Progress Check 1
Question 1
How will you categorise the following under domestic and industrial wastes ?
Rags, used containers, old newspapers, mine tailing (left overs), flyash, kitchen waste, broken bricks.
Answer
| Domestic | Industrial waste |
|---|---|
| Rags | Mine tailing (left overs) |
| Used containers | Flyash |
| Old newspapers | Broken bricks |
| Kitchen waste |
Question 2
What is bagasse?
Answer
Bagasse is the plant residue left after extracting the sugarcane juice. It is used as fire wood or in paper industry.
Question 3
Name any two categories of chemicals which are washed off as wastes from agricultural fields.
Answer
Pesticides and fertilizers
Question 4
What are the two portions into which the municipal sewage is separated?
Answer
- The degradable part
- The non-degradable part
Question 5
In which category of wastes will you include the non-functioning discarded
- Mobile phones
- Thermometers
- Photocopying machines
Answer
- e-Waste
- e-waste
- e-Waste
Progress Check 2
Question 1
Name the three categories of wastes under segregation.
Answer
- Reusable
- Degradable
- Non-degradable
Question 2
Which categories of wastes require dumping ?
Answer
Non-degradable
Question 3
Is it true that composting is a useful method contributing in crop farming ?
Answer
Yes, composting is a useful method contributing in crop farming as compost is good for soil and plant health.
Question 4
What is sludge ?
Answer
Sludge is solid precipitated material which is produced during secondary treatment of effluents and it can be used as a manure.
Question 5
Can incineration lead to certain kind of pollution? Yes/No.
Answer
Yes, incineration leads to certain kind of pollution as it results in release of fumes and gases.
Question 6
Name two types of devices used for removing particulate air pollutants.
Answer
- Scrubbers
- Electrostatic precipitators
Multiple Choice Type
Question 1
The 'Municipal solid waste' is the term used to describe what kind of solid waste ?
- Hazardous
- Toxic
- Non-hazardous
- Non-toxic
Answer
Non-hazardous
Reason — The 'Municipal solid waste' consists mostly of domestic wastes of township which is non-hazardous.
Question 2
The most rapidly increasing and much harmful waste today is
- plastics
- pesticides
- municipal sewage
- electronic waste
Answer
plastics
Reason — Plastics are non-degradable and are extremely harmful for environment.
Question 3
Out of the following, which substance can be recycled many times?
- Plastic
- Wood
- Organic materials
- Aluminium
Answer
Aluminium
Reason — Aluminium can be recycled many times as its quality is not hampered after recycling.
Question 4
Which of the following is not a waste from construction sites?
- Pebbles
- Bagasse
- Broken bricks
- Wood waste
Answer
Bagasse
Reason — Bagasse is sugarcane plant residue left after extraction of sugarcane juice.
Question 5
Which of the following is a kind of gaseous waste?
- Sewage
- Garbage
- Fly ash
- Effluents
Answer
Fly ash
Reason — It is gaseous waste and contains very fine solid particles.
Very Short Answer Type
Question 1
Name the following :
(a) The solid precipitated material produced during secondary treatment of the effluent, carried out in the Effluent Treatment Plants.
(b) The two types of devices commonly used for removing the particulate air pollutants.
(c) The process of disposal of waste by burning.
(d) The solid waste residue left after burning.
(e) The category of wastes given out from homes.
Answer
(a) Sludge
(b) Scrubbers, Electrostatic precipitators
(c) Incineration
(d) Ash
(e) Domestic wastes
Question 2
Correct the following statements by changing the first/last word only.
(a) Some of the electronic wastes may contain valuable metals such as potassium.
(b) Sludge is the gaseous waste of cement industry.
(c) Drains are used to remove gaseous and particulate air pollutants.
(d) Industrial liquid waste is termed as sewage.
(e) Rags are the plant residue left after extracting the sugarcane juice.
Answer
(a) Some of the electronic wastes may contain valuable metals such as gold, silver and copper .
(b) Fly ash is the gaseous waste of cement industry.
(c) Scrubbers are used to remove gaseous and particulate air pollutants.
(d) Domestic liquid waste is termed as sewage.
(e) Bagasse are the plant residue left after extracting the sugarcane juice.
Question 3
Match the items in Column I with as many items as possible in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| Cow dung | Sugarcane |
| Bagasse | Manure |
| Okhla khad | Food wastes |
| Lead and cadmium | e-wastes |
Answer
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| Cow dung | Manure |
| Bagasse | Sugarcane |
| Okhla khad | Food wastes |
| Lead and cadmium | e-wastes |
Short Answer Type
Question 1
Define the terms:
(a) Waste
(b) Fly ash
(c) E-wastes
(d) Composting
(e) Mine tailing
Answer
(a) Waste is any substance which is discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use.
(b) Fly ash is gaseous waste of cement industry which contains fine solid particles of non-combustible ash.
(c) e-Wastes are electronic wastes that consist of discarded appliances using electricity like computers, TVs, etc.
(d) Composting means putting the waste organic matter to decay so that it can be used for fertilizing the agricultural land.
(e) Mine tailing are the left-over material after the processing of the mined products like copper, silver, gold, etc.
Question 2
Give reasons for the following:
(a) Broken glass utensils are a kind of non-degradable waste.
(b) Landfills are coming up fast near large cities.
(c) Why is municipal sewage first separated into degradable and non-degradable wastes?
Answer
(a) Broken glass utensils are a kind of non-degradable waste as they cannot be decomposed and broken down by living micro-organisms. These need to be disposed in deeply dug pits so as to cause no harm. One of the applications of broken glass is that it can be used in glass industries in larger quantities after melting.
(b) Large cities are seeing huge population growth and they lack in the usage of efficient and safe disposal method for the waste generated in these cities. Large cities are producing large quantities of non-degradable waste that ends up in landfills for disposal. Due to these reasons, landfills are coming up fast near large cities.
(c) Municipal sewage is first separated into degradable and non-degradable wastes because degradable wastes can be broken down into non-toxic waste in septic tanks, while non-degradable waste requires to be buried at safe places in order to avoid hazardous effects.
Long Answer Type
Question 1
Define electronic waste and list at least six items which come under this category.
Answer
Electronic waste is the waste generated by discarded electrical items (i.e. the appliances that use electricity). Some items under this category are:
- Fluorescent tubes
- Lead acid batteries
- Mobile phones
- Refrigerators
- Electronic toys
- Radios
Question 2
List some of the common wastes produced in mining operation and mention how these can be reused.
Answer
Common wastes produced in mining operation are:
- Dust
- Coal
- Iron
- Copper
- Zinc
During operation of getting minerals, a large quantity of waste material is generated. This waste material is called mine tailing. The application of mine tailing is that it can be mixed with materials for tile production and masonry cement.
Question 3
Describe the procedure usually used to produce compost.
Answer
Composting means putting the waste organic matter to decay so that it can be used for fertilizing the agricultural land. The procedure to produce compost is described below:
- A trench of about 5m long, 1.5m wide and 1.5m deep is dug.
- A layer of well mixed refuse and waste is spread in it for about 30cm thickness.
- This layer is fully wetted with a watery mixture of cow-dung and some mud.
- A second layer of mixed refuse is spread over the first layer till the heap rises to project over the ground level by about half a metre.
- Leave the set up undisturbed for around 3 months during which water is sprinkled at regular intervals.
- A trench is then opened and the material is taken out and rearranged in conical heaps and covered with a layer of soil.
- Compost is ready after 50-60 days to be used in fields for cultivation or in garden flower beds, etc.
Question 4
Describe the usefulness of incineration of wastes, and also mention the precautions required in it.
Answer
Incineration is the disposal of waste by burning which causes the release of fumes and other toxic substances.
Usefulness of incineration of wastes:
- The ash left over occupies much less landfill space.
- Electricity can be generated from the heat released during burning.
Precautions:
- The process should be carried out at very high temperatures.
- Should be equipped with pollution control devices.
- Incinerators should be installed away from residential areas.
Structured / Application / Skill Type
The figure given below represents a device. Study the same and answer the following questions:
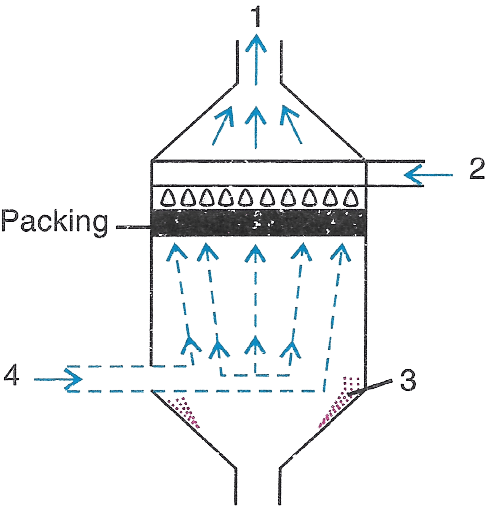
(a) Identify the device.
(b) Mention the specific purpose for which we can use this device.
(c) Label the guidelines 1, 2, 3 and 4.
(d) Name another similar kind of device which can also be used for the same purpose.
(e) Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the device mentioned by you in part (4) above.
Answer
(a) Scrubber.
(b) To remove gaseous and particulate air pollutants.
(c) The labelled guidelines are :
- 1 → Clean air
- 2 → Water spray
- 3 → Particulate matter
- 4 → Dirty air
(d) Electrostatic precipitator.
(e) Below is a neat and labelled diagram of an electrostatic precipitator :
