Computer Applications
A class teacher wants to arrange the names of her students in alphabetical order. Define a class NameSorter that stores the given names in a one-dimensional array. Sort the names in alphabetical order using Bubble Sort technique only and display the sorted names.
Aryan, Zoya, Ishaan, Neha, Rohan, Tanya, Manav, Simran, Kabir, Pooja
public class NameSorter
{
void bubbleSort(String names[]) {
int len = names.length;
_______(1)_________ {
_______(2)_________ {
_______(3)_________ {
String t = names[j];
_______(4)_________
_______(5)_________
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String arr[] = {"Aryan", "Zoya",
"Ishaan", "Neha",
"Rohan", "Tanya",
"Manav", "Simran",
"Kabir", "Pooja"
};
NameSorter obj = new NameSorter();
obj.bubbleSort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
Java Arrays
2 Likes
Answer
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++)if (names[j].compareToIgnoreCase(names[j + 1]) > 0)names[j] = names[j + 1];names[j + 1] = t;
Explanation
public class NameSorter
{
void bubbleSort(String names[]) {
int len = names.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) {
if (names[j].compareToIgnoreCase(names[j + 1]) > 0) {
String t = names[j];
names[j] = names[j + 1];
names[j + 1] = t;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String arr[] = {"Aryan", "Zoya",
"Ishaan", "Neha",
"Rohan", "Tanya",
"Manav", "Simran",
"Kabir", "Pooja"
};
NameSorter obj = new NameSorter();
obj.bubbleSort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
Variable Description Table
Method bubbleSort:
| Variable Name | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
names | String[] | An array of Strings that holds the list of names to be sorted. |
len | int | The length of the names array, indicating the number of names to be sorted. |
i | int | An index variable used as a loop counter for the outer loop to control the number of passes. |
j | int | An index variable used as a loop counter for the inner loop to compare adjacent elements. |
t | String | A temporary variable used to hold a name value during the swapping process. |
Method main:
| Variable Name | Data Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
arr | String[] | An array of Strings containing the names to be sorted. |
obj | NameSorter | An instance of the NameSorter class used to call the bubbleSort method. |
i | int | An index variable used as a loop counter to iterate over the sorted names for printing. |
Program Explanation
Let's analyze the Java program step by step to understand its functionality:
1. Class Definition:
- The class
NameSorteris defined, which contains a methodbubbleSortand themainmethod to execute the program.
2. bubbleSort Method:
- The method
bubbleSortaccepts an array of stringsnames[]as a parameter. This method will sort the strings in the array in alphabetical order.
3. Outer and Inner Loops:
- The
bubbleSortuses two nested loops to iterate through the array:- The outer loop runs from the beginning of the array to the second-to-last element (
len - 1). The variableiserves as the counter for this loop. - The inner loop runs from the start of the array up to the last unsorted element (
len - 1 - i). The variablejis the counter for the inner loop. - The decreasing upper bound in the inner loop
len - 1 - iis because with each complete pass through the array, the largest unsorted element gets correctly positioned at the end, reducing the number of elements needing comparison.
- The outer loop runs from the beginning of the array to the second-to-last element (
4. Comparison and Swapping:
- Inside the inner loop, a comparison is made between adjacent elements using
compareToIgnoreCase:- The
compareToIgnoreCasemethod is used to compare two strings lexicographically, returning a result based on whether the first string is considered greater, equal, or smaller than the second string, without regard to case. - If
names[j]is lexicographically greater thannames[j + 1](i.e.,compareToIgnoreCasereturns a positive number), the elements are swapped. This ensures larger elements "bubble up" to their correct position.
- The
5. Swapping Logic:
- A temporary string
tis used to facilitate the swapping ofnames[j]andnames[j+1]. The algorithm storesnames[j]int, assignsnames[j+1]tonames[j], and finally assignsttonames[j+1].
6. Main Method:
- The
mainmethod initializes an arrayarrwith several names in mixed order. - An instance
objof theNameSorterclass is created. - The
bubbleSortmethod is called on theobjinstance, passing thearrto be sorted. - After sorting, the program iterates through the sorted array and prints each name to the console, displaying the names in alphabetical order.
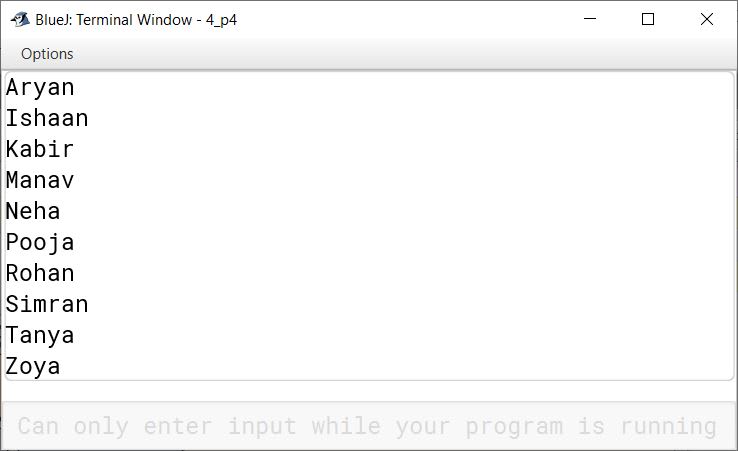
Output
Answered By
2 Likes
Related Questions
A single dimensional array contains 37 elements. Which of the following represents the index of its second-to-last element.
What is the output of the Java code given below?
String color[] = {"Blue", "Red", "Violet"}; System.out.println(color[2].length());- 6
- 5
- 3
- 2
Which of the following is a valid way to declare and initialize an integer array to store the ages of 50 students?
Define a class pin code and store the given pin codes in a single dimensional array. Sort these pin codes in ascending order using the Selection Sort technique only. Display the sorted array.
110061, 110001, 110029, 110023, 110055, 110006, 110019, 110033