Chemistry
(a) State Charles' law.
(b) Give its
(i) Graphical representation,
(ii) mathematical expression and
(iii) Significance.
Gas Laws
30 Likes
Answer
(a) Charles law states that pressure remaining constant, the volume of a given mass of dry gas increases or decreases by of its volume at 0°C for each 1°C increase or decrease in temperature, respectively.
(b) (i) Graphical representation of Charles' law : The relationship between the volume and the temperature of a gas can be plotted on a graph. A straight line is obtained.
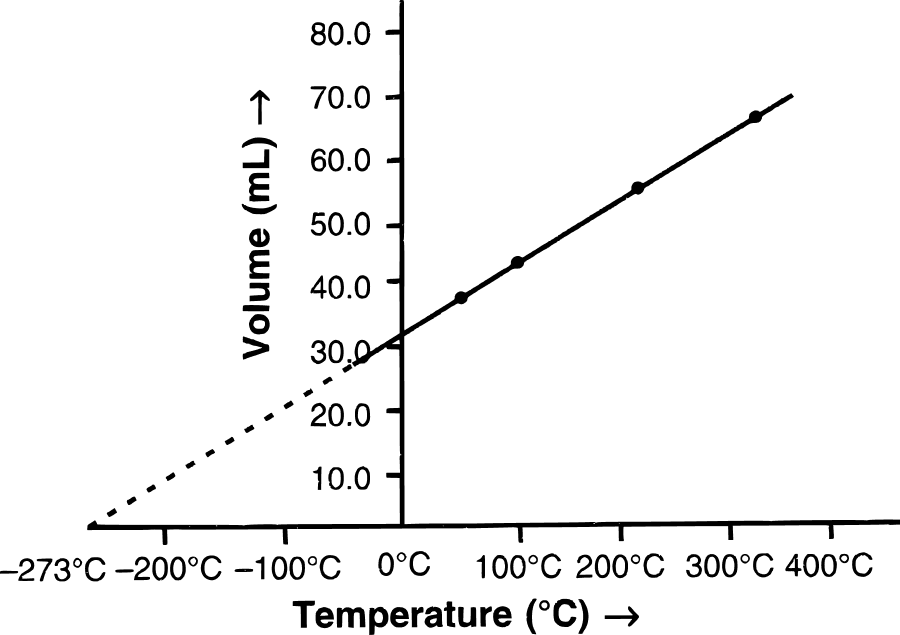
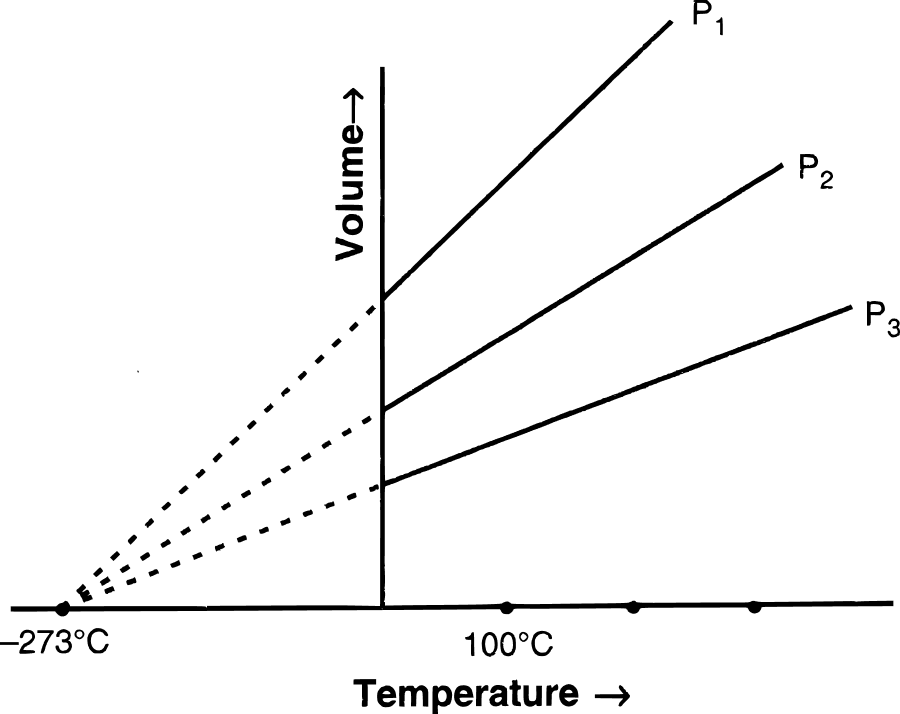
(ii) Mathematical expression of Charles' law :
Suppose, a gas occupies V1 cm3 at T1 temperature and V2 cm3 at T2 temperature, then by Charles' law:
V1 α T1
or V1 = kT1 (k is constant)
or = k and
V2 α T2
or = k
∴ = = k (at constant pressure)
(iii) Significance of Charles' Law :
Volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, hence, density decreases with an increase in temperature.
Answered By
20 Likes
Related Questions
How did Charles' law lead to the concept of an absolute scale of temperature?
(a) State Boyle's Law.
(b) Give its
(i) mathematical expression,
(ii) graphical representation and
(iii) significance.
What is meant by aqueous tension? How is the pressure exerted by a gas corrected to account for aqueous tension?
During the chemistry practical when hydrogen sulphide gas having offensive odour is prepared for some test in the laboratory, we can smell the gas from even 50 metres away. Explain the phenomenon.