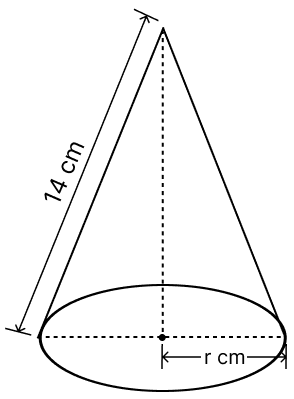
Diameter of the base of a cone is 10.5 cm and its slant height is 10 cm. Find its curved surface area.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of cone (d) = 10.5 cm
Slant height of cone (l) = 10 cm
By formula,
Radius of cone (r) = Diameter 2 = 10.5 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{10.5}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 10.5
By formula,
Curved surface area of cone (C.S.A.) = πrl
Substituting values we get :
C.S.A. = 22 7 × 5.25 × 10 = 1155 7 = 165 cm 2 \text{C.S.A.} = \dfrac{22}{7} × 5.25 × 10 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1155}{7} \\[1em] = 165 \text{ cm}^2 C.S.A. = 7 22 × 5.25 × 10 = 7 1155 = 165 cm 2
Hence, curved surface area of the cone = 165 cm2 .
Find the total surface area of a cone, if its slant height is 21 m and diameter of its base is 24 m.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of cone (d) = 24 m
Radius of cone (r) = Diameter 2 = 24 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{24}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 24
Slant height of the cone (l) = 21 m
Total surface area of the cone = Curved surface area of cone + area of the base
By formula,
Total surface area of the cone (T.S.A.) = πrl + πr2 = πr(l + r)
Susbtituting values we get :
= 22 7 × 12 × ( 12 + 21 ) = 22 7 × 12 × 33 = 8712 7 = 1244.57 m 2 = \dfrac{22}{7} \times 12 \times (12 + 21) \\[1em] = \dfrac{22}{7} \times 12 \times 33 \\[1em] = \dfrac{8712}{7} \\[1em] = 1244.57 \text{ m}^2 = 7 22 × 12 × ( 12 + 21 ) = 7 22 × 12 × 33 = 7 8712 = 1244.57 m 2
Hence, total surface area of the cone = 1244.57 m2 .
Curved surface area of a cone is 308 cm2 and its slant height is 14 cm. Find
(i) radius of the base and
(ii) total surface area of the cone.
Answer
(i) Let the radius be r cm.
Given,
Curved surface area of cone = 308 cm2
⇒ π r l = 308 ⇒ r = 308 π l ⇒ r = 308 22 7 × 14 ⇒ r = 308 22 × 2 ⇒ r = 308 44 ⇒ r = 7 cm \Rightarrow πrl = 308 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{308}{πl} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{308}{\dfrac{22}{7} \times 14} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{308}{22 \times 2} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{308}{44} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = 7 \text{ cm} ⇒ π r l = 308 ⇒ r = π l 308 ⇒ r = 7 22 × 14 308 ⇒ r = 22 × 2 308 ⇒ r = 44 308 ⇒ r = 7 cm
Hence, radius of the base of cone = 7 cm.
(ii) By formula,
Total surface area of cone (T.S.A.) = πr(l + r)
Substituting values we get :
T.S.A. = 22 7 \dfrac{22}{7} 7 22
= 22 7 \dfrac{22}{7} 7 22
= 22 × 21
= 462 cm2 .
Hence, the total surface area of the cone is 462 cm2 .
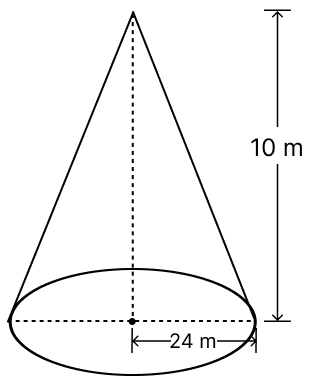
A conical tent is 10 m high and the radius of its base is 24 m. Find
(i) slant height of the tent.
(ii) cost of the canvas required to make the tent, if the cost of 1 m2 canvas is ₹ 70.
Answer
(i) Given,
Radius of conical tent (r) = 24 m
Height of conical tent (h) = 10 m
By formula,
Slant height of conical tent (l) = r 2 + h 2 \sqrt{r^2 + h^2} r 2 + h 2
Substituting values we get :
l = ( 24 ) 2 + ( 10 ) 2 = 576 + 100 = 676 = 26 m l = \sqrt{(24)^2 + (10)^2} \\[1em] = \sqrt{576 + 100} \\[1em] = \sqrt{676} = 26 \text{ m} l = ( 24 ) 2 + ( 10 ) 2 = 576 + 100 = 676 = 26 m
Hence, slant height of the conical tent is 26 m.
(ii) Given,
Curved surface area of the cone = πrl
= 22 7 \dfrac{22}{7} 7 22
= 13728 7 \dfrac{13728}{7} 7 13728 2
The cost of the canvas required to make the tent, at ₹ 70 per m2 = Curved surface area of the cone x ₹ 70
= 13728 7 \dfrac{13728}{7} 7 13728
= ₹ 137280.
Hence, the cost of the canvas is ₹ 137280.
What length of tarpaulin 3 m wide will be required to make conical tent of height 8 m and base radius 6 m? Assume that the extra length of material that will be required for stitching margins and wastage in cutting is approximately 20 cm (Use π = 3.14).
Answer
Given,
Height of tent (h) = 8 m
Radius of tent (r) = 6 m
By formula,
Slant height of tent (l) = r 2 + h 2 \sqrt{r^2 + h^2} r 2 + h 2
Substituting values we get :
l = ( 6 ) 2 + ( 8 ) 2 = 36 + 64 = 100 = 10 m . l = \sqrt{(6)^2 + (8)^2} \\[1em] = \sqrt{36 + 64} \\[1em] = \sqrt{100} = 10 m. l = ( 6 ) 2 + ( 8 ) 2 = 36 + 64 = 100 = 10 m .
By formula,
Curved surface area of cone = πrl
= 3.14 × 6 m × 10 m
= 188.4 m2 .
Area of tarpaulin used to make tent will be equal to curved surface area of tent.
So,
Area of the tarpaulin = Width of the tarpaulin × Length of the tarpaulin
⇒ 188.4 = 3 × length of the tarpaulin
⇒ Length of the tarpaulin = 188.4 3 \dfrac{188.4}{3} 3 188.4
Extra length of the material = 20 cm = 20 100 \dfrac{20}{100} 100 20
Total length required = 62.8 m + 0.2 m = 63 m.
Hence, the required length of the tarpaulin is 63 m.
The slant height and base diameter of a conical tomb are 25 m and 14 m respectively. Find the cost of white-washing its curved surface at the rate of ₹ 210 per 100 m2 .
Answer
Given,
Diameter of conical tomb (d) = 14 m
Radius of conical tomb (r) = Diameter 2 = 14 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{14}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 14
Slant height of conical tomb (l) = 25 m
By formula,
Curved surface area of conical tomb = πrl
= 22 7 \dfrac{22}{7} 7 22
= 550 m2 .
Given,
Cost of white-washing 100 m2 area = ₹ 210
Cost of white-washing 550 m2 area = ₹ 210 × 550 100 210 \times \dfrac{550}{100} 210 × 100 550
Hence, the cost of white-washing the conical tomb is ₹ 1155.
A joker’s cap is in the form of a right circular cone of base radius 7 cm and height 24 cm. Find the area of the sheet required to make 10 such caps.
Answer
Given,
Radius of conical cap (r) = 7 cm
Height of conical cap (h) = 24 cm
By formula,
Slant height of conical cap (l) = r 2 + h 2 \sqrt{r^2 + h^2} r 2 + h 2
Substituting values we get :
l = ( 7 ) 2 + ( 24 ) 2 = 49 + 576 = 625 = 25 cm . l = \sqrt{(7)^2 + (24)^2} \\[1em] = \sqrt{49 + 576} \\[1em] = \sqrt{625} = 25 \text{ cm}. l = ( 7 ) 2 + ( 24 ) 2 = 49 + 576 = 625 = 25 cm .
By formula,
Curved surface area of one conical cap = πrl
= 22 7 \dfrac{22}{7} 7 22
= 3850 7 \dfrac{3850}{7} 7 3850
= 550 cm2
Curved surface area of 10 such conical caps = 10 × 550 cm2 = 5500 cm2 .
Hence, area of sheet required for making 10 caps = 5500 cm2 .
A bus stop is barricaded from the remaining part of the road, by using 50 hollow cones made of recycled cardboard. Each cone has a base diameter of 40 cm and height 1 m. If the outer side of each of the cones is to be painted and the cost of painting is ₹ 12 per m2 , what will be the cost of painting all these cones? (Use π = 3.14 and take 1.04 \sqrt{1.04} 1.04
Answer
Given,
Diameter of cone (d) = 40 cm = 40 100 \dfrac{40}{100} 100 40
Radius of cone (r) = Diameter 2 = 0.4 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{0.4}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 0.4
Height of cone (h) = 1 m
Slant height of cone (l) = r 2 + h 2 \sqrt{r^2 + h^2} r 2 + h 2
Substituting values we get :
l = ( 0.2 ) 2 + ( 1 ) 2 = 0.04 + 1 = 1.04 = 1.02 m . l = \sqrt{(0.2)^2 + (1)^2} \\[1em] = \sqrt{0.04 + 1} \\[1em] = \sqrt{1.04} = 1.02 \text{ m}. l = ( 0.2 ) 2 + ( 1 ) 2 = 0.04 + 1 = 1.04 = 1.02 m .
By formula,
Curved surface area of each cone = πrl
= 3.14 × 0.2 m × 1.02 m
= 0.64056 m2
Curved surface area of 50 cones = 50 × 0.64056 m2 = 32.028 m2 .
Given,
Cost of painting = ₹ 12 per m2 .
Cost of painting of 32.028 m2 area = ₹ (32.028 × 12)
= ₹ 384.34 (approx.)
Hence, the cost of painting 50 such hollow cones = ₹ 384.34 (approx.)
Find the surface area of a sphere of radius 10.5 cm.
Answer
Given,
Radius of sphere (r) = 10.5 cm
By formula,
Surface area of the sphere (A) = 4πr2
Substituting values we get :
A = 4 × 22 7 × ( 10.5 ) 2 = 4 × 22 7 × 10.5 × 10.5 = 4 × 22 × 1.5 × 10.5 = 1386 cm 2 . A = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (10.5)^2 \\[1em] = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 10.5 \times 10.5 \\[1em] = 4 \times 22 \times 1.5 \times 10.5 \\[1em] = 1386 \text{ cm}^2. A = 4 × 7 22 × ( 10.5 ) 2 = 4 × 7 22 × 10.5 × 10.5 = 4 × 22 × 1.5 × 10.5 = 1386 cm 2 .
Hence, surface area of the sphere = 1386 cm2 .
Find the surface area of a sphere of radius 5.6 cm.
Answer
Given,
Radius of sphere (r) = 5.6 cm
By formula,
Surface area of the sphere (A) = 4πr2
Substituting values we get :
A = 4 × 22 7 × ( 5.6 ) 2 = 4 × 22 7 × 5.6 × 5.6 = 4 × 22 7 × 31.36 = 4 × 22 × 4.48 = 394.24 cm 2 A = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (5.6)^2 \\[1em] = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 5.6 \times 5.6 \\[1em] = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 31.36 \\[1em] = 4 \times 22 \times 4.48 \\[1em] = 394.24 \text{ cm}^2 A = 4 × 7 22 × ( 5.6 ) 2 = 4 × 7 22 × 5.6 × 5.6 = 4 × 7 22 × 31.36 = 4 × 22 × 4.48 = 394.24 cm 2
Hence, surface area of sphere = 394.24 cm2 .
Find the surface area of a sphere of radius 14 cm.
Answer
Given,
Radius of sphere (r) = 14 cm
By formula,
Surface area of the sphere (A) = 4πr2
Substituting values we get :
A = 4 × 22 7 × ( 14 ) 2 = 4 × 22 7 × 14 × 14 = 4 × 22 7 × 196 = 4 × 22 × 28 = 2464 cm 2 . A = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (14)^2 \\[1em] = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 14 \times 14 \\[1em] = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 196 \\[1em] = 4 \times 22 \times 28 \\[1em] = 2464 \text{ cm}^2. A = 4 × 7 22 × ( 14 ) 2 = 4 × 7 22 × 14 × 14 = 4 × 7 22 × 196 = 4 × 22 × 28 = 2464 cm 2 .
Hence, surface area of sphere = 2464 cm2 .
Find the surface area of a sphere of diameter 14 cm.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of sphere (d) = 14 cm
Radius of sphere (r) = Diameter 2 = 14 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{14}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 14
By formula,
Surface area of a sphere (A) = 4πr2
Substituting values we get :
A = 4 × 22 7 × ( 7 ) 2 = 4 × 22 7 × 7 × 7 = 4 × 22 × 7 = 616 cm 2 . A = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (7)^2 \\[1em] = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 7 \times 7 \\[1em] = 4 \times 22 \times 7 \\[1em] = 616 \text{ cm}^2. A = 4 × 7 22 × ( 7 ) 2 = 4 × 7 22 × 7 × 7 = 4 × 22 × 7 = 616 cm 2 .
Hence, the surface area of a sphere = 616 cm2 .
Find the surface area of a sphere of diameter 21 cm.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of sphere (d) = 21 cm
Radius of sphere (r) = Diameter 2 = 21 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{21}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 21
By formula,
Surface area of a sphere (A) = 4πr2
A = 4 × 22 7 × ( 10.5 ) 2 = 4 × 22 7 × 10.5 × 10.5 = 4 × 22 × 1.5 × 10.5 = 1386 cm 2 . A = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (10.5)^2 \\[1em] = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 10.5 \times 10.5 \\[1em] = 4 \times 22 \times 1.5 \times 10.5 \\[1em] = 1386 \text{ cm}^2. A = 4 × 7 22 × ( 10.5 ) 2 = 4 × 7 22 × 10.5 × 10.5 = 4 × 22 × 1.5 × 10.5 = 1386 cm 2 .
Hence, the surface area of a sphere = 1386 cm2 .
Find the surface area of a sphere of diameter 3.5 m.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of sphere (d) = 3.5 m
Radius of sphere (r) = Diameter 2 = 3.5 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{3.5}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 3.5
By formula,
Surface area of a sphere (A) = 4πr2
Substituting values we get :
A = 4 × 22 7 × ( 1.75 ) 2 = 4 × 22 7 × 1.75 × 1.75 = 4 × 22 × 0.25 × 1.75 = 38.5 m 2 . A = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (1.75)^2 \\[1em] = 4 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 1.75 \times 1.75 \\[1em] = 4 \times 22 \times 0.25 \times 1.75 \\[1em] = 38.5 \text{ m}^2. A = 4 × 7 22 × ( 1.75 ) 2 = 4 × 7 22 × 1.75 × 1.75 = 4 × 22 × 0.25 × 1.75 = 38.5 m 2 .
Hence, the surface area of a sphere = 38.5 m2 .
Find the total surface area of a hemisphere of radius 10 cm. (Use π = 3.14)
Answer
Given,
Radius of the hemisphere (r) = 10 cm
By formula,
Total Surface area of hemisphere (A) = 3πr2
Substituting values we get :
A = 3 × 3.14 × ( 10 ) 2 = 3 × 3.14 × 100 = 942 cm 2 . A = 3 \times 3.14 \times (10)^2 \\[1em] = 3 \times 3.14 \times 100 \\[1em] = 942 \text{ cm}^2. A = 3 × 3.14 × ( 10 ) 2 = 3 × 3.14 × 100 = 942 cm 2 .
Hence, the total surface area of the hemisphere is 942 cm2 .
The radius of a spherical balloon increases from 7 cm to 14 cm as air is being pumped into it. Find the ratio of surface areas of the balloon in the two cases.
Answer
Given,
Radius of the balloon before pumping air (r1 ) = 7 cm
Radius of the balloon after pumping air (r2 ) = 14 cm
Initial surface area = 4πr1 2
Surface area after pumping air into ballon = 4πr2 2
Ratio = Initial surface area Surface area after pumping air into ballon \dfrac{\text{Initial surface area}}{\text{Surface area after pumping air into ballon}} Surface area after pumping air into ballon Initial surface area
= 4 π r 1 2 4 π r 2 2 = r 1 2 r 2 2 = ( r 1 r 2 ) 2 = ( 7 14 ) 2 = ( 1 2 ) 2 = 1 4 = 1 : 4. = \dfrac{4πr_1^2}{4πr_2^2} \\[1em] = \dfrac{r_1^2}{r_2^2} \\[1em] = \Big(\dfrac{r_1}{r_2}\Big)^2 \\[1em] = \Big(\dfrac{7}{14}\Big)^2 \\[1em] = \Big(\dfrac{1}{2}\Big)^2 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{4} \\[1em] = 1 : 4. = 4 π r 2 2 4 π r 1 2 = r 2 2 r 1 2 = ( r 2 r 1 ) 2 = ( 14 7 ) 2 = ( 2 1 ) 2 = 4 1 = 1 : 4.
Hence, the ratio of the surface area of the balloons = 1 : 4.
A hemispherical bowl made of brass has inner diameter 10.5 cm. Find the cost of tin-plating it on the inside at the rate of ₹ 16 per 100 cm2 .
Answer
Given,
Inner diameter of hemispherical bowl (d) = 10.5 cm
Inner radius of hemispherical bowl (r) = Diameter 2 = 10.5 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{10.5}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 10.5
Curved surface area of hemispherical bowl = 2πr2
= 2 × 22 7 × ( 5.25 ) 2 = 2 × 22 7 × 27.5625 = 2 × 22 × 3.9375 = 173.25 cm 2 . = 2 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (5.25)^2 \\[1em] = 2 \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 27.5625 \\[1em] = 2 \times 22 \times 3.9375 \\[1em] = 173.25 \text{ cm}^2. = 2 × 7 22 × ( 5.25 ) 2 = 2 × 7 22 × 27.5625 = 2 × 22 × 3.9375 = 173.25 cm 2 .
Given,
The cost of tin-plating 100 cm2 of the bowl = ₹ 16
∴ The cost of tin-plating 1 cm2 of the bowl = ₹ 16 100 \dfrac{16}{100} 100 16
∴ The cost of tin-plating 173.25 cm2 area of the bowl = ₹ 16 100 × 173.25 \dfrac{16}{100} \times 173.25 100 16 × 173.25
Hence, the cost of tin-plating the hemispherical bowl is ₹ 27.72.
Find the radius of a sphere whose surface area is 154 cm2 .
Answer
Given,
The surface area of the sphere = 154 cm2
∴ 4 π r 2 = 154 ⇒ r 2 = 154 4 π ⇒ r 2 = 154 4 × 22 7 ⇒ r 2 = 154 × 7 4 × 22 ⇒ r 2 = 49 4 ⇒ r = 49 4 ⇒ r = 7 2 = 3.5 cm \therefore 4πr^2 = 154 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{154}{4π} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{154}{4 \times \dfrac{22}{7}} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{154 \times 7}{4 \times 22} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{49}{4} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \sqrt{\dfrac{49}{4}} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{7}{2} = 3.5 \text{ cm} ∴ 4 π r 2 = 154 ⇒ r 2 = 4 π 154 ⇒ r 2 = 4 × 7 22 154 ⇒ r 2 = 4 × 22 154 × 7 ⇒ r 2 = 4 49 ⇒ r = 4 49 ⇒ r = 2 7 = 3.5 cm
Hence, the radius of the sphere = 3.5 cm.
The diameter of the moon is approximately one fourth of the diameter of the earth. Find the ratio of their surface areas.
Answer
Given,
⇒ Diameter of the moon (d) = 1 4 \dfrac{1}{4} 4 1
⇒ d 2 = 1 4 × D \dfrac{d}{2} = \dfrac{1}{4} \times D 2 d = 4 1 × D
⇒ Radius of the moon (r) = 1 4 \dfrac{1}{4} 4 1
⇒ r = 1 4 \dfrac{1}{4} 4 1
⇒ r R = 1 4 \dfrac{r}{R} = \dfrac{1}{4} R r = 4 1
Now,
Surface area of earth = 4πR2
Surface area of moon = 4πr2
The ratio of their surface areas = Surface area of moon Surface area of earth \dfrac{\text{Surface area of moon}}{\text{Surface area of earth}} Surface area of earth Surface area of moon
= 4 π r 2 4 π R 2 = r 2 R 2 = ( r R ) 2 = ( 1 4 ) 2 = 1 16 . = \dfrac{4πr^2}{4πR^2} \\[1em] = \dfrac{r^2}{R^2} \\[1em] = \Big(\dfrac{r}{R}\Big)^2 \\[1em] = \Big(\dfrac{1}{4}\Big)^2 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{16}. = 4 π R 2 4 π r 2 = R 2 r 2 = ( R r ) 2 = ( 4 1 ) 2 = 16 1 .
Hence, the ratio of their surface area = 1 : 16.
A hemispherical bowl is made of steel, 0.25 cm thick. The inner radius of the bowl is 5 cm. Find the outer curved surface area of the bowl.
Answer
Given,
The inner radius of the bowl (r) = 5 cm
Thickness of steel = 0.25 cm
Outer radius of the bowl (R) = inner radius of the bowl + thickness of steel = 5 cm + 0.25 cm = 5.25 cm
Outer curved surface area of the hemisphere = 2πR2
= 2 × 22 7 \dfrac{22}{7} 7 22 2
= 44 7 × 27.5625 \dfrac{44}{7} \times 27.5625 7 44 × 27.5625
= 44 × 3.9375
= 173.25 cm2 .
Hence, the outer curved surface area of the bowl is 173.25 cm2 .
A right circular cylinder just encloses a sphere of radius r. Find
(i) surface area of the sphere,
(ii) curved surface area of the cylinder,
(iii) ratio of the areas obtained in (i) and (ii).
Answer
From figure,
Radius of cylinder = radius of sphere = r
Height of cylinder = Diameter of sphere = 2r
(i) By formula,
Surface area of sphere = 4πr2
Hence, surface area of sphere = 4πr2 .
(ii) By formula,
Curved surface area of cylinder = 2πrh
= 2πr × 2r
= 4πr2 .
Hence, curved surface area of cylinder = 4πr2 .
(iii) Ratio = Surface area of sphere C.S.A. of cylinder = 4 π r 2 4 π r 2 = 1 1 \dfrac{\text{Surface area of sphere}}{\text{C.S.A. of cylinder}} = \dfrac{4πr^2}{4πr^2} = \dfrac{1}{1} C.S.A. of cylinder Surface area of sphere = 4 π r 2 4 π r 2 = 1 1
Hence, the ratio between these two surface area is 1 : 1.
Find the volume of the right circular cone with radius 6 cm, height 7 cm.
Answer
Given,
Radius of the cone (r) = 6 cm
Height of the cone (h) = 7 cm
By formula,
Volume of the cone (V) = 1 3 π r 2 h \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h 3 1 π r 2 h
Substituting values we get :
V = 1 3 × 22 7 × 6 2 × 7 = 1 3 × 22 × 36 = 22 × 12 = 264 cm 3 . V = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 6^2 \times 7 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times 22 \times 36 \\[1em] = 22 \times 12 \\[1em] = 264 \text{ cm}^3. V = 3 1 × 7 22 × 6 2 × 7 = 3 1 × 22 × 36 = 22 × 12 = 264 cm 3 .
Hence, volume of cone = 264 cm3 .
Find the volume of the right circular cone with radius 3.5 cm, height 12 cm.
Answer
Given,
Radius of the cone (r) = 3.5 cm
Height of the cone (h) = 12 cm
By formula,
Volume of the cone (V) = 1 3 π r 2 h \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h 3 1 π r 2 h
Substituting values we get :
V = 1 3 × 22 7 × ( 3.5 ) 2 × 12 = 1 3 × 22 7 × 12.25 × 12 = 22 × 1.75 × 4 = 154 cm 3 . V = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (3.5)^2 \times 12 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 12.25 \times 12 \\[1em] = 22 \times 1.75 \times 4 \\[1em] = 154 \text{ cm}^3. V = 3 1 × 7 22 × ( 3.5 ) 2 × 12 = 3 1 × 7 22 × 12.25 × 12 = 22 × 1.75 × 4 = 154 cm 3 .
Hence, volume of cone = 154 cm3 .
Find the capacity in litres of a conical vessel with radius 7 cm, slant height 25 cm.
Answer
Given,
Radius of the conical vessel (r) = 7 cm
Slant height of the conical vessel (l) = 25 cm
Let height of cone = h cm
We know that,
⇒ l2 = r2 + h2
⇒ h2 = l2 - r2
⇒ h = l 2 − r 2 \sqrt{l^2 - r^2} l 2 − r 2
Substituting values we get :
⇒ h = ( 25 ) 2 − ( 7 ) 2 ⇒ h = 625 − 49 ⇒ h = 576 = 24 cm . \Rightarrow h = \sqrt{(25)^2 - (7)^2} \\[1em] \Rightarrow h = \sqrt{625 - 49} \\[1em] \Rightarrow h = \sqrt{576} = 24 \text{ cm}. ⇒ h = ( 25 ) 2 − ( 7 ) 2 ⇒ h = 625 − 49 ⇒ h = 576 = 24 cm .
By formula,
Capacity of the conical vessel (V) = 1 3 π r 2 h \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h 3 1 π r 2 h
Substituting values we get :
V = 1 3 × 22 7 × 7 2 × 24 = 1 3 × 22 7 × 49 × 24 = 22 × 7 × 8 = 1232 cm 3 . = 1232 × ( 1 1000 ) l [ ∵ 1000 cm 3 = 1 litre] = 1.232 l . V = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 7^2 \times 24 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 49 \times 24 \\[1em] = 22 \times 7 \times 8 \\[1em] = 1232 \text{ cm}^3.\\[1em] = 1232 \times \Big(\dfrac{1}{1000}\Big) \text{ l} \quad [∵ 1000 \text{ cm}^3 = 1 \text{ litre] }\\[1em] = \text{1.232} \text{ l}. V = 3 1 × 7 22 × 7 2 × 24 = 3 1 × 7 22 × 49 × 24 = 22 × 7 × 8 = 1232 cm 3 . = 1232 × ( 1000 1 ) l [ ∵ 1000 cm 3 = 1 litre] = 1.232 l .
Hence, capacity of the conical vessel = 1.232 l.
Find the capacity in litres of a conical vessel with height 12 cm, slant height 13 cm.
Answer
Given,
Height of the conical vessel (h) = 12 cm
Slant height of the conical vessel (l) = 13 cm
Let radius of the vessel = r cm
We know that,
⇒ l2 = r2 + h2
⇒ r2 = l2 - h2
⇒ r = l 2 − h 2 \sqrt{l^2 - h^2} l 2 − h 2
Substituting values we get :
r = ( 13 ) 2 − ( 12 ) 2 = 169 − 144 = 25 = 5 cm r = \sqrt{(13)^2 - (12)^2} \\[1em] = \sqrt{169 - 144} \\[1em] = \sqrt{25} = 5 \text{ cm} r = ( 13 ) 2 − ( 12 ) 2 = 169 − 144 = 25 = 5 cm
By formula,
Capacity of the conical vessel (V) = 1 3 π r 2 h \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h 3 1 π r 2 h
Substituting values we get :
V = 1 3 × 22 7 × 5 2 × 12 = 1 3 × 22 7 × 300 = 6600 21 = 2200 7 = 2200 7 × 1 1000 l [ ∵ 1000 cm 3 = 1 l ] = 22 70 l = 11 35 l . V = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 5^2 \times 12 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 300 \\[1em] = \dfrac{6600}{21} \\[1em] = \dfrac{2200}{7} \\[1em] = \dfrac{2200}{7} \times \dfrac{1}{1000} \text{ l} \quad [∵ 1000 \text{ cm}^3 = 1 l] \\[1em] = \dfrac{22}{70} \text{ l} \\[1em] = \dfrac{11}{35} \text{ l}. V = 3 1 × 7 22 × 5 2 × 12 = 3 1 × 7 22 × 300 = 21 6600 = 7 2200 = 7 2200 × 1000 1 l [ ∵ 1000 cm 3 = 1 l ] = 70 22 l = 35 11 l .
Hence, capacity of the conical vessel = 11 35 \dfrac{11}{35} 35 11
The height of a cone is 15 cm. If its volume is 1570 cm3 , find the radius of the base. (Use π = 3.14)
Answer
Given,
Height of the cone (h) = 15 cm
Let radius of base of cone be r cm.
Volume of cone = 1570 cm3
Substituting values we get :
∴ 1 3 π r 2 h = 1570 ⇒ r 2 = 1570 × 3 π h ⇒ r 2 = 1570 × 3 3.14 × 15 ⇒ r 2 = 4710 47.1 ⇒ r 2 = 100 ⇒ r = 100 ⇒ r = 10 cm . \therefore \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h = 1570 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{1570 \times 3}{πh} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{1570 \times 3}{3.14 \times 15} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{4710}{47.1} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = 100 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \sqrt{100} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = 10 \text{ cm}. ∴ 3 1 π r 2 h = 1570 ⇒ r 2 = πh 1570 × 3 ⇒ r 2 = 3.14 × 15 1570 × 3 ⇒ r 2 = 47.1 4710 ⇒ r 2 = 100 ⇒ r = 100 ⇒ r = 10 cm .
Hence, radius of the base = 10 cm.
If the volume of a right circular cone of height 9 cm is 48π cm3 , find the diameter of its base.
Answer
Given,
Height of the cone (h) = 9 cm
Let radius of base of cone be r cm.
Volume of cone = 48π cm3
Substituting values we get :
⇒ 1 3 π r 2 h = 48 π ⇒ r 2 = 48 π × 3 π h ⇒ r 2 = 48 × 3 h ⇒ r 2 = 48 × 3 9 ⇒ r 2 = 144 9 ⇒ r 2 = 16 ⇒ r = 16 ⇒ r = 4 cm . \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h = 48π \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{48π \times 3}{πh} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = 48 \times \dfrac{3}{h} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = 48 \times \dfrac{3}{9} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{144}{9} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = 16 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \sqrt{16} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = 4 \text{ cm}. ⇒ 3 1 π r 2 h = 48 π ⇒ r 2 = πh 48 π × 3 ⇒ r 2 = 48 × h 3 ⇒ r 2 = 48 × 9 3 ⇒ r 2 = 9 144 ⇒ r 2 = 16 ⇒ r = 16 ⇒ r = 4 cm .
By formula,
Diameter = 2 × radius = 2 × 4 cm = 8 cm.
Hence, the diameter of base of cone is 8 cm.
A conical pit of top diameter 3.5 m is 12 m deep. What is its capacity in kilolitres?
Answer
Given,
Diameter of the conical pit (d) = 3.5 m
Radius of the conical pit (r) = Diameter 2 = 3.5 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{3.5}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 3.5
Depth of the conical pit (h) = 12 m
By formula,
Volume of conical pit (V) = 1 3 π r 2 h \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h 3 1 π r 2 h
Substituting values we get :
V = 1 3 × 22 7 × ( 1.75 ) 2 × 12 = 1 3 × 22 7 × 3.0625 × 12 = 22 × 0.4375 × 4 = 38.5 m 3 . V = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (1.75) ^2 \times 12 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 3.0625 \times 12 \\[1em] = 22 \times 0.4375 \times 4 \\[1em] = 38.5 \text{ m}^3. V = 3 1 × 7 22 × ( 1.75 ) 2 × 12 = 3 1 × 7 22 × 3.0625 × 12 = 22 × 0.4375 × 4 = 38.5 m 3 .
As,
1 m3 = 1000 Litres = 1 kilo litres
38.5 m3 = 38.5 × 1 kilo litres = 38.5 kl.
Hence, the capacity of the conical pit is 38.5 kilo litres.
The volume of a right circular cone is 9856 cm3 . If the diameter of the base is 28 cm, find
(i) height of the cone
(ii) slant height of the cone
(iii) curved surface area of the cone
Answer
Given,
Volume of cone = 9856 cm3
Diameter of the cone (d) = 28 cm
Radius of the cone (r) = Diameter 2 = 28 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{28}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 28
(i) Let height of cone be h cm.
Volume of the cone = 9856 cm3
Substituting values we get :
⇒ 1 3 π r 2 h = 9856 ⇒ h = 9856 × 3 π r 2 ⇒ h = 9856 × 3 22 7 × 1 4 2 ⇒ h = 9856 × 3 × 7 22 × 196 ⇒ h = 206976 4312 ⇒ h = 48 cm . \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h = 9856 \\[1em] \Rightarrow h = 9856 \times \dfrac{3}{πr^2} \\[1em] \Rightarrow h = 9856 \times \dfrac{3}{\dfrac{22}{7} \times 14^2} \\[1em] \Rightarrow h = 9856 \times \dfrac{3 \times 7}{22 \times 196} \\[1em] \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{206976}{4312} \\[1em] \Rightarrow h = 48 \text{ cm}. ⇒ 3 1 π r 2 h = 9856 ⇒ h = 9856 × π r 2 3 ⇒ h = 9856 × 7 22 × 1 4 2 3 ⇒ h = 9856 × 22 × 196 3 × 7 ⇒ h = 4312 206976 ⇒ h = 48 cm .
Hence, the height of the cone = 48 cm.
(ii) Let slant height of the cone be l cm.
By formula,
⇒ l = r 2 + h 2 ⇒ l = ( 14 ) 2 + ( 48 ) 2 ⇒ l = 196 + 2304 ⇒ l = 2500 = 50 cm . \Rightarrow l = \sqrt{r^2 + h^2} \\[1em] \Rightarrow l = \sqrt{(14)^2 + (48)^2} \\[1em] \Rightarrow l = \sqrt{196 + 2304} \\[1em] \Rightarrow l = \sqrt{2500} = 50 \text{ cm}. ⇒ l = r 2 + h 2 ⇒ l = ( 14 ) 2 + ( 48 ) 2 ⇒ l = 196 + 2304 ⇒ l = 2500 = 50 cm .
Hence, the slant height of the cone = 50 cm.
(iii) By formula,
Curved surface area of cone = πrl
Substituting values we get :
⇒ Curved surface area of cone = 22 7 \dfrac{22}{7} 7 22
= 22 x 2 x 50
= 44 x 50
= 2200 cm2 .
Hence, curved surface area of cone = 2200 cm2 .
A right triangle ABC with sides 5 cm, 12 cm and 13 cm is revolved about the side 12 cm. Find the volume of the solid so obtained.
Answer
On revolving,
Triangle around side 12 cm it becomes a cone with height 12 cm.
From figure,
Radius of the cone (r) = 5 cm
Height of the cone (h) = 12 cm
Volume of the cone (V) = 1 3 π r 2 h \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h 3 1 π r 2 h
Substituting values we get :
V = 1 3 × π × 5 2 × 12 = 1 3 × π × 25 × 12 = 100 π cm 3 V = \dfrac{1}{3} \times π \times 5^2 \times 12 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times π \times 25 \times 12 \\[1em] = 100π\text{ cm}^3 V = 3 1 × π × 5 2 × 12 = 3 1 × π × 25 × 12 = 100 π cm 3
Hence, the volume of the cone is 100π cm3 .
If the triangle ABC in the Question 7 above is revolved about the side 5 cm, then find the volume of the solid so obtained. Find also the ratio of the volumes of the two solids obtained in Questions 7 and 8.
Answer
On revolving,
Triangle around side 5 cm it becomes a cone with height 12 cm.
From figure,
Radius of the cone (r) = 12 cm
Height of the cone (h) = 5 cm
By formula,
Volume of the cone (V) = 1 3 π r 2 h \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h 3 1 π r 2 h
Substituting values we get :
V = 1 3 × π × 1 2 2 × 5 = 1 3 × π × 144 × 5 = 1 3 × π × 720 = 240 π cm 3 . V = \dfrac{1}{3} \times π \times 12^2 \times 5 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times π \times 144 \times 5 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times π \times 720 \\[1em] = 240π \text{ cm}^3. V = 3 1 × π × 1 2 2 × 5 = 3 1 × π × 144 × 5 = 3 1 × π × 720 = 240 π cm 3 .
Volume of the cone = 240π cm3
Volume of the cone in question 7 = 100π cm3
Ratio = Volume of the cone in question 7 : Volume of the cone in question 8
= 100π : 240π
= 5 : 12
Hence, the volume of the cone is 240π cm3 and the required ratio is 5 : 12.
A heap of wheat is in the form of a cone whose diameter is 10.5 m and height is 3 m. Find its volume. The heap is to be covered by canvas to protect it from rain. Find the area of the canvas required.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of the conical heap (d) = 10.5 m
Radius of the conical heap (r) = Diameter 2 = 10.5 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{10.5}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 10.5
Height of the conical heap (h) = 3 m
By formula,
Volume of the conical heap (V) = 1 3 π r 2 h \dfrac{1}{3}πr^2h 3 1 π r 2 h
Substituting values we get :
V = 1 3 × 22 7 × ( 5.25 ) 2 × 3 = 1 3 × 22 7 × 27.5625 × 3 = 1 3 × 22 7 × 82.6875 = 1819.125 21 = 86.625 m 3 V = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (5.25)^2 \times 3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 27.5625 \times 3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 82.6875 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1819.125}{21} \\[1em] = \text{86.625 m}^3 V = 3 1 × 7 22 × ( 5.25 ) 2 × 3 = 3 1 × 7 22 × 27.5625 × 3 = 3 1 × 7 22 × 82.6875 = 21 1819.125 = 86.625 m 3
By formula,
Slant height (l) = r 2 + h 2 \sqrt{r^2 + h^2} r 2 + h 2
Substituting values we get :
l = ( 5.25 ) 2 + ( 3 ) 2 = 27.5625 + 9 = 36.5625 = 6.047 m l = \sqrt{(5.25)^2 + (3)^2} \\[1em] = \sqrt{27.5625 + 9} \\[1em] = \sqrt{36.5625} \\[1em] = 6.047 \text{ m} l = ( 5.25 ) 2 + ( 3 ) 2 = 27.5625 + 9 = 36.5625 = 6.047 m
The area of the canvas required to cover the heap of wheat (A) = Curved surface area of conical heap = πrl
Substituting values we get :
A = 22 7 × 5.25 × 6.047 = 698.4285 7 = 99.775 m 2 . A = \dfrac{22}{7} \times 5.25 \times 6.047 \\[1em] = \dfrac{698.4285}{7} \\[1em] = 99.775 \text{ m}^2. A = 7 22 × 5.25 × 6.047 = 7 698.4285 = 99.775 m 2 .
Hence, the volume of the conical heap is 86.625 m3 and the area of the canvas required is 99.775 m2 .
Find the volume of a sphere whose radius is 7 cm.
Answer
Given,
Radius of the sphere (r) = 7 cm
By formula,
Volume of the sphere (V) = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
Substituting values we get :
V = 4 3 × 22 7 × 7 3 = 4 3 × 22 7 × 343 = 88 21 × 343 = 88 3 × 49 = 4312 3 = 1437 1 3 cm 3 . V = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 7^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 343 \\[1em] = \dfrac{88}{21} \times 343 \\[1em] = \dfrac{88}{3} \times 49 \\[1em] = \dfrac{4312}{3} \\[1em] = 1437 \dfrac{1}{3} \text{ cm}^3. V = 3 4 × 7 22 × 7 3 = 3 4 × 7 22 × 343 = 21 88 × 343 = 3 88 × 49 = 3 4312 = 1437 3 1 cm 3 .
Hence, the volume of sphere = 1437 1 3 1437 \dfrac{1}{3} 1437 3 1 3 .
Find the volume of a sphere whose radius is 0.63 m.
Answer
Given,
Radius of the sphere (r) = 0.63 m
By formula,
Volume of the sphere = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
Substituting values we get :
= 4 3 × 22 7 × ( 0.63 ) 3 = 4 3 × 22 7 × 0.250047 = 88 21 × 0.250047 = 22.004 21 = 1.05 m 3 = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (0.63)^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 0.250047 \\[1em] = \dfrac{88}{21} \times 0.250047 \\[1em] = \dfrac{22.004}{21} \\[1em] = \text{1.05 m}^3 = 3 4 × 7 22 × ( 0.63 ) 3 = 3 4 × 7 22 × 0.250047 = 21 88 × 0.250047 = 21 22.004 = 1.05 m 3
Hence, the volume of sphere = 1.05 m3 .
Find the amount of water displaced by a solid spherical ball of diameter 28 cm.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of the spherical ball (d) = 28 cm
Radius of the spherical ball (r) = Diameter 2 = 28 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{28}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 28
By formula,
The amount of water displaced = volume of the sphere (V) = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
Substituting values we get :
V = 4 3 × 22 7 × ( 14 ) 3 = 4 3 × 22 7 × 2744 = 88 21 × 2744 = 241472 21 = 11498 2 3 cm 3 . V = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (14)^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 2744 \\[1em] = \dfrac{88}{21} \times 2744 \\[1em] = \dfrac{241472}{21} \\[1em] = 11498\dfrac{2}{3} \text{ cm}^3. V = 3 4 × 7 22 × ( 14 ) 3 = 3 4 × 7 22 × 2744 = 21 88 × 2744 = 21 241472 = 11498 3 2 cm 3 .
Hence, the amount of water displaced = 11498 2 3 11498\dfrac{2}{3} 11498 3 2 3 .
Find the amount of water displaced by a solid spherical ball of diameter 0.21 m.
Answer
Given,
Diameter of the spherical ball (d) = 0.21 m
Radius of the spherical ball (r) = Radius = Diameter 2 = 0.21 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{0.21}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 0.21
By formula,
The amount of water displaced = volume of a sphere (V) = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
Substituting values we get :
V = 4 3 × 22 7 × ( 0.105 ) 3 = 88 21 × 0.001157625 = 88 21 × 0.001157625 = 0.101871 21 = 0.004851 m 3 . V = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (0.105)^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{88}{21} \times 0.001157625 \\[1em] = \dfrac{88}{21} \times 0.001157625 \\[1em] = \dfrac{0.101871}{21} \\[1em] = 0.004851\text{ m}^3. V = 3 4 × 7 22 × ( 0.105 ) 3 = 21 88 × 0.001157625 = 21 88 × 0.001157625 = 21 0.101871 = 0.004851 m 3 .
Hence, the amount of water displaced = 0.004851 m3 .
The diameter of a metallic ball is 4.2 cm. What is the mass of the ball, if the density of the metal is 8.9 g per cm3 ?
Answer
Given,
The diameter of the metallic ball (d) = 4.2 cm
Radius of the metallic ball (r) = Diameter 2 = 4.2 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{4.2}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 4.2
The density of the metal = 8.9 g per cm3
We know that,
Density = Mass Volume \dfrac{\text{Mass}}{\text{Volume}} Volume Mass
Mass = Density × Volume ...........(1)
By formula,
Volume of the metallic ball (V) = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
Substituting values we get :
V = 4 3 × 22 7 × ( 2.1 ) 3 = 4 3 × 22 7 × 9.261 = 88 21 × 9.261 = 814.968 21 = 38.808 cm 3 V = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (2.1)^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 9.261 \\[1em] = \dfrac{88}{21} \times 9.261 \\[1em] = \dfrac{814.968}{21} \\[1em] = \text{38.808 cm}^3 V = 3 4 × 7 22 × ( 2.1 ) 3 = 3 4 × 7 22 × 9.261 = 21 88 × 9.261 = 21 814.968 = 38.808 cm 3
Substituting value in equation (1), we get :
Mass of the metallic ball = 8.9 × 38.808
= 345.39 g
Hence, the mass of the ball is 345.39 g.
The diameter of the moon is approximately one-fourth of the diameter of the earth. What fraction of the volume of the earth is the volume of the moon?
Answer
Given,
⇒ Diameter of the moon (d) = 1 4 \dfrac{1}{4} 4 1
⇒ d 2 = 1 4 × D 2 \dfrac{\text{d}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{4} \times \dfrac{D}{2} 2 d = 4 1 × 2 D
⇒ The radius of the moon = 1 4 \dfrac{1}{4} 4 1
Let radius of moon be r and radius of earth be R.
⇒ r = 1 4 × R \dfrac{1}{4}\times R 4 1 × R
⇒ r = R 4 \dfrac{R}{4} 4 R
Since, earth and moon are spherical.
Volume of the earth (V) = 4 3 π R 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πR^3 3 4 π R 3
Volume of the moon (v) = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
Substituting value of r from equation (1) in above equation, we get :
⇒ v = 4 3 × π × ( R 4 ) 3 ( From equation (1) ) ⇒ v = 4 3 × π × R 4 × R 4 × R 4 ⇒ v = 1 64 × 4 3 π R 3 ⇒ v = 1 64 × V . \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{4}{3}\times π \times \Big(\dfrac{R}{4}\Big)^3 (\text{From equation (1)}) \\[1em] \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{4}{3} \times π \times \dfrac{R}{4} \times \dfrac{R}{4} \times \dfrac{R}{4} \\[1em] \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{1}{64} \times \dfrac{4}{3}π R^3 \\[1em] \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{1}{64} \times V. ⇒ v = 3 4 × π × ( 4 R ) 3 ( From equation (1) ) ⇒ v = 3 4 × π × 4 R × 4 R × 4 R ⇒ v = 64 1 × 3 4 π R 3 ⇒ v = 64 1 × V .
Hence, the volume of the moon is 1 64 \dfrac{1}{64} 64 1
How many litres of milk can a hemispherical bowl of diameter 10.5 cm hold?
Answer
Given,
Diameter of the hemispherical ball (d) = 10.5 cm
Radius of the hemispherical ball (r) = Diameter 2 = 10.5 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{10.5}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 10.5
By formula,
Volume of the hemispherical ball (V) = 2 3 π r 3 \dfrac{2}{3}πr^3 3 2 π r 3
Substituting values we get :
V = 2 3 × 22 7 × ( 5.25 ) 3 = 44 21 × 144.703 = 6366.9375 21 = 303.1875 = 303.1875 1000 ( ∵ 1000 cm 3 = 1 L ) = 0.3031875 ≈ 0.303 l V = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (5.25)^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{44}{21} \times 144.703 \\[1em] = \dfrac{6366.9375}{21} \\[1em] = 303.1875 \\[1em] = \dfrac{303.1875}{1000} (∵ 1000 \text{ cm}^3 = 1 \text{ L}) \\[1em] = 0.3031875 \\[1em] \approx 0.303 \text{ l} V = 3 2 × 7 22 × ( 5.25 ) 3 = 21 44 × 144.703 = 21 6366.9375 = 303.1875 = 1000 303.1875 ( ∵ 1000 cm 3 = 1 L ) = 0.3031875 ≈ 0.303 l
Hence, the hemispherical bowl can hold 0.303 litres of milk.
A hemispherical tank is made up of an iron sheet 1 cm thick. If the inner radius is 1 m, then find the volume of the iron used to make the tank.
Answer
Given,
Inner radius of the tank (r) = 1 m
Thickness of iron = 1 cm = 1 100 \dfrac{1}{100} 100 1
Outer radius of the tank (R) = Inner radius + Thickness = 1 m + 0.01 m = 1.01 m
Volume of iron used (V) = Volume of tank with outer radius - Volume of tank with inner radius
V = 2 3 π R 3 − 2 3 π r 3 = 2 3 π ( R 3 − r 3 ) = 2 3 × 22 7 × [ ( 1.01 ) 3 − ( 1 ) 3 ] = 2 3 × 22 7 × [ 1.030301 − 1 ] = 2 3 × 22 7 × 0.030301 = 44 21 × 0.030301 = 1.333244 21 = 0.06348 m 3 . V = \dfrac{2}{3}πR^3 - \dfrac{2}{3}πr^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{2}{3}π(R^3 - r^3) \\[1em] = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times [(1.01)^3 - (1)^3] \\[1em] = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times [1.030301 - 1 ] \\[1em] = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 0.030301 \\[1em] = \dfrac{44}{21} \times 0.030301 \\[1em] = \dfrac{1.333244}{21} \\[1em] = \text{0.06348 m}^3. V = 3 2 π R 3 − 3 2 π r 3 = 3 2 π ( R 3 − r 3 ) = 3 2 × 7 22 × [( 1.01 ) 3 − ( 1 ) 3 ] = 3 2 × 7 22 × [ 1.030301 − 1 ] = 3 2 × 7 22 × 0.030301 = 21 44 × 0.030301 = 21 1.333244 = 0.06348 m 3 .
Hence, volume of iron used to make the tank = 0.06348 m3 .
Find the volume of a sphere whose surface area is 154 cm2 .
Answer
Let the radius of the sphere be r.
By formula,
Surface area of the sphere = 4πr2
Substituting values we get :
⇒ 4 π r 2 = 154 ⇒ r 2 = 154 4 π ⇒ r 2 = 154 4 × 22 7 ⇒ r 2 = 154 × 7 4 × 22 ⇒ r 2 = 49 4 ⇒ r = 49 4 ⇒ r = 7 2 cm . \Rightarrow 4πr^2 = 154 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{154}{4π} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{154}{4 \times \dfrac{22}{7}} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{154 \times 7}{4 \times 22} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{49}{4} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \sqrt{\dfrac{49}{4}} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{7}{2} \text{ cm}. ⇒ 4 π r 2 = 154 ⇒ r 2 = 4 π 154 ⇒ r 2 = 4 × 7 22 154 ⇒ r 2 = 4 × 22 154 × 7 ⇒ r 2 = 4 49 ⇒ r = 4 49 ⇒ r = 2 7 cm .
By formula,
Volume of a sphere (V) = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
V = 4 3 × 22 7 × ( 7 2 ) 3 = 4 3 × 22 7 × 343 8 = 11 3 × 49 = 539 3 = 179 2 3 cm 3 V = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times \Big(\dfrac{7}{2}\Big)^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times \dfrac{343}{8} \\[1em] = \dfrac{11}{3} \times 49 \\[1em] = \dfrac{539}{3} \\[1em] = 179 \dfrac{2}{3} \text{ cm}^3 V = 3 4 × 7 22 × ( 2 7 ) 3 = 3 4 × 7 22 × 8 343 = 3 11 × 49 = 3 539 = 179 3 2 cm 3
Hence, volume of the sphere is 179 2 3 cm 3 179 \dfrac{2}{3} \text{ cm}^3 179 3 2 cm 3
A dome of a building is in the form of a hemisphere. From inside, it was white-washed at the cost of ₹ 4989.60. If the cost of white-washing is ₹ 20 per square metre, find the
(i) inside surface area of the dome,
(ii) volume of the air inside the dome.
Answer
(i) Given,
Inside of dome was white-washed at the cost of ₹ 4989.60.
Cost of white washing = ₹ 20 per square metre.
Inside surface area of the dome
= Total cost for white-washing the dome inside Rate of white-washing \dfrac{\text{Total cost for white-washing the dome inside}}{\text{Rate of white-washing}} Rate of white-washing Total cost for white-washing the dome inside
⇒ 4989.60 20 \dfrac{4989.60}{20} 20 4989.60 2
Hence, inner surface area of the dome = 249.48 m2 .
(ii) Let 'r' be the radius of a hemispherical dome.
Inner surface area of the hemispherical dome = 2πr2
Substituting values we get :
⇒ 2 π r 2 = 249.48 ⇒ r 2 = 249.48 2 π ⇒ r 2 = 249.48 2 × 22 7 ⇒ r 2 = 249.48 × 7 44 ⇒ r 2 = 5.67 × 7 ⇒ r 2 = 39.69 ⇒ r = 39.69 ⇒ r = 6.3 m \Rightarrow 2πr^2 = 249.48 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{249.48}{2π} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{249.48}{2 \times \dfrac{22}{7}} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = \dfrac{249.48 \times 7}{44} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = 5.67 \times 7\\[1em] \Rightarrow r^2 = 39.69 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = \sqrt{39.69} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r = 6.3 \text{ m} ⇒ 2 π r 2 = 249.48 ⇒ r 2 = 2 π 249.48 ⇒ r 2 = 2 × 7 22 249.48 ⇒ r 2 = 44 249.48 × 7 ⇒ r 2 = 5.67 × 7 ⇒ r 2 = 39.69 ⇒ r = 39.69 ⇒ r = 6.3 m
The volume of the air inside the dome will be the same as the volume of the hemisphere.
Now the volume of the air inside the dome (v) = 2 3 π r 3 \dfrac{2}{3}πr^3 3 2 π r 3
v = 2 3 × 22 7 × 6.3 × 6.3 × 6.3 = 2 3 × 22 7 × 6.3 × 39.69 = 2 3 × 22 7 × 250.047 = 44 21 × 250.047 = 11002.068 21 = 523.9 m 3 v = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 6.3 \times 6.3 \times 6.3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 6.3 \times 39.69 \\[1em] = \dfrac{2}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 250.047 \\[1em] = \dfrac{44}{21} \times 250.047 \\[1em] = \dfrac{11002.068}{21} \\[1em] = 523.9 \text{ m}^3 v = 3 2 × 7 22 × 6.3 × 6.3 × 6.3 = 3 2 × 7 22 × 6.3 × 39.69 = 3 2 × 7 22 × 250.047 = 21 44 × 250.047 = 21 11002.068 = 523.9 m 3
Hence, the volume of the air inside the dome is 523.9 m3 .
Twenty seven solid iron spheres, each of radius r and surface area S are melted to form a sphere with surface area S′. Find the
(i) radius r′ of the new sphere,
(ii) ratio of S and S′.
Answer
By formula,
The volume of a sphere = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
The volume of 27 solid spheres with radius r = 27 × 4 3 π r 3 = 36 π r 3 27 \times \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 = 36πr^3 27 × 3 4 π r 3 = 36 π r 3
The volume of the new sphere with radius r' = 4 3 π ( r ′ ) 3 \dfrac{4}{3}π(r')^3 3 4 π ( r ′ ) 3
(i) Volume of the new sphere = Volume of 27 solid spheres
⇒ 4 3 π ( r ′ ) 3 = 36 π r 3 ( From equation (1) and (2) ) ⇒ ( r ′ ) 3 = 36 r 3 × 3 4 ⇒ ( r ′ ) 3 = 9 r 3 × 3 ⇒ ( r ′ ) 3 = 27 r 3 ⇒ r ′ = 27 r 3 3 ⇒ r ′ = 3 r \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}π(r')^3 = 36πr^3 (\text{From equation (1) and (2)}) \\[1em] \Rightarrow (r')^3 = 36r^3 \times \dfrac{3}{4} \\[1em] \Rightarrow (r')^3 = 9r^3 \times 3 \\[1em] \Rightarrow (r')^3 = 27r^3 \\[1em] \Rightarrow r' = \sqrt[3]{27r^3} \\[1em] \Rightarrow r' = 3r ⇒ 3 4 π ( r ′ ) 3 = 36 π r 3 ( From equation (1) and (2) ) ⇒ ( r ′ ) 3 = 36 r 3 × 4 3 ⇒ ( r ′ ) 3 = 9 r 3 × 3 ⇒ ( r ′ ) 3 = 27 r 3 ⇒ r ′ = 3 27 r 3 ⇒ r ′ = 3 r
Hence, radius of the new sphere r' = 3r.
(ii) By formula,
Surface area of each iron sphere (S) = 4πr2
Surface area of the new sphere (S') = 4 π ( r ′ ) 2 = 4 π ( 3 r ) 2 = 36 π r 2 4π(r')^2 = 4π(3r)^2 = 36πr^2 4 π ( r ′ ) 2 = 4 π ( 3 r ) 2 = 36 π r 2
Required ratio = 4 π r 2 36 π r 2 \dfrac{4πr^2}{36πr^2} 36 π r 2 4 π r 2
The ratio of the S and S’ = 1 9 \dfrac{1}{9} 9 1
Hence, the ratio of S and S’ is 1 : 9.
A capsule of medicine is in the shape of a sphere of diameter 3.5 mm. How much medicine (in mm3 ) is needed to fill this capsule?
Answer
Given,
Diameter of the spherical capsule (d) = 3.5 mm
Radius of the spherical capsule (r) = Diameter 2 = 3.5 2 \dfrac{\text{Diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{3.5}{2} 2 Diameter = 2 3.5
Medicine needed to fill the capsule = Volume of the spherical capsule
∴ Medicine needed to fill the capsule (v) = 4 3 π r 3 \dfrac{4}{3}πr^3 3 4 π r 3
v = 4 3 × 22 7 × ( 1.75 ) 3 = 4 3 × 22 7 × 5.359375 = 88 21 × 5.359375 = 471.625 21 = 22.46 mm 3 v = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times (1.75)^3 \\[1em] = \dfrac{4}{3} \times \dfrac{22}{7} \times 5.359375 \\[1em] = \dfrac{88}{21} \times 5.359375 \\[1em] = \dfrac{471.625}{21} \\[1em] = 22.46 \text{ mm}^3 v = 3 4 × 7 22 × ( 1.75 ) 3 = 3 4 × 7 22 × 5.359375 = 21 88 × 5.359375 = 21 471.625 = 22.46 mm 3
Hence, the medicine needed to fill the capsule = 22.46 mm3 .