Chemistry
Explain the terms :
(a) Lone pair of electrons
(b) Coordinate bond
Explain diagrammatically the lone pair effect of:
(a) The nitrogen atom of the ammonia molecule leading to the formation of ammonium ions [NH4]+
(b) The oxygen atom of the H2O molecule leading to formation of hydronium [H3O]+ and hydroxyl ions [OH]-
Chemical Bonding
50 Likes
Answer
(a) Lone pair of electrons — They are a pair of electrons not shared with any other atom.
(b) Coordinate Bond — It is a type of covalency which involves one of the combining atoms contributing both of the shared electrons. i.e., a bond formed by a shared pair of electrons with both electrons coming from the same atom.
(a) Formation of ammonium ions [NH4]+

In ammonia, the 'N' atom contains one lone pair of electrons after completing it's octet. This lone pair is accepted by the hydrogen ion of water leading to the formation of a coordinate covalent bond:
(b) Formation of hydronium (H3O)+ and hydroxyl ions [OH]-
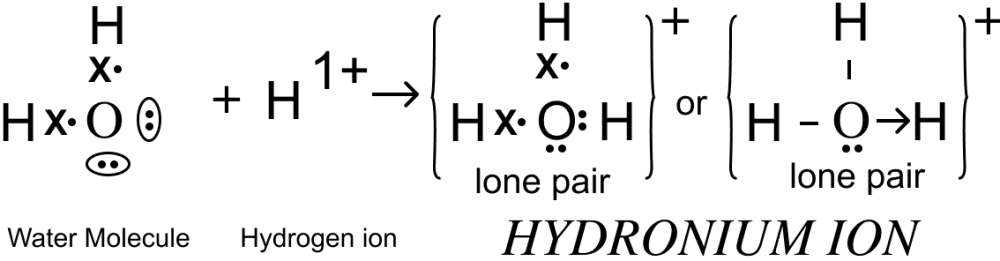
In water, the 'O' atom contains two lone pairs of electrons after completing it's octet. These lone pairs are accepted by the hydrogen ion leading to the formation of coordinate covalent bond:
Answered By
21 Likes
Related Questions
Give reasons for the following:
A molecule of methane has four single covalent bonds.
Give reasons for the following:
Formation of ammonia involves one atom of nitrogen sharing three electron pairs one with each of the three atoms of hydrogen.
Give reasons for the following:
Electrovalent compounds are soluble in water, insoluble in organic solvents, good conductors of electricity in molten or aq. solution state, have high melting points and undergo electrolytic dissociation on passage of electric current, while covalent compounds are soluble in organic solvents, insoluble in water, non-conductors of electricity, have low melting points and undergo ionization on passage of electric current.
Give reasons for the following:
NH3 gas a covalent compound does not conduct electricity but it's aq. soln. NH4OH is a weak electrolyte.