Mathematics
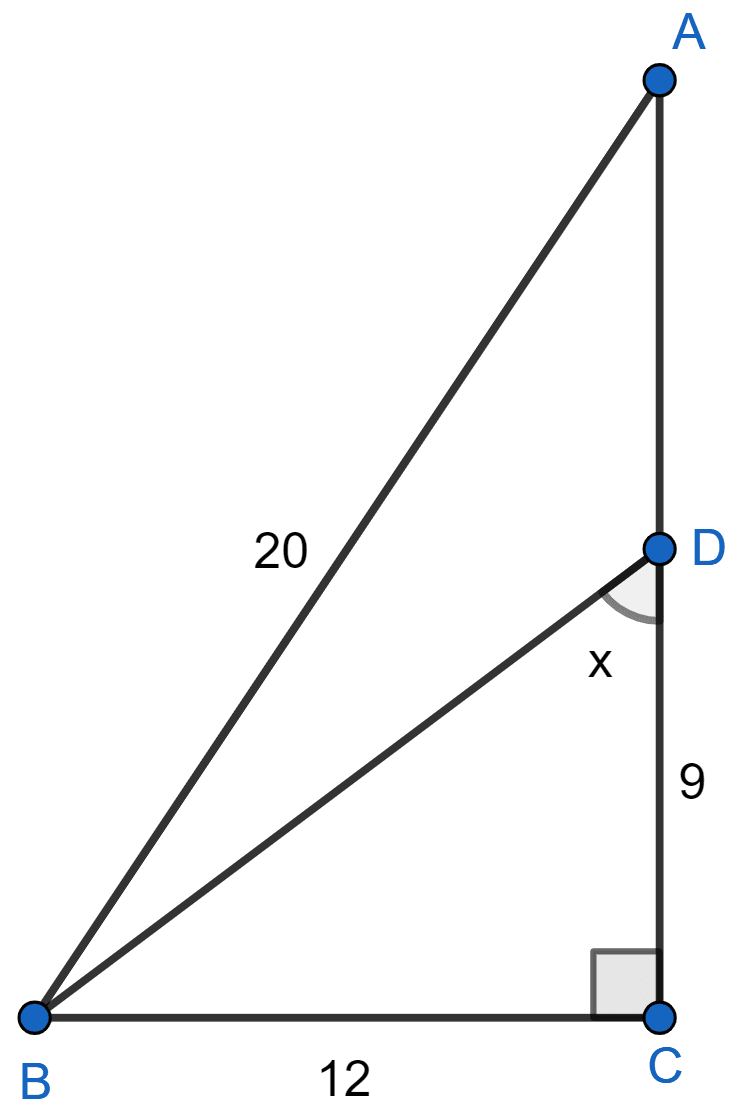
From the figure (1) given below, find the values of :
(i) sin ∠ABC
(ii) tan x - cos x + 3 sin x
Trigonometrical Ratios
31 Likes
Answer
(i) In right angle triangle ABC,
By pythagoras theorem we get :
⇒ AB2 = AC2 + BC2
⇒ 202 = AC2 + 122
⇒ 400 = AC2 + 144
⇒ AC2 = 400 - 144
⇒ AC2 = 256
⇒ AC = = 16.
Hence, sin ∠ABC = .
(ii) In right angle triangle BCD,
By pythagoras theorem we get :
⇒ BD2 = BC2 + CD2
⇒ BD2 = 122 + 92
⇒ BD2 = 144 + 81
⇒ BD2 = 225
⇒ BD =
⇒ BD = 15.
By formula,
Substituting values in tan x - cos x + 3 sin x we get :
Hence, tan x - cos x + 3 sin x =
Answered By
19 Likes
Related Questions
From the figure (i) given below, calculate all the six t-ratios for both acute angles.

From the figure (ii) given below, find the values of x and y in terms of t-ratios of θ.

From the figure (2) given below, find the values of :
(i) 5 sin x
(ii) 7 tan x
(iii) 5 cos x - 17 sin y - tan x

If q cos θ = p, find tan θ - cot θ in terms of p and q.