Mathematics
In an isosceles triangle ABC, AB = AC and D is a point on BC produced. Prove that AD2 = AC2 + BD × CD.
Pythagoras Theorem
43 Likes
Answer
Draw AP ⊥ BC.
APD is right triangle
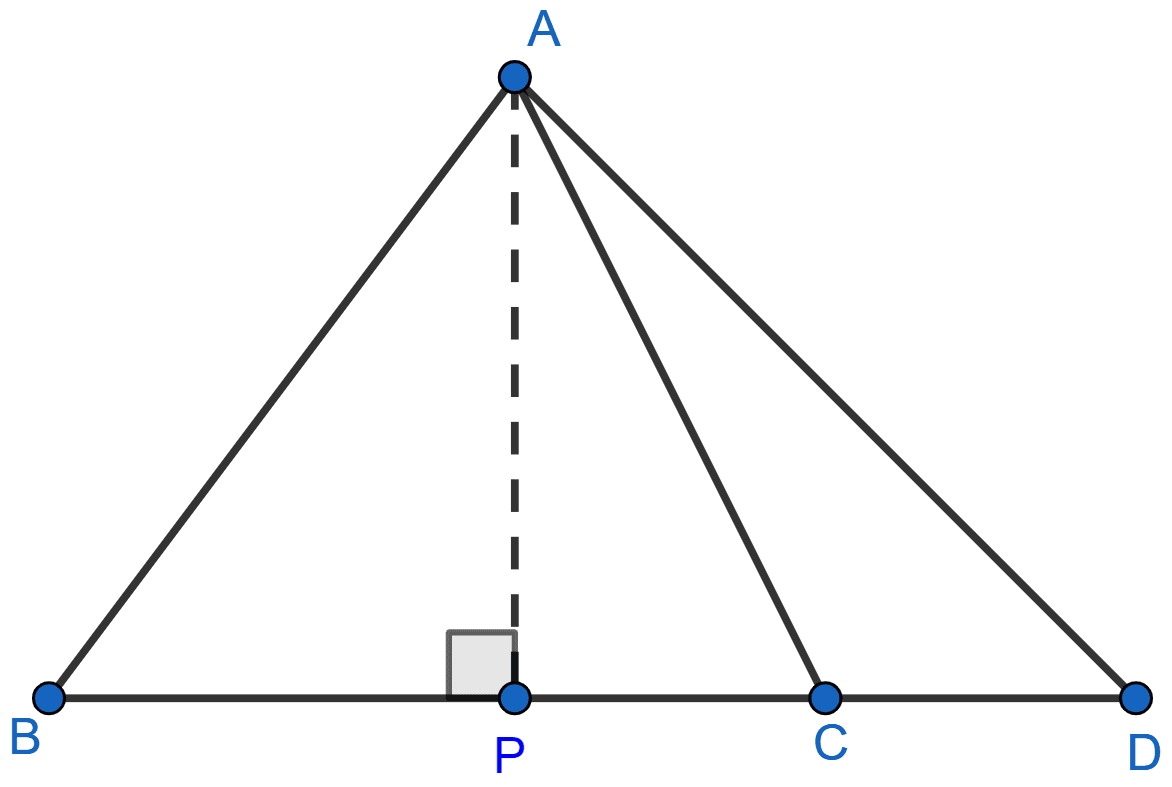
By pythagoras theorem we get,
⇒ AD2 = AP2 + PD2
⇒ AD2 = AP2 + (PC + CD)2
⇒ AD2 = AP2 + PC2 + CD2 + 2PC.CD ……(i)
APC is right triangle,
By pythagoras theorem we get,
⇒ AC2 = AP2 + PC2 ……(ii)
Substituting the value of AP2 + PC2 from (ii) in (i) we get,
⇒ AD2 = AC2 + CD2 + 2PC.CD …….(iii)
Since, ABC is an isosceles triangle,
⇒ PC = [∵ altitude to the base of an isosceles triangle bisects the base]
⇒ AD2 = AC2 + CD2 +
⇒ AD2 = AC2 + CD2 + BC.CD
⇒ AD2 = AC2 + CD(CD + BC)
From figure, CD + BC = BD
⇒ AD2 = AC2 + CD.BD
Hence, proved that AD2 = AC2 + BD × CD.
Answered By
26 Likes
Related Questions
In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠B = 90° = ∠D. Prove that
2AC2 - BC2 = AB2 + AD2 + DC2.
In a △ABC, ∠A = 90°, CA = AB and D is a point on AB produced. Prove that
DC2 - BD2 = 2AB × AD.
In a △ABC, if AB = cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 12 cm, then ∠B is
120°
90°
60°
45°
If the sides of a rectangular plot are 15 m and 8 m, then the length of its diagonal is
17 m
23 m
21 m
17 cm