The Loops of Henle lie in
- Renal Cortex
- Renal Medulla
- Renal Pelvis
- Renal Artery
Answer
Renal Medulla
Reason — The Loops of Henle are structures within the kidneys that extend into the renal medulla.
The antiseptic present in tears:
- Iodine
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Lysozyme
- Lysosome
Answer
Lysozyme
Reason — Lysozyme is an enzyme that plays a role in the immune system, particularly in defense against bacterial infections.
Assertion (A) : The foetus respires but does not breathe.
Reason (R): The maternal blood supplies oxygen to the foetus through placenta.
- A is True and R is False
- A is False and R is True
- Both A and R are True
- Both A and R are False
Answer
Both A and R are True
Reason — Respiration refers to the metabolic process by which cells break down nutrients (such as glucose) to produce energy, usually in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The foetus obtains oxygen and nutrients from the mother through the placenta.
During ventricular systole, the atrioventricular valves (P) ............... and semilunar valves (Q) ............... .
- P-close, Q-open
- P-close, Q-close
- P-open, Q-close
- P-open, Q-open
Answer
P-close, Q-open
Reason — During ventricular systole, which is the phase of the cardiac cycle when the ventricles contract to pump blood out of the heart, the atrioventricular valves (P) closes and semilunar valves (Q) opens.
The two cerebral hemispheres are joined by a sheet of fibres called:
- Pons
- Corpus luteum
- Hypothalamus
- Corpus callosum
Answer
Corpus callosum
Reason — The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that connects the two cerebral hemispheres of the brain. It facilitates communication between the left and right hemispheres.
The onset of menstruation in a human female is called:
- Menopause
- Menarche
- Ovulation
- Oogenesis
Answer
Menarche
Reason — Menarche refers to the first occurrence of menstruation in girls, marking the onset of puberty and reproductive maturity.
Assertion (A): Rods and Cones are photoreceptors in the sclera of eyeball.
Reason (R): Rods are sensitive to dim light.
- A is True and R is False.
- A is False and R is True.
- Both A and R are True.
- Both A and R are False.
Answer
A is False and R is True
Reason — Rods and cones are located in the retina, not the sclera.
Priya tried to match the hormones with their effect on the human body. She tabulated the pairs as follows:
| Hormone | Effect on the body |
|---|---|
| P | Stimulates conversion of Glycogen to Glucose |
| Q | Reabsorption of water by the Nephrons. |
Identify the correct pair of hormones.
- P- Insulin, Q- Glucagon
- P- Adrenaline, Q- Oxytocin
- P- Glucagon, Q- Vasopressin
- P- Vasopressin, Q- Adrenaline
Answer
P- Glucagon, Q- Vasopressin
Reason — Glucagon is a hormone produced by the pancreas that stimulates the conversion of glycogen (stored form of glucose in the liver) to glucose. Vasopressin, also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), is produced by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. It acts on the kidney increasing reabsorption of water by the nephrons.
While studying the stages in the evolution of man, a well-developed chin is observed in
- Homo habilis
- Homo erectus
- Homo sapiens
- Australopithecus
Answer
Homo sapiens
Reason — A well-developed chin is a characteristic feature observed in Homo sapiens.
A pair of corresponding chromosomes of the same shape, size and one from each parent is called:
- Autosomes
- Allosomes
- Analogous chromosomes
- Homologous chromosomes
Answer
Homologous chromosomes
Reason — Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that have the same genes at the same loci.
Assertion (A): We urinate more in summer.
Reason (R): Sweat glands are more active in summer.
- A is True and R is False
- A is False and R is True
- Both A and R are True
- Both A and R are False
Answer
A is False and R is True
Reason — Urine output is less in summers as most of the water is lost in form of sweat.
Rahul inserted a hairpin into his right ear to remove ear wax. He felt a sudden sharp pain with loss of hearing. This was due to:
- Rupture of eardrum
- Rupture of vestibule
- Rupture of cornea
- Rupture of pinna
Answer
Rupture of eardrum
Reason — Rupture of the eardrum, also known as tympanic membrane perforation, is a condition where there is a tear or hole in the thin membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear.
Assertion (A): All food chains begin with herbivores.
Reason (R): Green plants are heterotrophs.
- A is True and R is False
- A is False and R is True
- Both A and R are True
- Both A and R are False
Answer
Both A and R are False
Reason — All food chains begin with producers i.e., green plants.
A biology teacher asked her students to give two examples of vestigial organs in the human body.
Raj said: Wisdom teeth and Pinna
Sonu said: Body hair and large intestine
Lata said: Vermiform appendix and wisdom teeth
Abhay said: Pinna and Ossicles
Who were correct?
- Abhay and Sonu
- Sonu and Lata
- Raj and Lata
- Abhay and Raj
Answer
Raj and Lata
Reason — Wisdom teeth, Pinna and Vermiform appendix are vestigial organs whereas large intestine, ossicles and body hairs perform important functions in human body, hence, are not vestigial organs.
During a practical exam, a plant cell in a particular solution was placed under a compound microscope. Students were told to observe the cell and name the tonicity of the solution and mention the process that occurred in the cell.
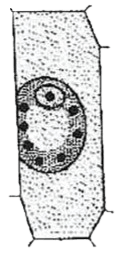
- Isotonic, Endosmosis
- Hypotonic, Active Transport
- Hypertonic, Endosmosis
- Hypertonic, Exosmosis
Answer
Hypertonic, Exosmosis
Reason — If the solution is hypertonic, exosmosis occurs i.e., the sap moves outward from the cell to the solution. This outward movement of cell sap leads to shrinking of cell.
Name the following:
(a) The basic units of heredity.
(b) The undesirable change in the environment leading to its deterioration.
(c) The structure that connects placenta and the human foetus.
(d) The statistical study of human population.
(e) The nitrogenous base that pairs with adenine.
Answer
(a) Genes
(b) Pollution
(c) Umbilical Cord
(d) Demography
(e) Thymine
Given below is the transverse section of the spinal cord. Read the information below the diagram and fill in the blanks:

The spinal cord extends from the medulla oblongata of the brain and runs down through the whole length of the vertebral column. The spinal cord is covered by the meninges. It conducts impulses from the skin and muscles to the brain. It also conducts impulses from the brain to the muscles of the trunk and limbs.
The spinal cord is a part of the (a) ............... Nervous System. The grey matter in the picture given above consists of (b) ............... while the white matter consists of (c) ............... . The spinal cord is concerned with the (d) ............... actions below the neck. (e) ............... is the bony structure that protects the spinal cord.
Answer
The spinal cord is a part of the (a) Central Nervous System. The grey matter in the picture given above consists of (b) cytons while the white matter consists of (c) axons. The spinal cord is concerned with the (d) reflex actions below the neck. (e) Vertebral column is the bony structure that protects the spinal cord.
Arrange and rewrite the terms in each group in the correct order so as to be in a logical sequence beginning with the term that is underlined.
(a) Apical meristem, Positive phototropism, Auxins, Cell elongation.
(b) Urethra, Urinary bladder, Ureter, Kidney.
(c) Auditory canal, Organ of Corti, Stapes, Malleus.
(d) Cell membrane, Chromatin fibres, Cell wall, Cytoplasm.
(e) Lungs, Right auricle, Inferior venacava, Pulmonary Artery.
Answer
(a) Auxins, Apical meristem, Cell elongation, Positive phototropism
(b) Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder, Urethra
(c) Auditory canal, Malleus, Stapes, Organ of Corti
(d) Chromatin fibres, Cytoplasm, Cell membrane, Cell wall
(e) Inferior venacava, Right auricle, Pulmonary Artery, Lungs
Read the explanations given below and name the structure:
Example: The largest gland in the human body that secretes bile.
Answer: Liver.
(a) Food conducting tissue in vascular plants.
(b) A cell formed by the fusion of gametes.
(c) The smallest blood vessels in the human body.
(d) A tubular passage that connects the pharynx and the middle ear.
(e) The openings on the barks of trees through which transpiration occurs.
Answer
(a) Phloem
(b) Zygote
(c) Capillaries
(d) Eustachian Tube
(e) Lenticels
Given below is a cross section of the human eye. Match the structures marked (a) to (e) with their correct functions:
Example: (f) - 6. Holds the lens in position
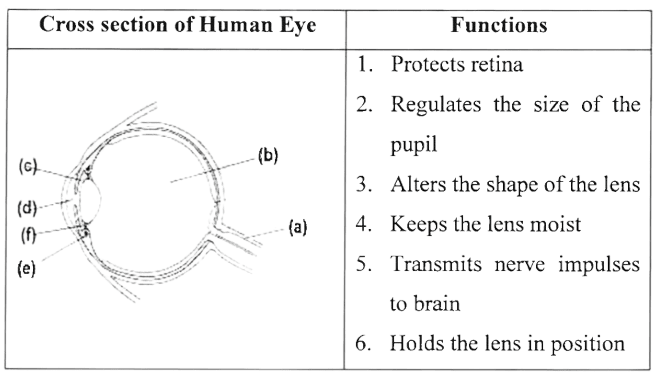
Answer
(a) - 5. Transmits nerve impulses to brain
(b) - 1. Protects retina
(c) - 2. Regulates the size of the pupil
(d) - 4. Keeps the lens moist
(e) - 3. Alters the shape of the lens
Explain the term — Active transport.
Answer
Active transport is the passage of a substance (salt or ion) from its lower to higher concentration through a living cell membrane using energy from the cell.
Name the structures through which Transpiration and Guttation occur in a plant.
Answer
Transpiration occurs through stomata, lenticel and cuticle. Guttation occurs through hydathodes.
How does the rate of Transpiration differ when there is :
(a) High temperature
(b) High humidity
Answer
(a) High temperature — The rate of transpiration increases with increase in temperature.
(b) High humidity — The rate of transpiration decreases with increase in humidity.
Write the overall chemical equation for Photosynthesis.
Answer
Sam observed a slide containing the lower epidermis of a leaf under a microscope. A number of tiny openings between the epidermal cells were present as shown below in the diagram:

(a) What are these tiny openings called?
(b) Name the cells that regulate the opening and closing of the structures.
(c) Which ion is responsible for the opening and closing of the openings?
Answer
(a) Stomata
(b) Guard cells
(c) Potassium ions
Why is Adrenaline called ‘The Emergency Hormone"?
Answer
Adrenaline is known as the Emergency hormone because it prepares the body to meet any emergency situation, for "fight" i.e. to face danger or for "flight" i.e. to run away from it. Extra energy and strength is provided to the body in that situation. It stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. When excited or angry, the adrenal medulla produces a lot of Adrenaline preparing the body for any emergency.
Expand the abbreviation — ADH. Give one example of a diuretic substance.
Answer
ADH stands for Antidiuretic Hormone. One example of a diuretic substance is caffeine.
Mention the significance of the following minerals:
(a) Iodine in our food.
(b) Magnesium for green plants.
Answer
(a) Iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroxine by thyroid gland.
(b) Magnesium is required for the synthesis of chlorophyll.
State two objectives of Swachh Bharat Abhiyan.
Answer
Two objectives of Swachh Bharat Abhiyan are:
- To eliminate open defecation: The mission aims to ensure that all households have access to toilets and promote the construction and use of sanitary latrines.
- To promote cleanliness and hygiene: It seeks to create awareness about sanitation and cleanliness practices, improve waste management systems, and maintain cleanliness in public spaces.
Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a root hair.
Answer
Labelled diagram of a root hair is given below:

Mention one characteristic of roots for absorbing water from the soil.
Answer
One characteristic of roots for absorbing water from the soil is presence of thin cell walls in root hairs. This allows easy entry of water in the root hairs from the soil.
What is Parthenocarpy? Give one example.
Answer
Parthenocarpy is a phenomenon in plants where fruits develop without fertilization of ovules. In other words, fruits are formed without the need for pollination and fertilization. One example of a parthenocarpic fruit is the banana.
State the difference between Micturition and Parturition.
Answer
| Micturition | Parturition |
|---|---|
| Micturition refers to the process of urination, which is the expulsion of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. | Parturition refers to the expulsion of the fully developed foetus from the uterus at the end of gestation. |
Write any two functions of Lymph.
Answer
The two key functions of lymph are:
- It drains excess tissue fluid into blood.
- Fats from the intestine are absorbed through lymphatics.
Study the picture given below and answer the questions:

(a) How does water get polluted?
(b) What is the effect of water pollution on human life?
(c) Mention one control measure to stop the pollution of water bodies.
Answer
(a) Water gets polluted due to:
- Factories and industrial facilities releasing pollutants such as chemicals, heavy metals, and toxins into water bodies.
- Pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers used in agriculture can wash into rivers, lakes, and streams through runoff, especially after heavy rainfall.
(b) Contaminated water can carry pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites that cause waterborne diseases like cholera, dysentery, hepatitis A, and giardiasis. Long-term exposure to polluted water containing harmful chemicals, such as heavy metals (e.g., lead, mercury) and industrial pollutants, can result in chronic health issues.
(c) By ensuring that all industrial, agricultural, and municipal wastewater is properly treated before being released into water bodies, harmful pollutants and contaminants can be significantly reduced.
State Mendel’s Law of Segregation
Answer
During the formation of gametes (sperm or eggs), the two alleles for a given gene separate, or segregate, so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene. When gametes fuse during fertilization, the resulting offspring inherits one allele from each parent, restoring the diploid number of alleles for that gene.
What are Tropic hormones? Give one example.
Answer
Tropic hormones are hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands to produce and release their hormones. They act on target glands rather than directly on tissues or organs. Tropic hormones play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes by controlling the activity of other endocrine glands. For example: TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) activates thyroid to secrete thyroxin.
Differentiate between the terms Phenotype and Genotype.
Answer
| Phenotype | Genotype |
|---|---|
| The phenotype is the observable physical or physiological traits of an organism resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. | The genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, specifically the alleles or combinations of alleles it possesses for a particular gene or set of genes. |
| It represents the underlying genetic code that contributes to an organism’s traits. | It represents how the genetic information is expressed in the organism. |
What is the significance of Testes being placed in Scrotal sacs?
Answer
Testes are responsible for the production of male gametes i.e., sperms. The normal body temperature does not allow the maturation of the sperms. Being suspended outside the body cavity, the temperature in the scrotal sac is 2 to 3°C lower than that of the body which is the suitable temperature for the maturation of the sperms.
Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a human sperm.
Answer
Labelled diagram of a human sperm is shown below:

What is the scientific name of the pea plant that Mendel used for his experiments?
Answer
Pisum Sativum
Mention the surgical methods of contraception in:
(a) Men
(b) Women
Answer
(a) Men - Vasectomy
(b) Women - Tubectomy
Name two harmful effects of noise pollution.
Answer
Two harmful effects of noise pollution are:
- Disturbs sleep.
- Interrupts concentration of thoughts
Which parts of a plant exhibit:
(a) Negative Geotropism
(b) Positive Hydrotropism
Answer
(a) Negative Geotropism - Shoot
(b) Positive Hydrotropism - Root
Kathak is an Indian classical dance which involves a lot of spinning by the dancers. The learners of this dance experience dizziness in the beginning while spinning.

(a) Name the part of the membranous labyrinth responsible for this dizziness.
(b) Give a suitable reason for your answer.
(c) Mention the nerve that carries the impulse for dizziness to the brain.
Answer
(a) Semicircular canal
(b) The fluid in the semi-circular canals continue to spin for a short time even after the dancer stops. This results in dizziness.
(c) Auditory nerve
How does Transpiration help in the uptake of water from the soil?
Answer
Transpiration is the process by which water is lost from the plant, primarily through small openings called stomata on the leaves. As water evaporates from the leaf surfaces, it creates a negative pressure (or suction) within the leaf's xylem vessels. This negative pressure in the leaf creates a "suction effect" that pulls water upward from the roots through the xylem vessels.
Given below are two statements which are incorrect. Rewrite the correct Statements:
(a) Fresh water fish when placed in hypertonic salt solution absorb water and burst.
(b) Seminiferous tubules secrete Testosterone.
Answer
(a) Freshwater fish when placed in a hypertonic salt solution lose water and may shrink.
(b) Seminiferous tubules are involved in the production of sperm, while testosterone is secreted by the interstitial cells (Leydig cells) in the testes.
During Mitosis what is the position of chromatids in:
(a) Metaphase
(b) Anaphase
Answer
(a) Metaphase - In the equatorial plane.
(b) Anaphase - Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles.
Chris was watching the display of fireworks in the sky.

(a) Trace the path of the light rays using the following terms:
Fovea, Lens, Conjunctiva, Pupil, Cornea
(b) Name the nerve that carries the impulse for vision to the brain.
Answer
(a) Conjunctiva → Cornea → Pupil → Lens → Fovea
(b) Optic Nerve.
Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a Malpighian Capsule.
Answer
Below labelled diagram shows Malpighian Capsule:
