Physics
A boy uses monochromatic green light to find the refractive index. When a ray of monochromatic green light enters in a liquid medium from air medium as shown in the figure given below, the angle 1 is 45° and angle 2 is 30°.
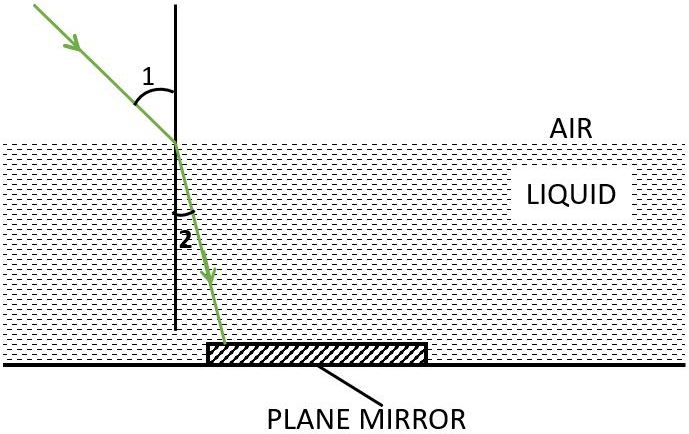
(a) Determine the refractive index of the liquid.
(b) Represent in the diagram showing the path of the ray after it strikes the mirror and re-enters air. Mark in the diagram wherever necessary.
(c) Draw the diagram again, if plane mirror becomes normal to the refracted ray inside the liquid. Name the principle used.
Refraction Plane Surfaces
4 Likes
Answer
(a) Refractive index of the liquid is given by Snell's law and is shown as below,
airμliquid =
airμliquid =
Hence, the refractive index of the lens is 1.4
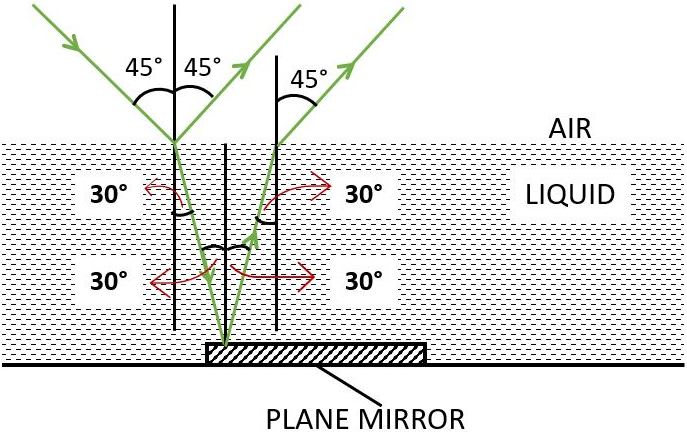
(b) Below labelled diagram shows the path of the ray after it strikes the mirror and re-enters in air:
(c) Below labelled diagram shows the path of the ray when it strikes the plane mirror normally inside the liquid:
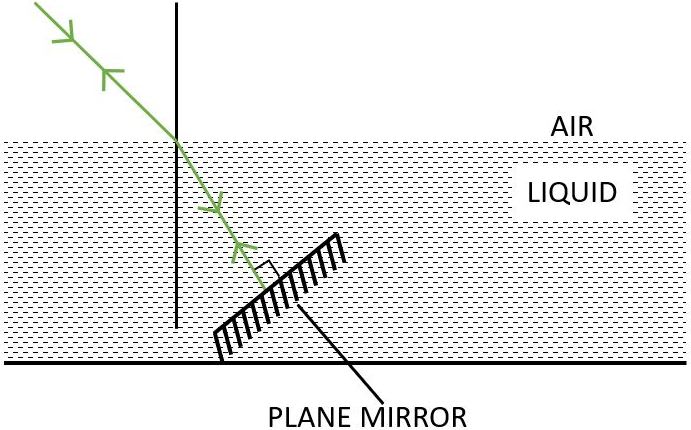
The principle of reversibility is used.
Answered By
3 Likes
Related Questions
If a light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it, so on changing the temperature of the liquid, at a particular temperature, the glass piece is not seen.
(a) At what situation, the glass piece will not be seen?
(b) Why the light of a single colour is used?
(c) How can you define the term refractive index of a medium? State whether it can be less than 1 or not.
(a) Mention one difference between reflection of light from a plane mirror and total internal reflection of light from a prism.
(b) When an empty test tube is placed in a beaker of water and viewed from above, its surface appears as a mirror. Explain.
(a) Define power of a lens.
(b) A child is using a spectacle with power of -2.5D. What is meant by the negative sign?
(c) Find the focal length of the lens used.
The diagram given below shows a lens as combination of glass prisms of different refractive indices. Copy the diagram and answer the following questions.

(a) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(b) Complete the ray diagram when AB is between optical centre and 2F.