Mathematics
Given sin θ = , find cos θ + sin θ in terms of p and q.
Trigonometrical Ratios
45 Likes
Answer
Let ABC be a right angle triangle with ∠C = θ and ∠B = 90°.
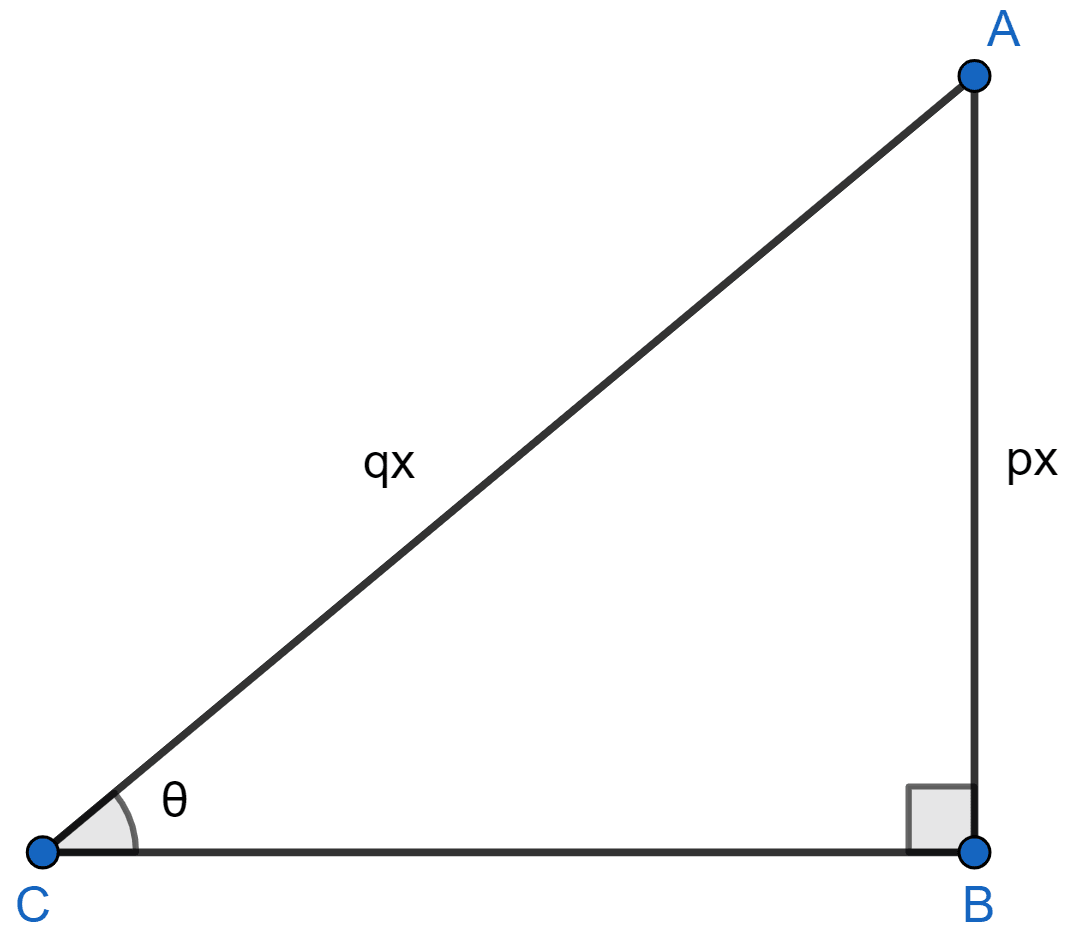
By formula,
sin θ = ……..(1)
Given,
sin θ = ………(2)
From (1) and (2) we get,
Let AB = px and AC = qx.
In right angled triangle ABC,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ BC2 = AC2 - AB2
⇒ BC2 = (qx)2 - (px)2
⇒ BC2 = q2x2 - p2x2
⇒ BC2 = x2(q2 - p2)
⇒ BC =
⇒ BC =
In right angled triangle ABC,
By formula,
cos θ =
= .
Substituting values in cos θ + sin θ we get,
Hence, cos θ + sin θ =
Answered By
25 Likes