Mathematics
Angles of a quadrilateral are (4x)°, 5(x + 2)°, (7x - 20)° and 6(x + 3)°. Find:
(i) the value of x.
(ii) each angle of the quadrilateral.
Geometrical Shapes
5 Likes
Answer
(i) It is given that the angles of a quadrilateral are (4x)°, 5(x + 2)°, (7x - 20)° and 6(x + 3)°.
As we know, the sum of all angles in a quadrilateral is 360°.
So,
⇒ ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
⇒ (4x)° + 5(x + 2)° + (7x - 20)° + 6(x + 3)° = 360°
⇒ 4x° + 5x° + 10° + 7x° - 20° + 6x° + 18° = 360°
⇒ 22x° + 8° = 360°
⇒ 22x° = 360° - 8°
⇒ 22x° = 352°
⇒ x° =
⇒ x° = 16°
Hence, the value of x is 16.
(ii) Each angle is (4x)°, 5(x + 2)°, (7x - 20)° and 6(x + 3)°:
= (4 16)°, 5(16 + 2)°, (7 16 - 20)° and 6(16 + 3)°
= 64°, 5(18)°, (122 - 20)° and 6(19)°
= 64°, 90°, 92° and 114°
Hence, the angles of the quadrilateral are 64°, 90°, 92° and 114°.
Answered By
4 Likes
Related Questions
In quadrilateral ABCD, sides AB and DC are parallel to each other. If ∠A : ∠D = 2 : 3 and ∠B : ∠C = 7 : 8; find all the angles of quadrilateral ABCD.
In quadrilateral ABCD; 2∠A = 3∠B = 2∠C = 6∠D. Find all the angles of the quadrilateral.
The sum of interior angles of a regular polygon is thrice the sum of its exterior angles. Find the number of sides in the polygon.
Use the information given in the following figure to find:
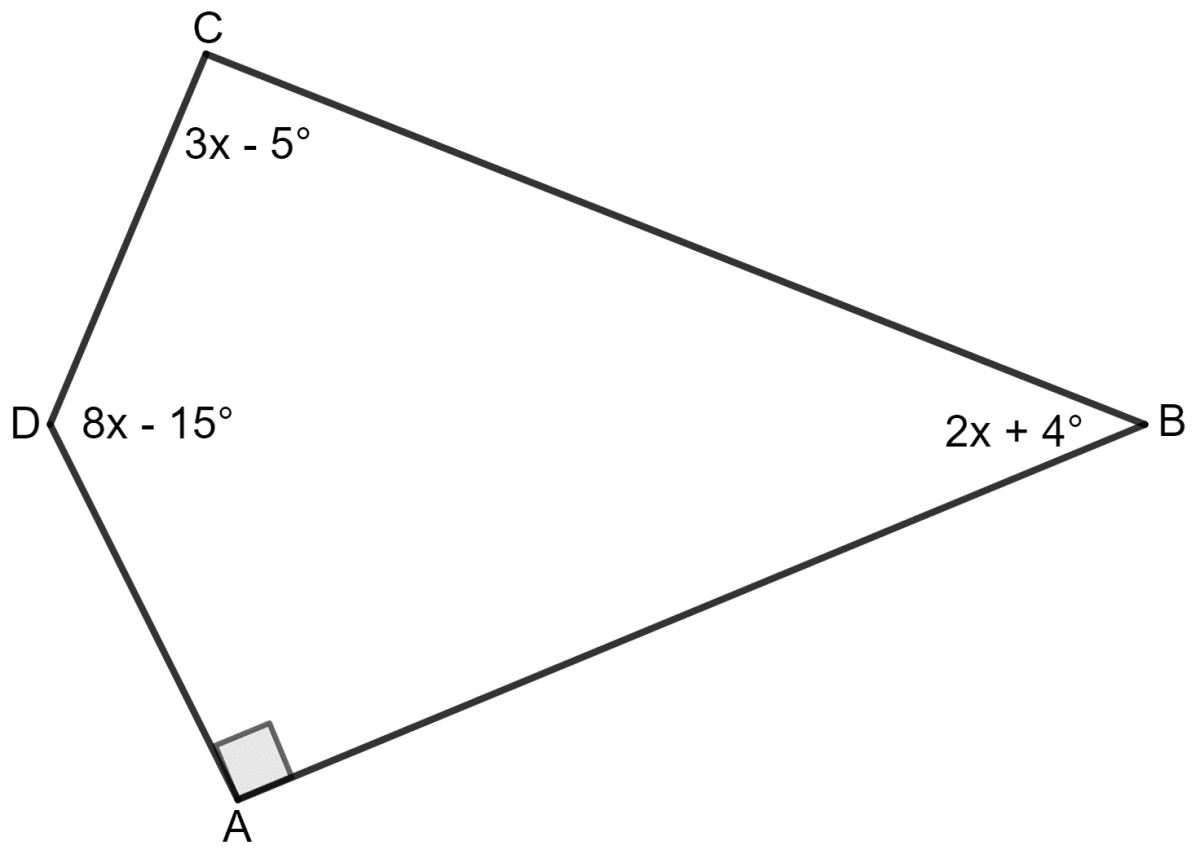
(i) x.
(ii) ∠B and ∠C.