Biology
The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:

(i) What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
(ii) Name the structure that acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
(iii) Label the parts numbered 1 to 4 in the diagram.
(iv) How can the above cell be brought back to its original condition? Mention the scientific term for the recovery of the cell.
(v) State any two features of the above plant cell which is not present in animal cells.
Answer
(i) The cell is in plasmolysed or flaccid state.
(ii) Plasma membrane
(iii) Parts numbered 1 to 4 are:
- 1 → Cell wall
- 2 → Strong sugar solution
- 3 → Cell membrane
- 4 → Nucleus
(iv) If the cell is placed in the hypotonic solution (water), the cell will be brought to it's original condition. The scientific term for the recovery of the cell is deplasmolysis.
(v) Cell wall, large prominent vacuole.
Related Questions
Given below is a representation of a kind of pollution. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:

(i) Name the kind of pollution.
(ii) List any three common sources of this pollution.
(iii) Mention three harmful effects of this pollution on human health.
(iv) Explain the term 'Pollutant'.
(v) Name two soil pollutants.
Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of what is mentioned in brackets:
Renal cortex and Renal medulla [Parts of the nephrons present]
Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of what is mentioned in brackets:
NADP and ATP [Expand the abbreviation]
The diagrams given below represent the relationship between a mouse and a physiological process that occurs in green plants. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow:
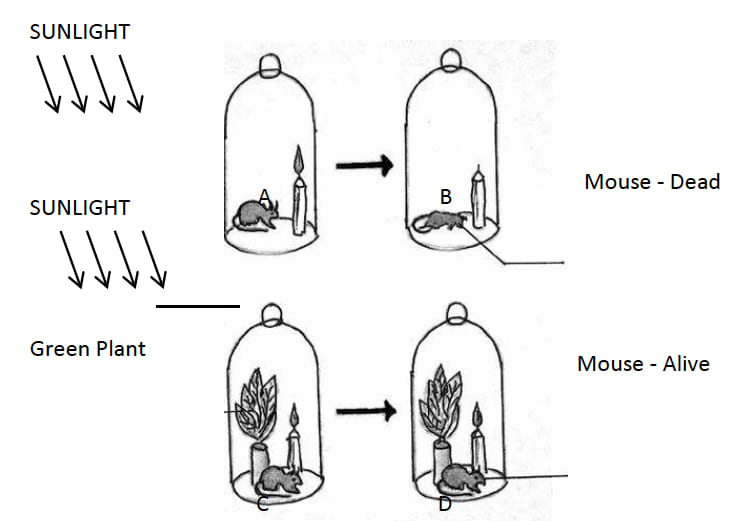
(i) Name the physiological process occurring in the green plant that has kept the mouse alive.
(ii) Explain the physiological process mentioned above.
(iii) Why did the mouse die in bell jar B?
(iv) What is the significance of the process as stated in (i) for life on earth.
(v) Represent the above mentioned physiological process in the form of a chemical equation.