Mathematics
In the given figure, O is the center of the circumcircle ABC. Tangents A and C intersect at P. Given angle AOB = 140° and angle APC = 80°; find the angle BAC.

Circles
14 Likes
Answer
Join OC

∴ PA and PC are the tangents
∴ OA ⊥ PA and OC ⊥ PC
In quadrilateral APCO,
⇒ ∠APC + ∠AOC = 180°
⇒ 80° + ∠AOC = 180°
⇒ ∠AOC = 180° - 80°
⇒ ∠AOC = 100°
From figure,
∠BOC = 360° - (∠AOB + ∠AOC)
= 360° - (140° + 100°)
= 360° - 240° = 120°.
We know that,
The angle at the centre of a circle is twice the angle at the circumference, subtended by the same arc.
Now arc BC subtends ∠BOC at the centre and ∠BAC at the remaining part of the circle.
∴ ∠BAC = ∠BOC = = 60°.
Hence, ∠BAC = 60°.
Answered By
7 Likes
Related Questions
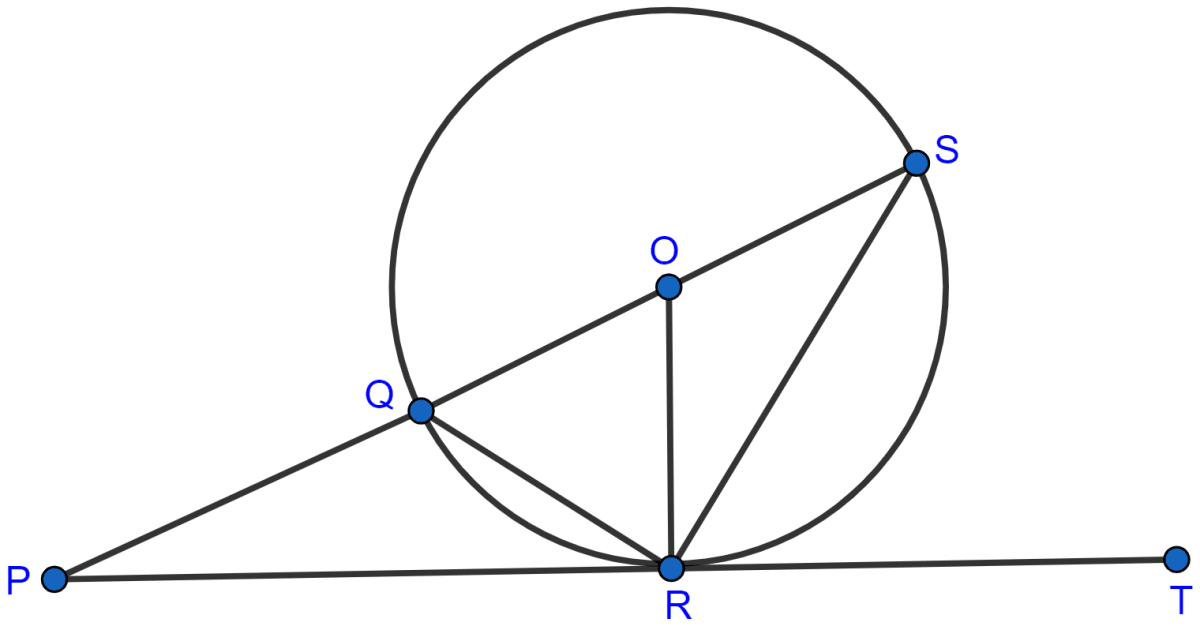
In the given figure, PT touches the circle with center O at point R. Diameter SQ is produced to meet the tangent TR at P.
Given ∠SPR = x° and ∠QRP = y°;
prove that :
(i) ∠ORS = y°
(ii) write an expression connecting x and y.
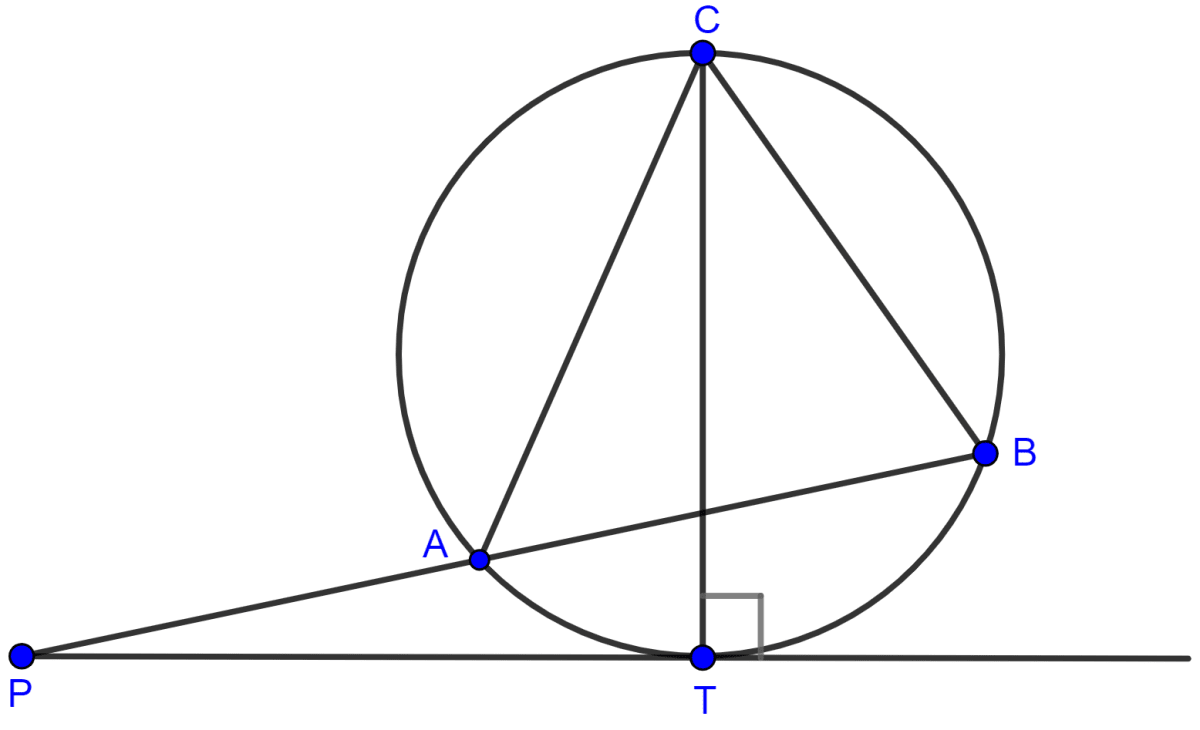
PT is a tangent to the circle at T. If ∠ABC = 70° and ∠ACB = 50°; calculate :
(i) ∠CBT
(ii) ∠BAT
(iii) ∠APT
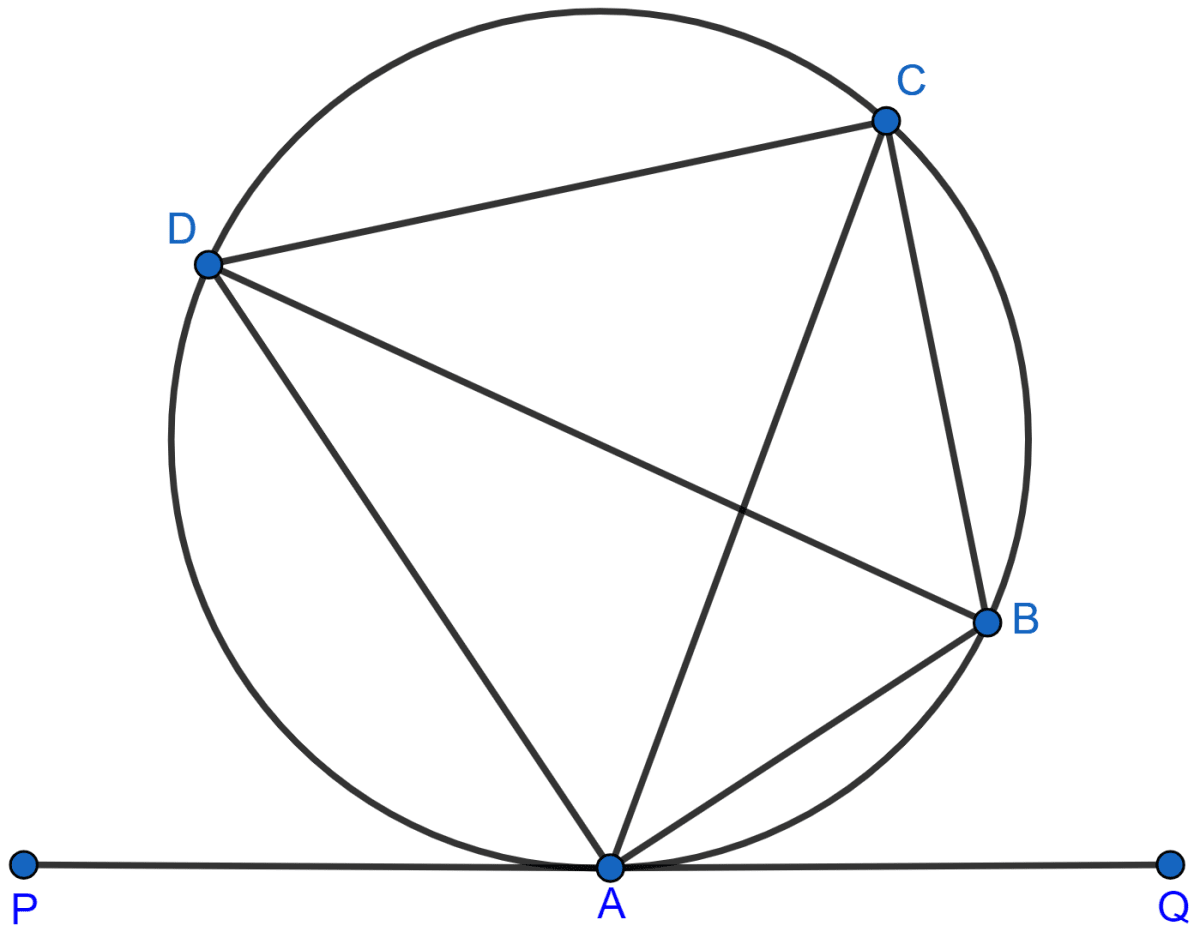
In the given figure, PQ is a tangent to the circle at A. AB and AD are bisectors of ∠CAQ and ∠PAC. If ∠BAQ = 30°, prove that : BD is diameter of the circle.
Chords AB and CD of a circle intersect each other at point O such that OA : OC = 4 : 7. Then OB : OD is equal to :
4 : 7
5 : 4
7 : 4
4 : 5
