Mathematics
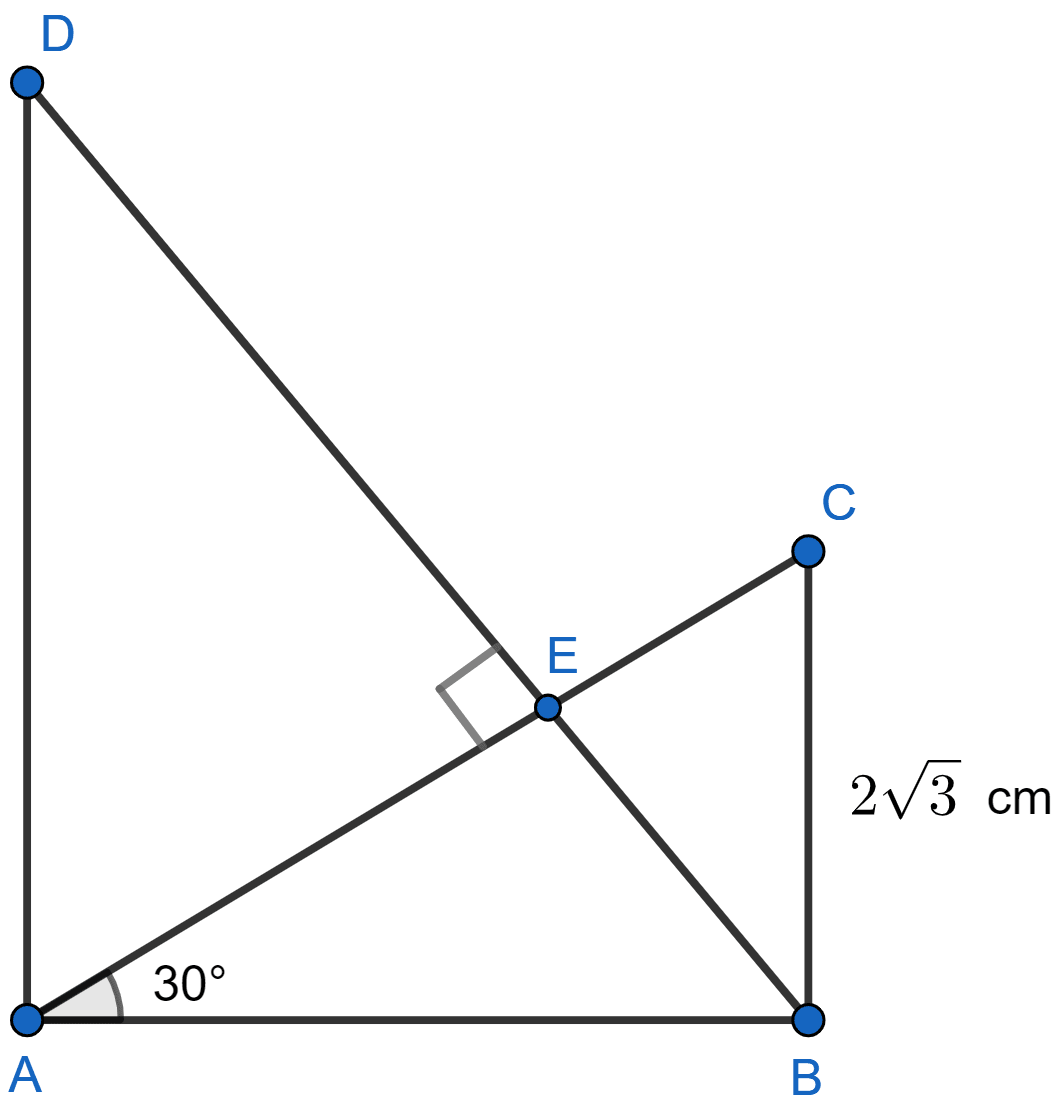
In the adjoining figure, ABC is right-angled triangle at B and ABD is right angled triangle at A. If BD ⊥ AC and BC = cm, find the length of AD.
Trigonometrical Ratios
17 Likes
Answer
In △ABC,
tan 30° =
In △ABE,
90° = 30° + ∠ABE [As, exterior angle is equal to sum of two opposite interior angles]
∠ABE = 90° - 30° = 60°.
From figure,
∠ABD = ∠ABE = 60°
In △ABD,
tan ∠ABD = tan 60° =
Hence, AD = cm.
Answered By
6 Likes
Related Questions
Without using trigonometrical tables, evaluate the following :
5 sin 50° sec 40°- 3 cos 59° cosec 31°
Prove that :
When 0° < A < 90°, solve the following equations :
(i) sin 3A = cos 2A
(ii) tan 5A = cot A
Find the value of θ if
(i) sin (θ + 36°) = cos θ, where θ and θ + 36° are acute angles.
(ii) sec 4θ = cosec (θ - 20°), where 4θ and θ - 20° are acute angles.