Mathematics
AD is drawn perpendicular to base BC of an equilateral triangle ABC. Given BC = 10 cm, find the length of AD, correct to 1 place of decimal.
Pythagoras Theorem
37 Likes
Answer
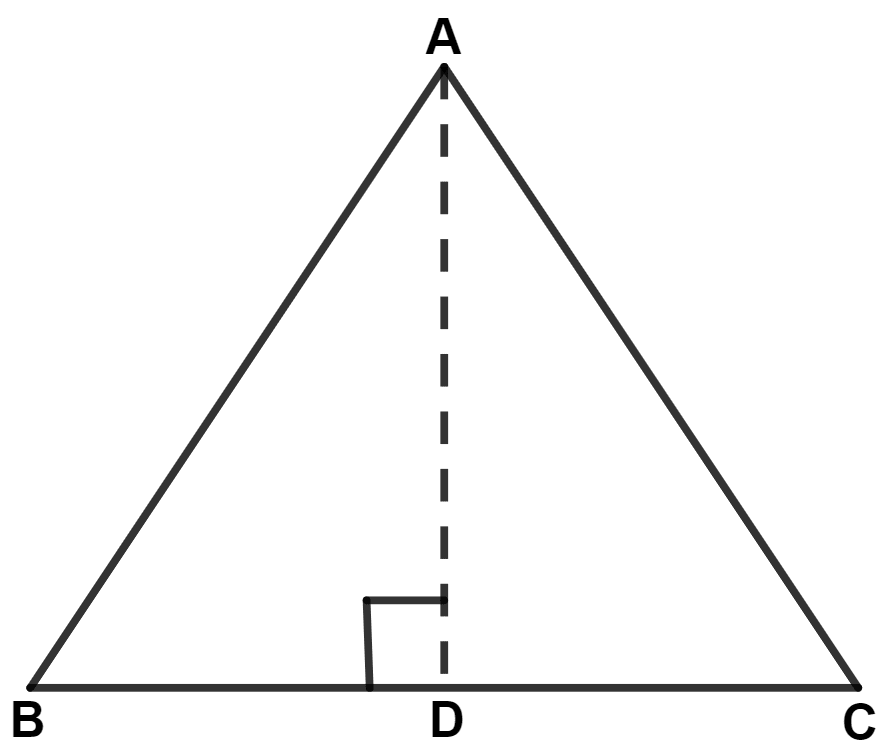
In △ ABD and △ ACD,
⇒ ∠ADB = ∠ADC (Both equal to 90°)
⇒ AD = AD (Common side)
⇒ AB = AC (Since, ABC is an equilateral triangle)
∴ △ ABD ≅ △ ACD (By S.A.S. axiom)
We know that,
Corresponding parts of congruent triangle are equal.
∴ BD = CD = = 5 cm.
In right-angled triangle ABD,
By pythagoras theorem,
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2 = (Perpendicular)2 + (Base)2
⇒ AB2 = AD2 + BD2
⇒ 102 = AD2 + 52
⇒ AD2 = 102 - 52
⇒ AD2 = 100 - 25
⇒ AD2 = 75
⇒ AD = = 8.7 cm.
Hence, AD = 8.7 cm.
Answered By
26 Likes
Related Questions
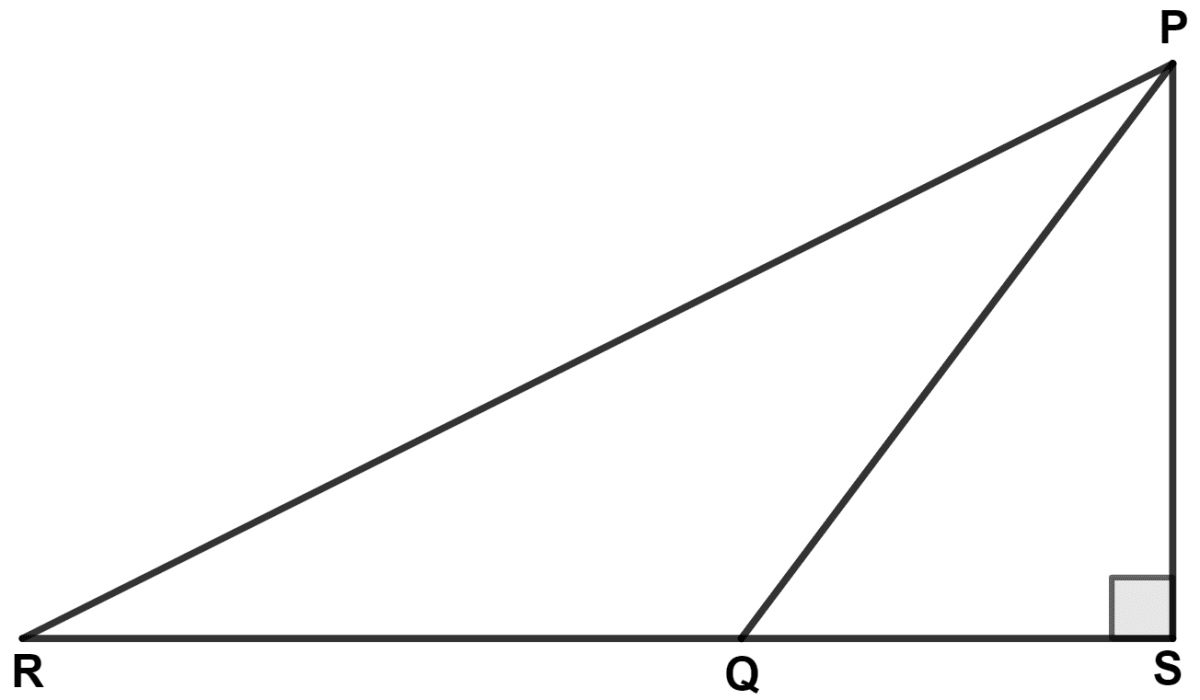
In the figure : ∠PSQ = 90°, PQ = 10 cm, QS = 6 cm and RQ = 9 cm. Calculate the length of PR.
In a quadrilateral PQRS, ∠Q = ∠S = 90° then prove that 2PR2 - QR2 = PQ2 + PS2 + SR2.
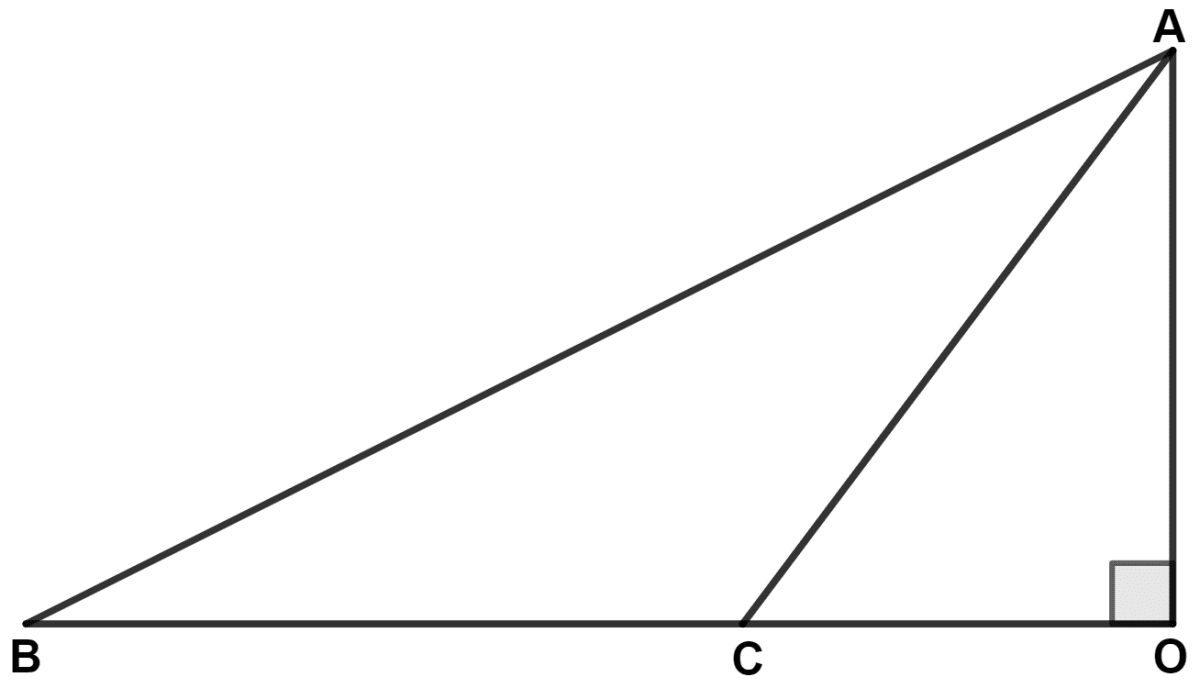
In triangle ABC, given below, AB = 8 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 3 cm. Calculate the length of OC.
In triangle ABC,
AB = AC = x; BC = 10 cm and the area of the triangle is 60 cm2. Find x.