material of prism (i.e on refractive index μ)
- The angle of prism (A)
Related Questions
What is a prism? With the help of a diagram of the principal section of a prism, indicate its refracting surfaces, refracting angle and base.
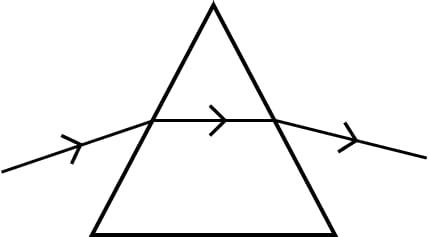
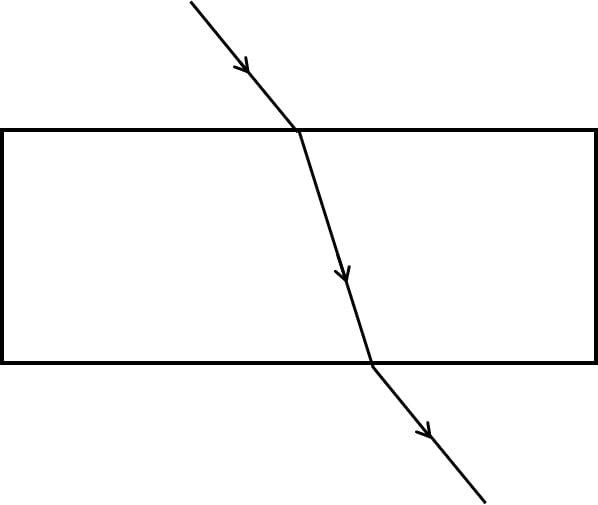
The diagrams (a) and (b) in figure below show the refraction of a ray of light of single colour through a prism and a parallel sided glass slab, respectively.
(a)
(b)
(i) In each diagram, label the incident, refracted, emergent rays and the angle of deviation.
(ii) In what way the direction of the emergent ray in the two cases differ with respect to the incident ray? Explain your answer.
(a) How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism change with increase in the angle of incidence. Draw a curve showing the variation in the angle of deviation with the angle of incidence at a prism surface.
(b) Using the curve in part (a) above, how would you infer that for a given prism, the angle of minimum deviation 𝛿min is unique for light of a given wavelength.
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic ray through a prism when it suffers minimum deviation. How is the angle of emergence related to the angle of incidence in this position.