Java Number Programs (ICSE Classes 9 / 10)
A special two-digit number is such that when the sum of its digits is added to the product of its digits, the result is equal to the original two-digit number.
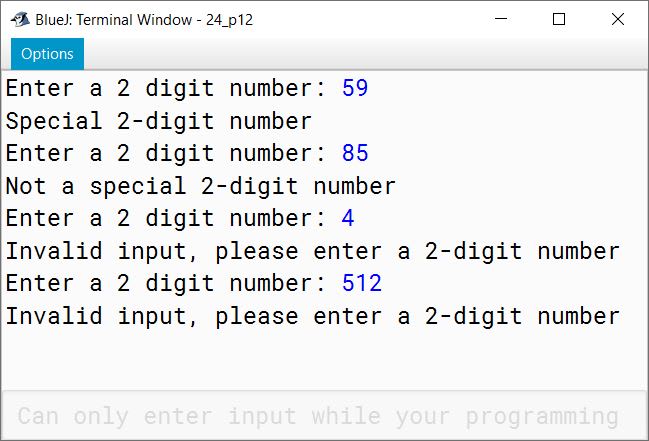
Example: Consider the number 59.
Sum of digits = 5 + 9 = 14
Product of digits = 5 * 9 = 45
Sum of the sum of digits and product of digits = 14 + 45 = 59
Write a program to accept a two-digit number. Add the sum of its digits to the product of its digits. If the value is equal to the number input, then display the message "Special two—digit number" otherwise, display the message "Not a special two-digit number".
Java
Java Iterative Stmts
ICSE 2014
295 Likes
Answer
import java.util.Scanner;
public class KboatSpecialNumber
{
public void checkNumber() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a 2 digit number: ");
int orgNum = in.nextInt();
int num = orgNum;
int count = 0, digitSum = 0, digitProduct = 1;
while (num != 0) {
int digit = num % 10;
num /= 10;
digitSum += digit;
digitProduct *= digit;
count++;
}
if (count != 2)
System.out.println("Invalid input, please enter a 2-digit number");
else if ((digitSum + digitProduct) == orgNum)
System.out.println("Special 2-digit number");
else
System.out.println("Not a special 2-digit number");
}
}Variable Description Table
Program Explanation
Output
Answered By
114 Likes